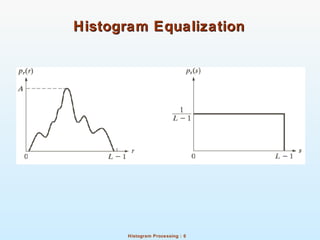
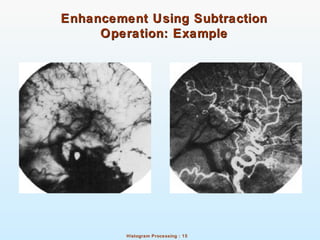
Histograms show the distribution of pixel intensities in an image by counting the number of pixels for each intensity value. Normalized histograms provide an estimate of the probability of each intensity occurring. Histogram equalization transforms the pixel intensity distribution of an image to a uniform distribution in order to increase contrast. It does this by using the cumulative distribution function to map intensities to new output values. Local histogram equalization performs this on neighborhoods within an image to enhance local details. Arithmetic and logical operations can also be used for image enhancement, such as AND, OR, and subtraction between images on a pixel-by-pixel basis.