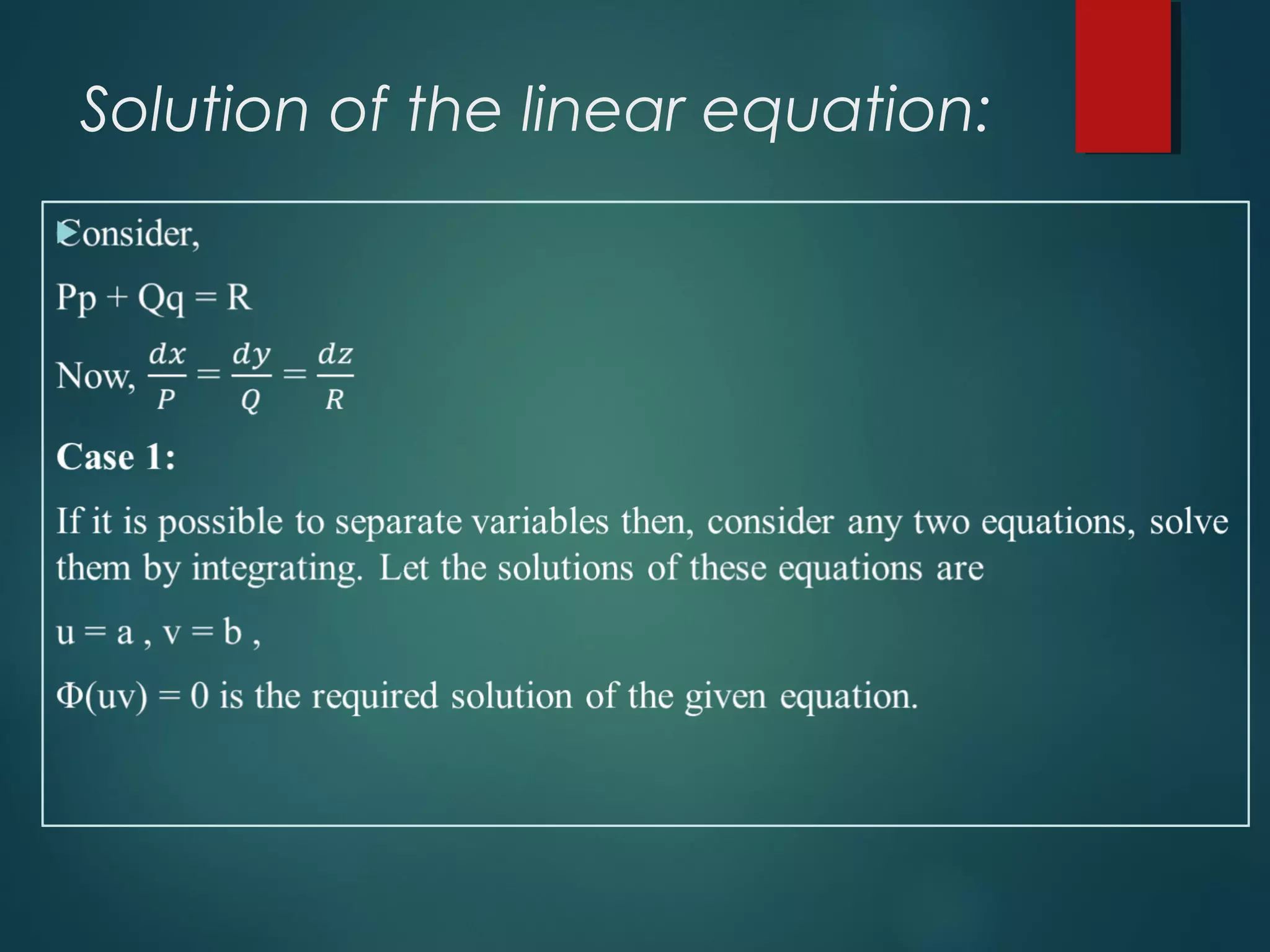
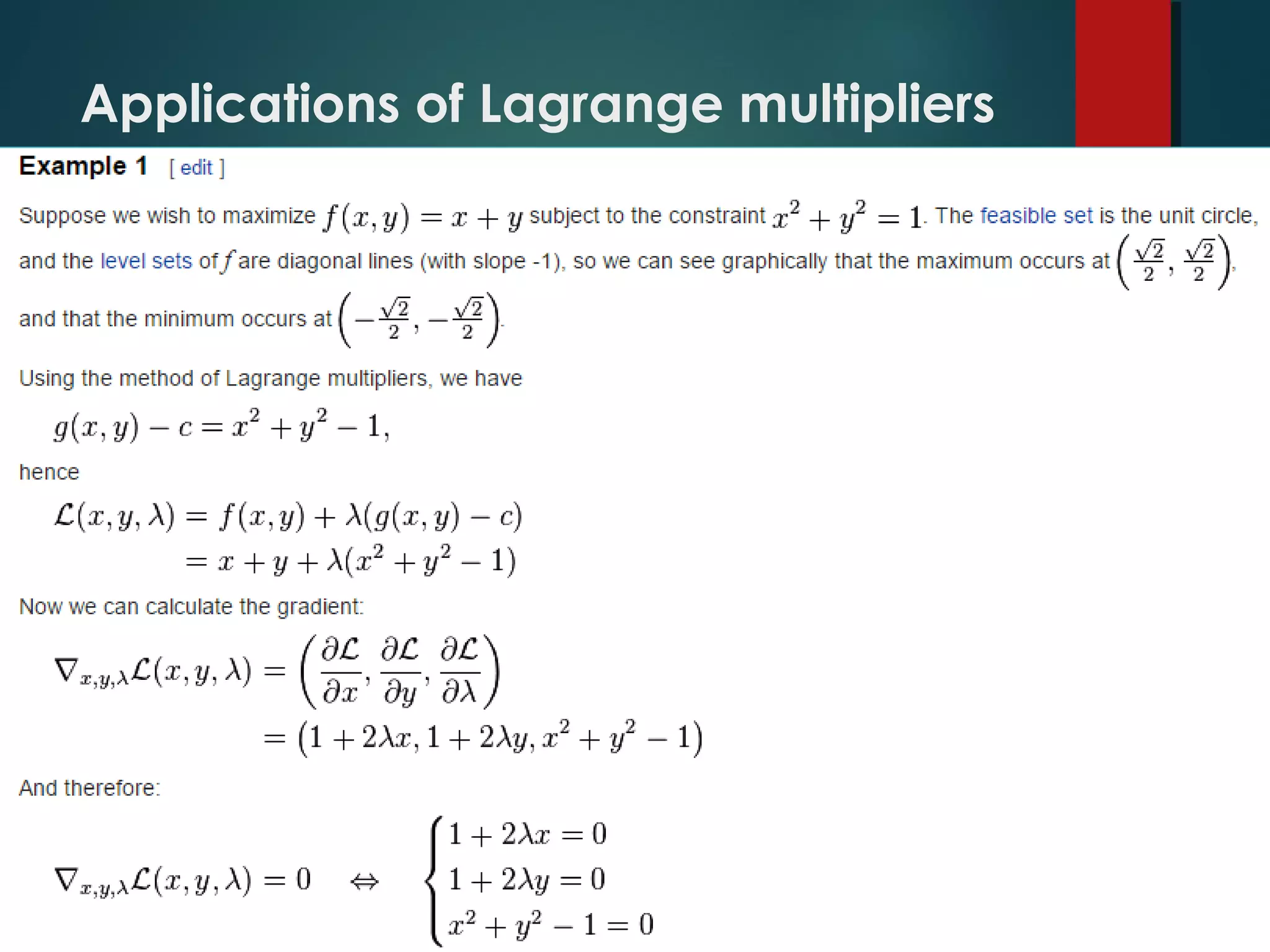
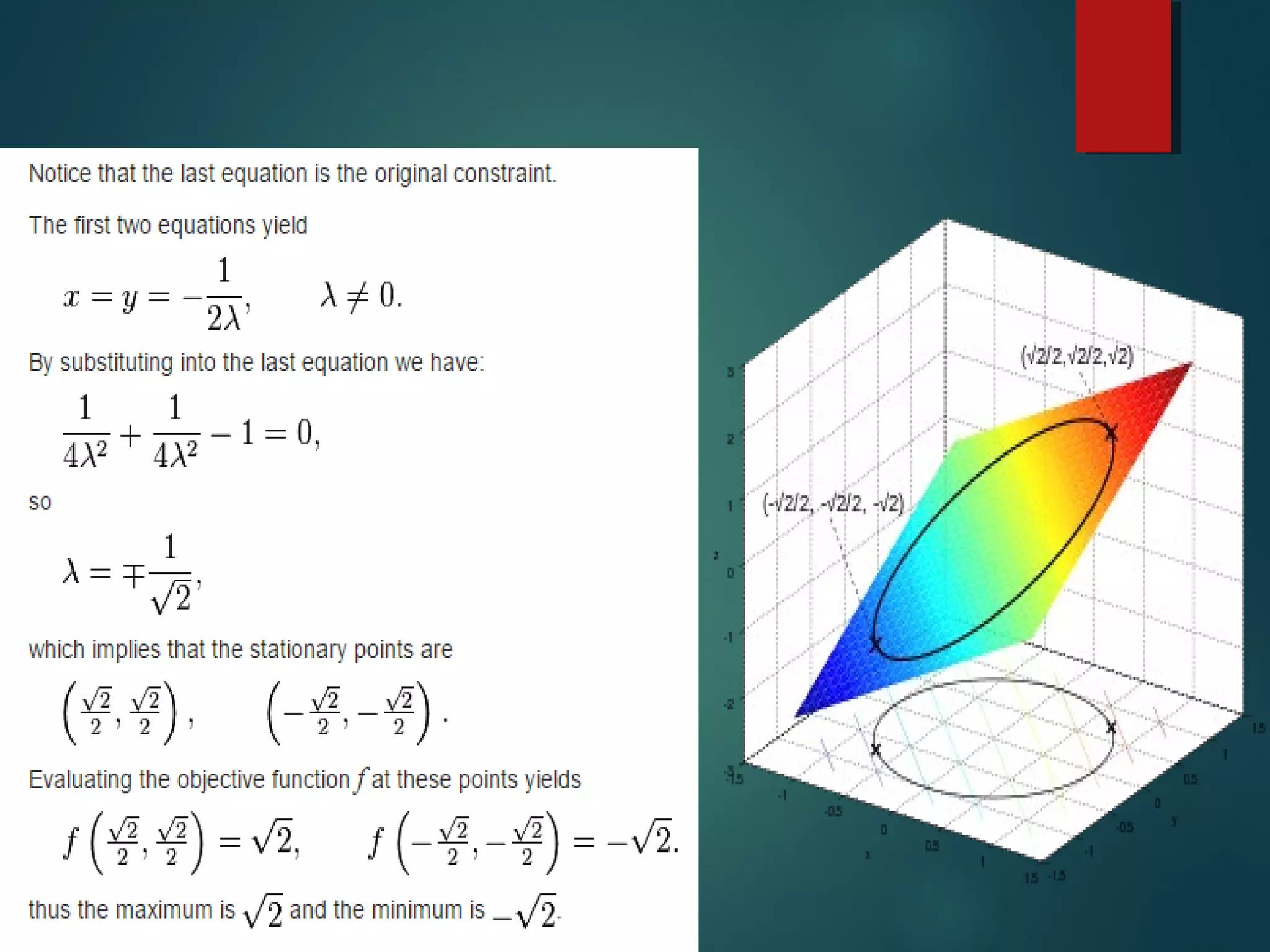
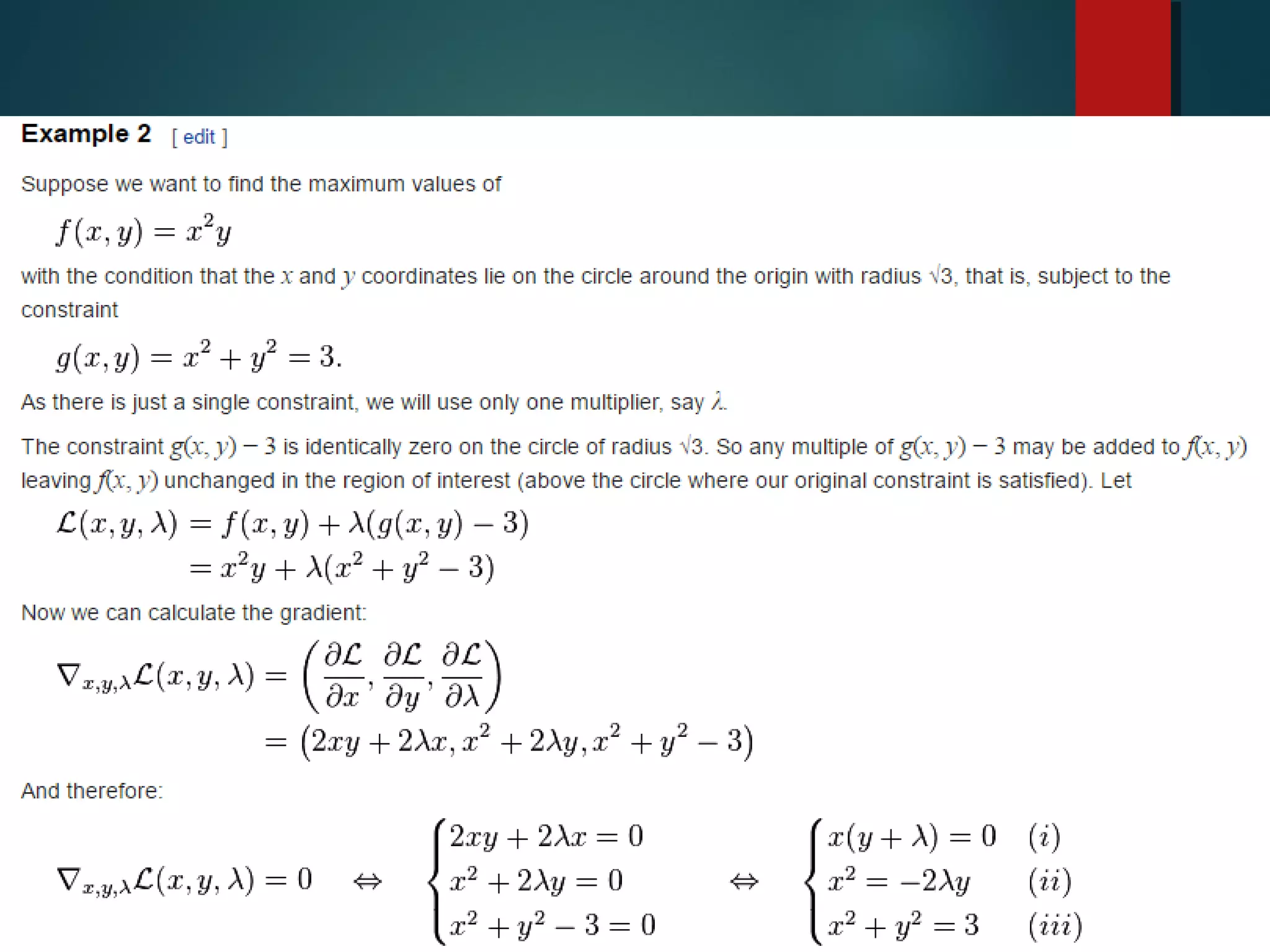
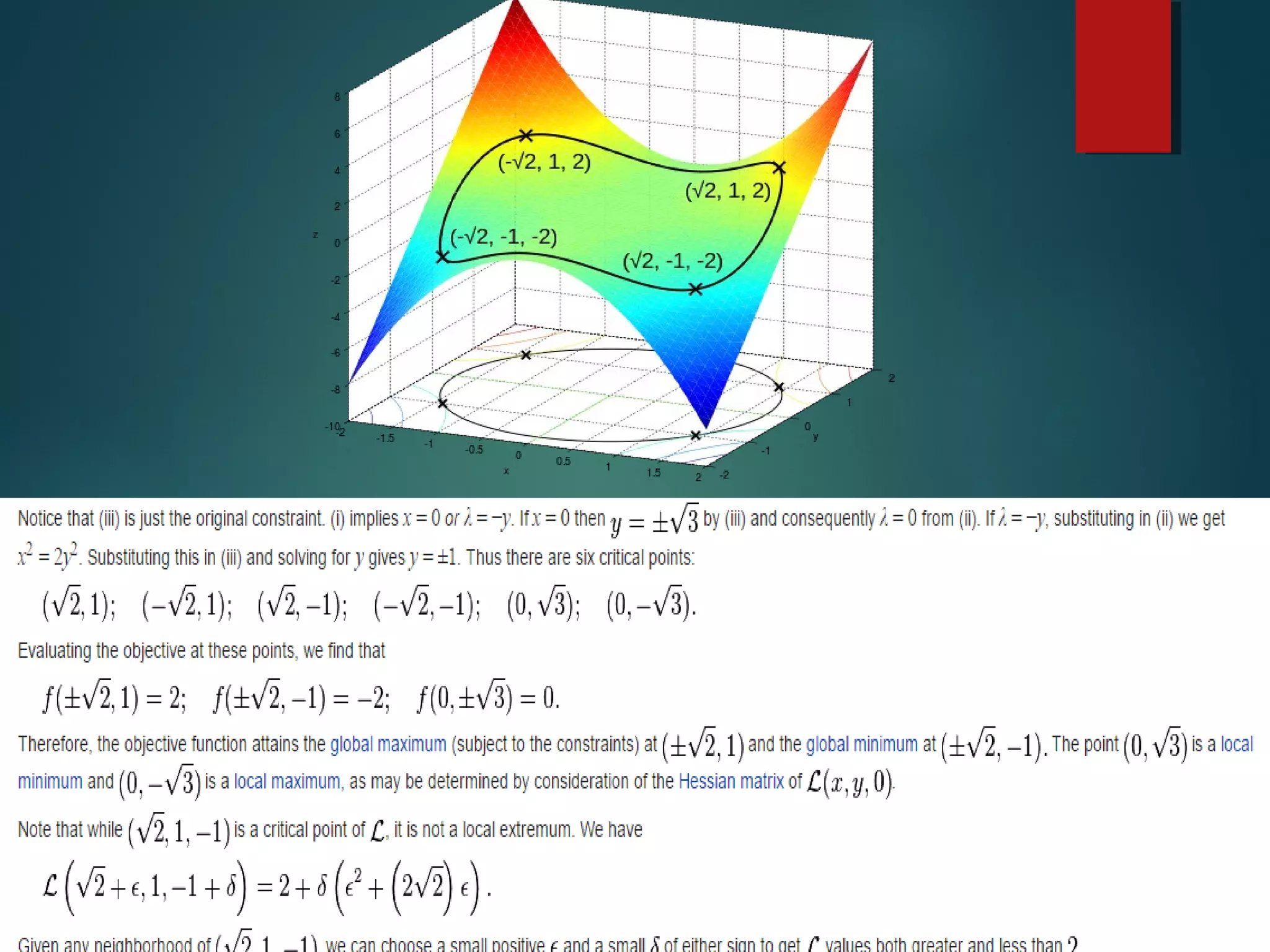
This presentation introduces five presenters and focuses on Lagrange's linear equation and its applications. Specifically, it defines Lagrange's linear partial differential equation as involving a dependent variable z and two independent variables x and y. It also discusses solving linear equations and applications in mathematics, economics, control theory, and nonlinear programming. In economics, the Lagrange multiplier represents the shadow price of a constraint like a budget. In control theory, Lagrange multipliers are interpreted as costate variables in optimal control problems.