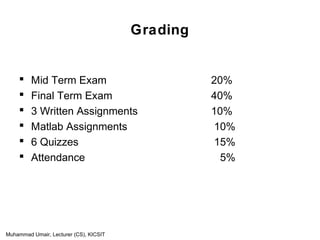
This document outlines the content of a lecture on signals and systems. The key points are:
- Signals represent patterns of variation over time and can be continuous or discrete. Systems process input signals to produce output signals.
- The course will cover time and frequency domain analysis, Laplace transforms, Fourier transforms, sampling theory and z-transforms.
- Students will be assessed via exams, assignments and quizzes. Recommended reading materials are listed.
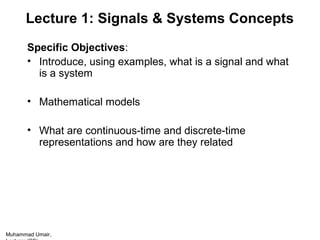
- The specific lecture will introduce signals, systems, their mathematical representations in continuous and discrete time, and properties like causality, linearity and time-invariance. Exercises are to read the first chapter of a referenced text.




![Muhammad Umair, Lecturer (CS), KICSIT
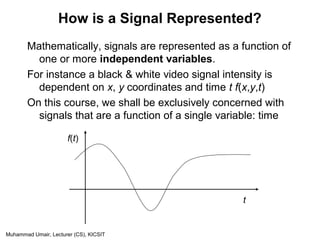
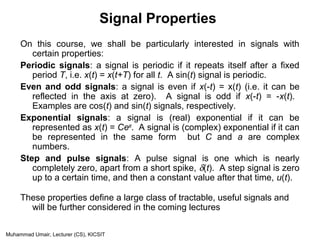
Continuous & Discrete-Time Signals
Continuous-Time Signals
Most signals in the real world are
continuous time, as the scale is
infinitesimally fine.
Eg voltage, velocity,
Denote by x(t), where the time
interval may be bounded (finite) or
infinite
Discrete-Time Signals
Some real world and many digital
signals are discrete time, as they
are sampled
E.g. pixels, daily stock price
(anything that a digital computer
processes)
Denote by x[n], where n is an integer
value that varies discretely
Sampled continuous signal
x[n] =x(nk) – k is sample time
x(t)
t
x[n]
n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-131002071259-phpapp01/85/Lecture1-Intro-To-Signa-9-320.jpg)
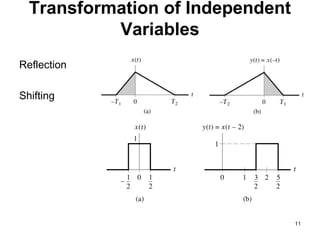
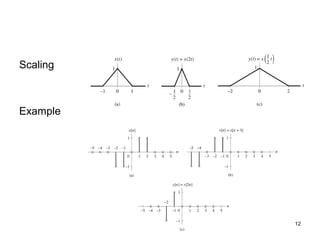

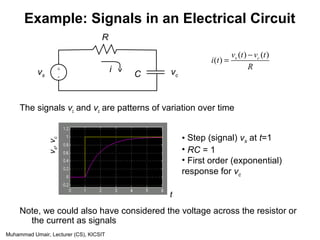
![Muhammad Umair, Lecturer (CS), KICSIT
Continuous & Discrete-Time
Mathematical Models of Systems
Continuous-Time Systems
Most continuous time systems
represent how continuous
signals are transformed via
differential equations.
E.g. circuit, car velocity
Discrete-Time Systems
Most discrete time systems
represent how discrete signals
are transformed via difference
equations
E.g. bank account, discrete car
velocity system
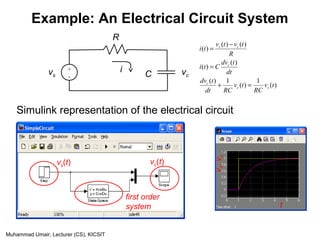
)(
1
)(
1)(
tv
RC
tv
RCdt
tdv
sc
c
=+
)()(
)(
tftv
dt
tdv
m =+ ρ
First order differential equations
][]1[01.1][ nxnyny +−=
][]1[][ nf
m
nv
m
m
nv
∆+
∆
=−
∆+
−
ρρ
First order difference equations
∆
∆−−∆
=
∆ ))1(()()( nvnv
dt
ndv](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-131002071259-phpapp01/85/Lecture1-Intro-To-Signa-16-320.jpg)

