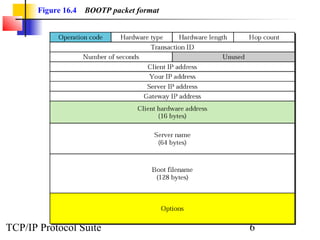
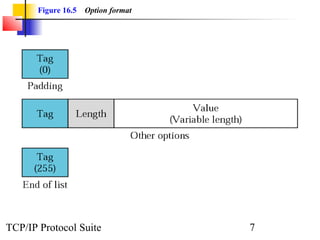
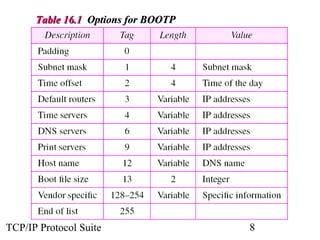
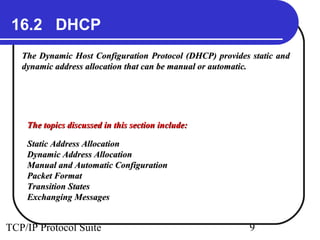
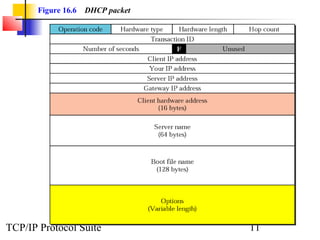
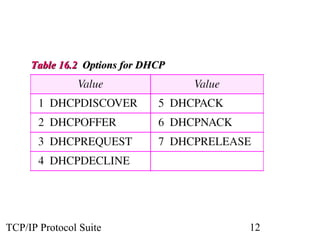
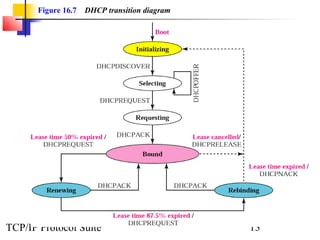
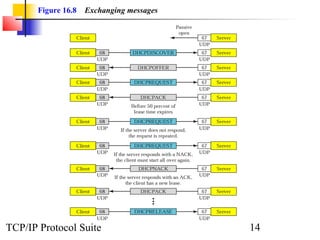
This document discusses BOOTP and DHCP protocols. It provides objectives that will be covered, including the types of information required by systems on boot-up and how BOOTP and DHCP operate. BOOTP provides IP addresses and other network configuration details, while DHCP provides static and dynamic address allocation manually or automatically. The document includes figures illustrating operations, packet formats, and state diagrams for both protocols.