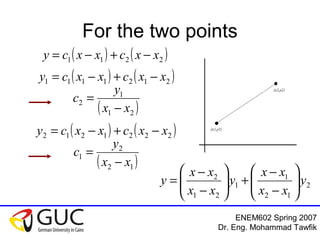
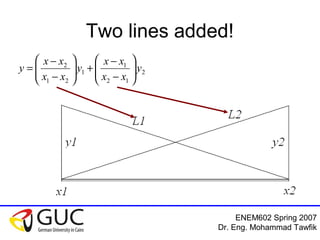
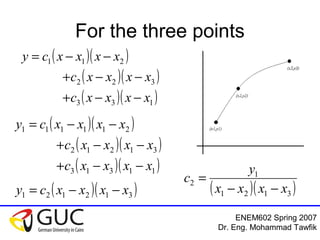
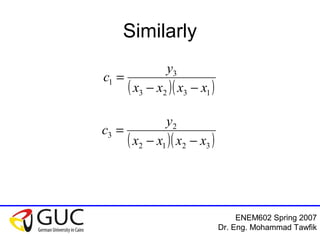
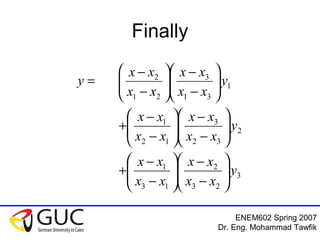
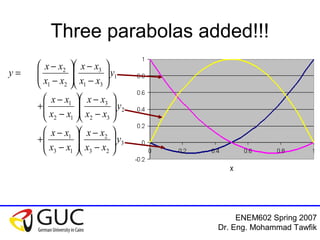
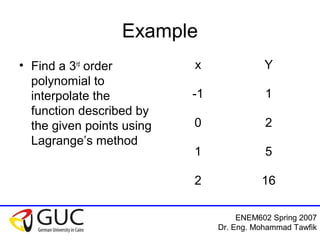
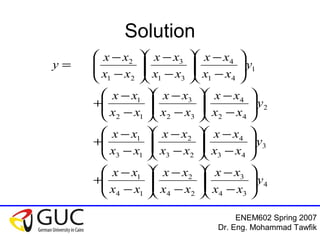
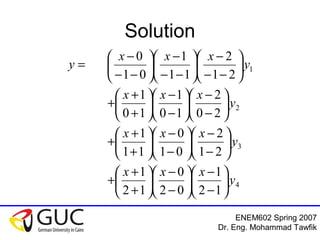
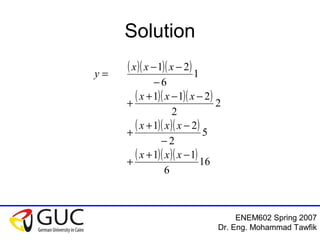
This document contains lecture slides from an ENEM602 engineering mathematics course taught by Dr. Eng. Mohammad Tawfik in Spring 2007. It discusses Lagrange interpolation, which is a method for interpolating a polynomial that passes through a set of points. The document provides examples of using Lagrange interpolation for 2, 3 and 4 points. It derives the general Lagrange interpolation formula and shows an example of applying it to find a 3rd order polynomial to interpolate 4 given data points. Students are assigned homework problems applying Lagrange interpolation.