1) Newton Raphson method is a numerical technique used to find roots of algebraic and transcendental equations. It uses successive approximations, starting from an initial guess, to find better approximations for the roots of the equations.
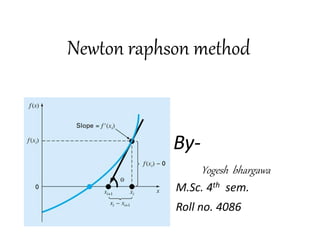
2) The method involves calculating the derivative of the function f(x) and determining the next approximation using the formula xn+1 = xn - f(xn)/f'(xn).
3) An example of finding the root of x3 - 2x - 5 = 0 is shown, starting from an initial guess of 2.5 and iteratively applying the Newton Raphson formula to obtain the root as 2.094551482.



![Algorithm for f(x)=0
• Calculate f’(x) symbolically.
• Choose an initial guess 𝑥0as given below
let [a,b] be any interval such that f(a)<0 and f(b)>0 , then
𝑥0=
𝑎+𝑏
2
.
• then 𝑥1 = 𝑥0 −
𝑓 𝑥0
𝑓′ 𝑥0
.
• Similarly 𝑥2 = 𝑥1 −
𝑓 𝑥1
𝑓′(𝑥1)
.
• Then by repetition of this process we can find 𝑥3 , 𝑥4 , 𝑥5 … …
• At last we reach at a stage where we find 𝒙𝒊+𝟏 = 𝒙𝒊.
• Then we will stop.
• Hence 𝒙𝒊 will be the required root of given equation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ypgesh-150707075830-lva1-app6892/85/newton-raphson-method-7-320.jpg)






