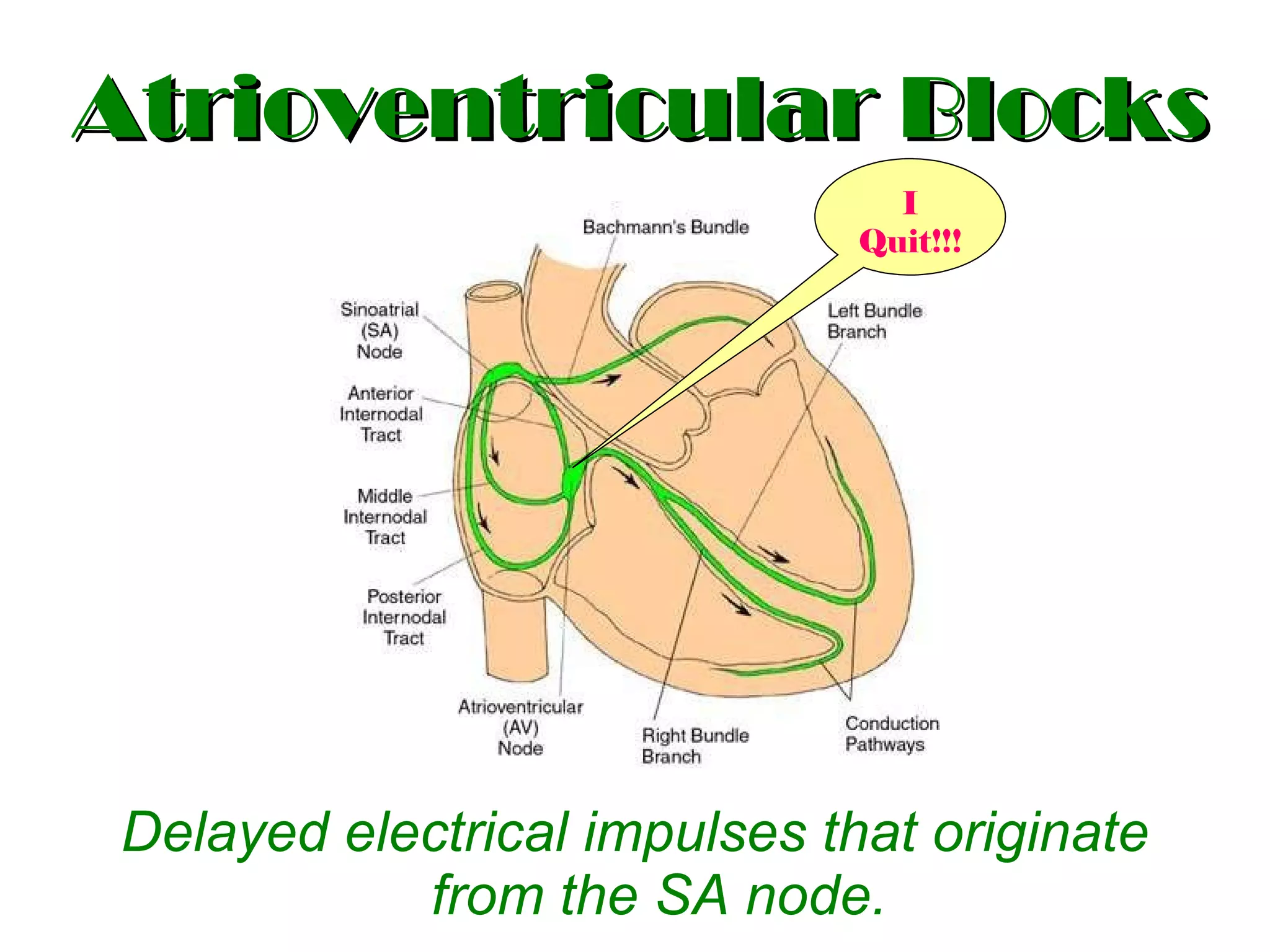
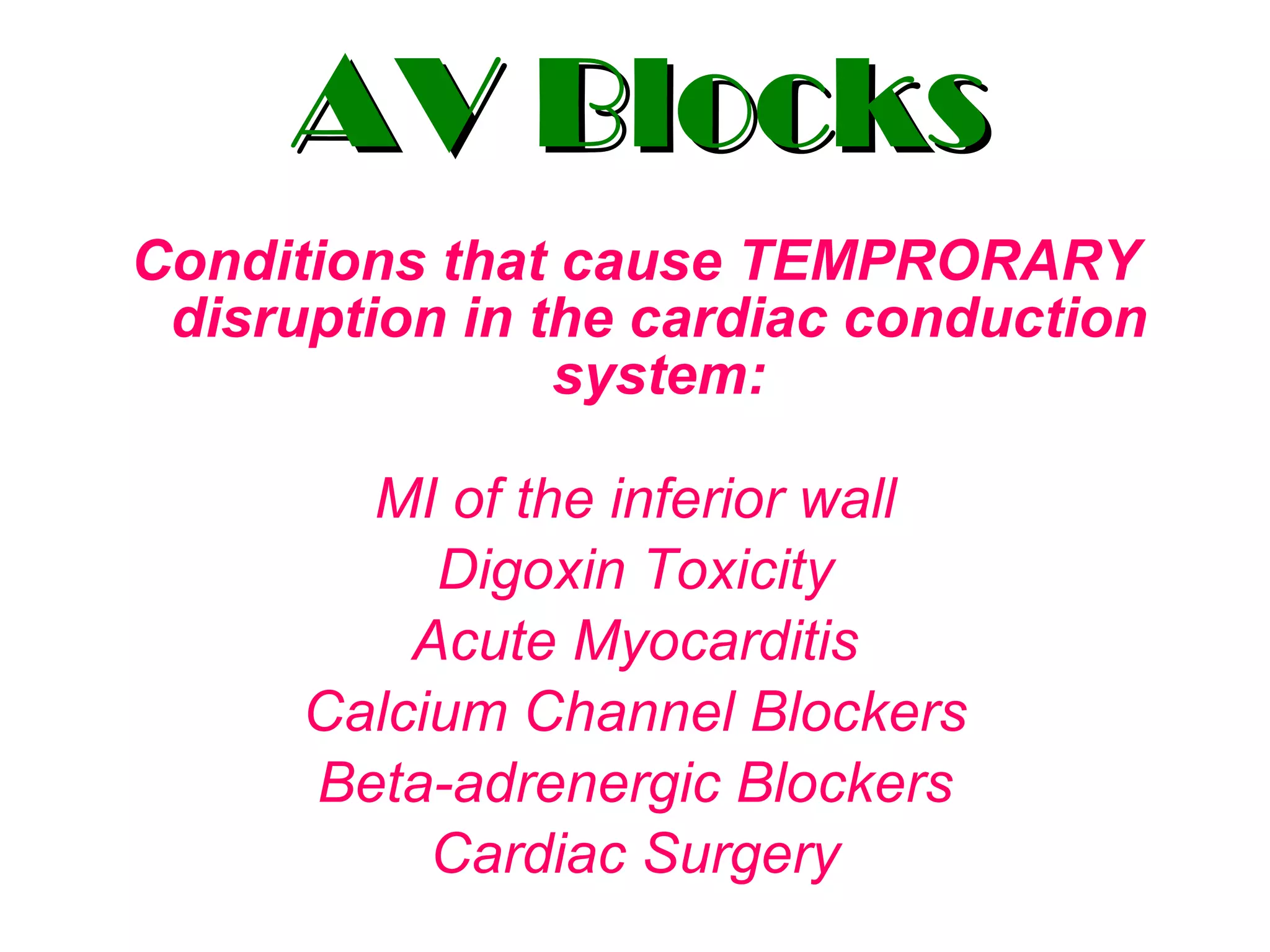
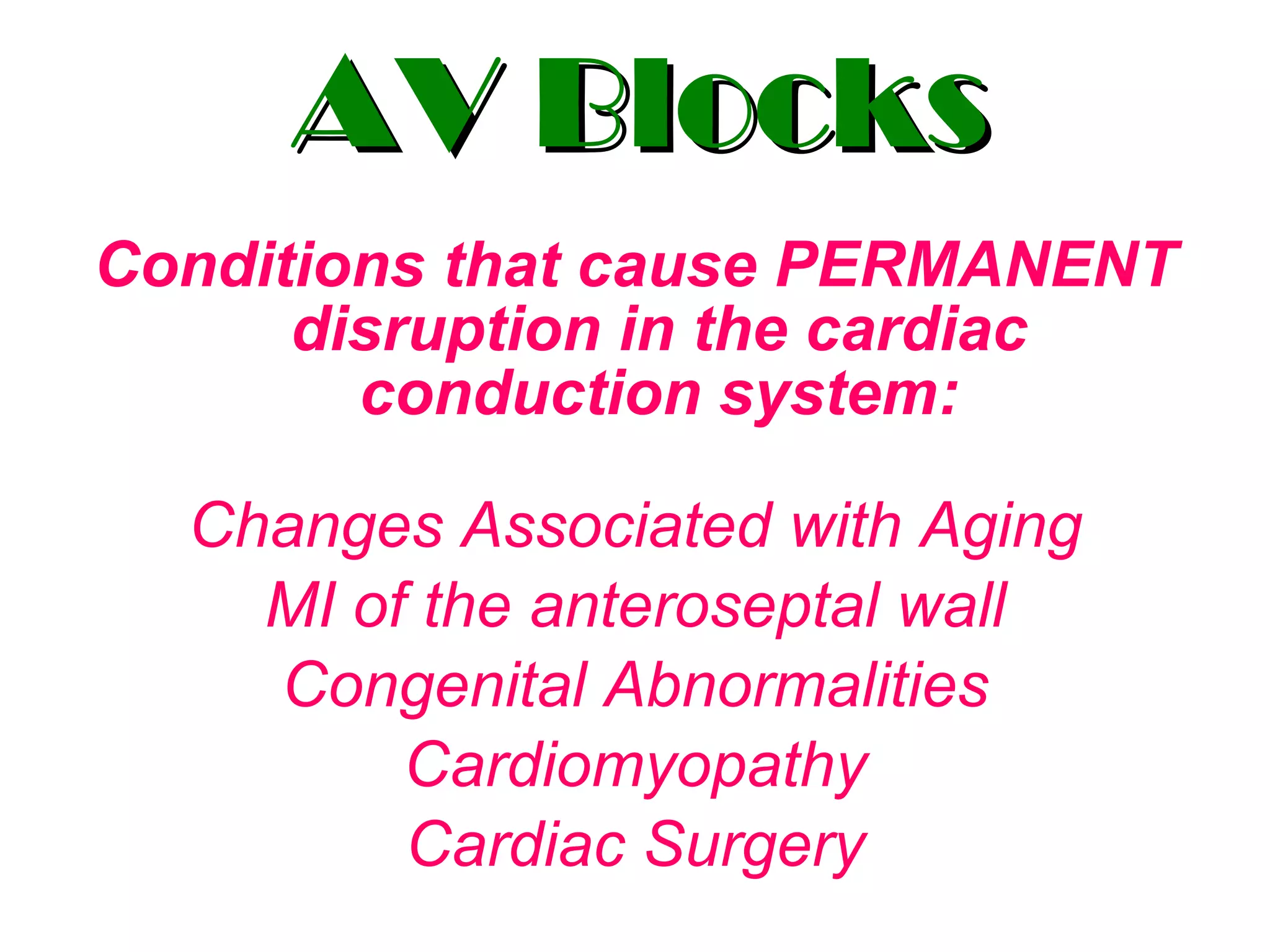
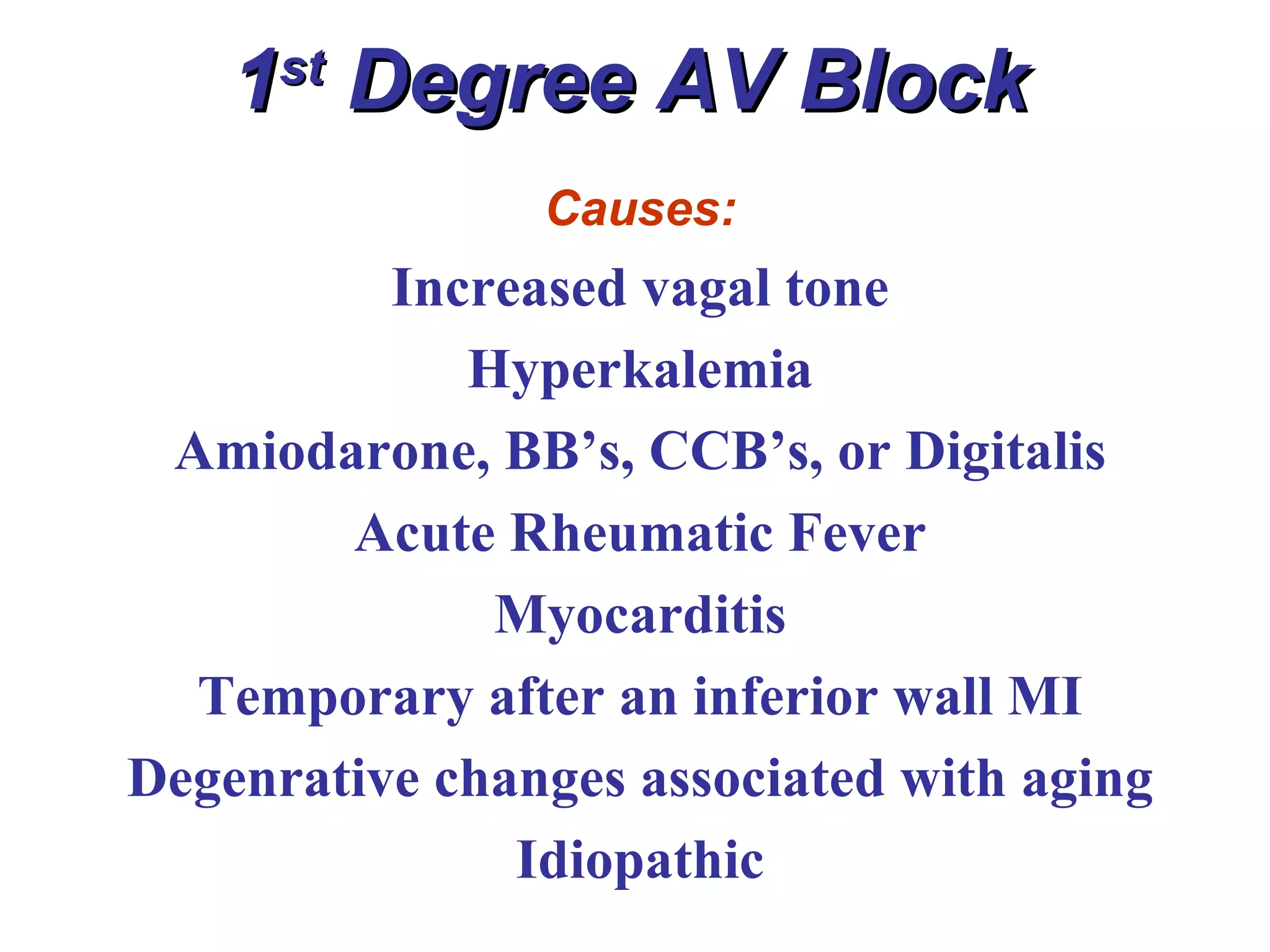
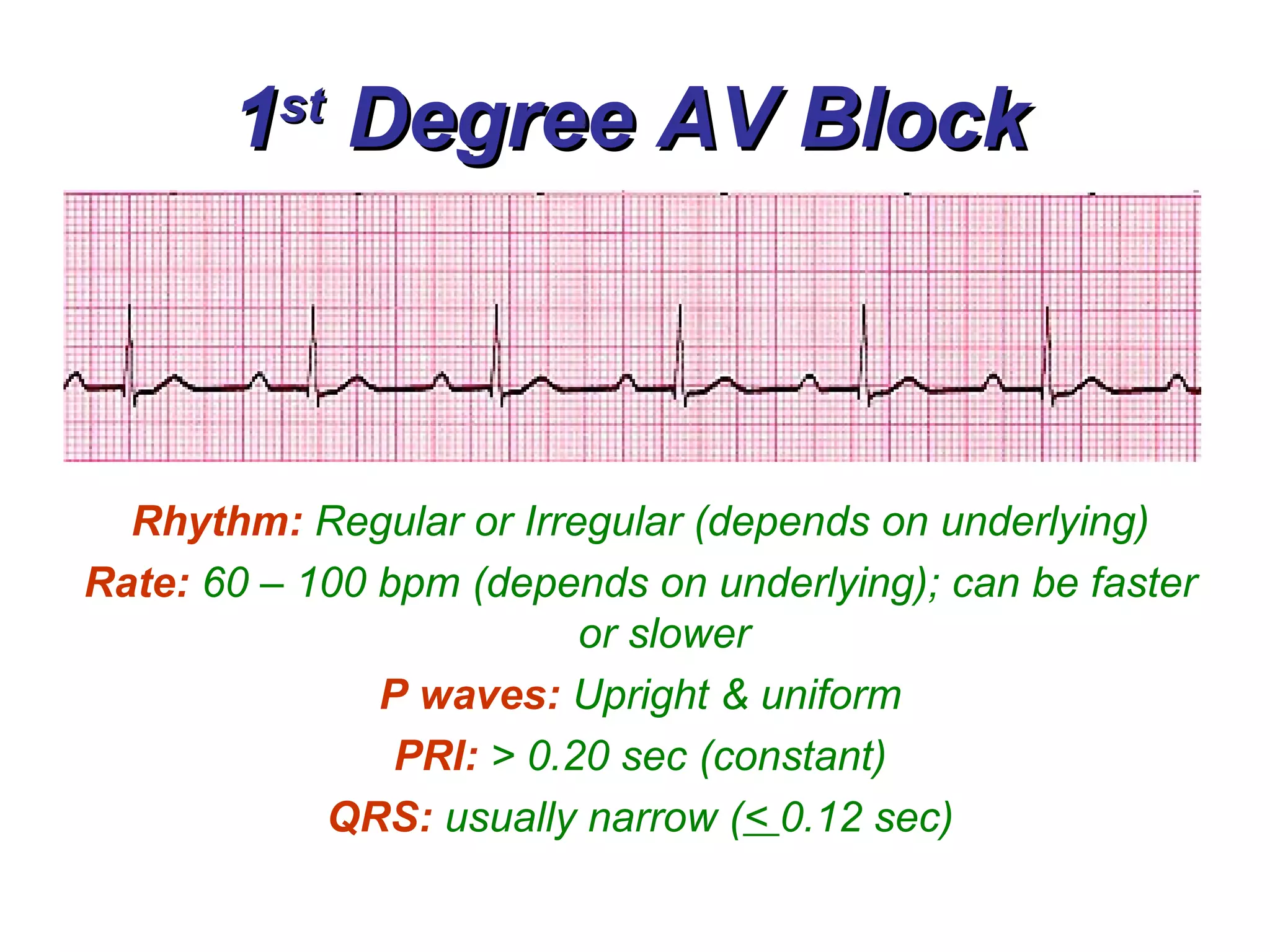
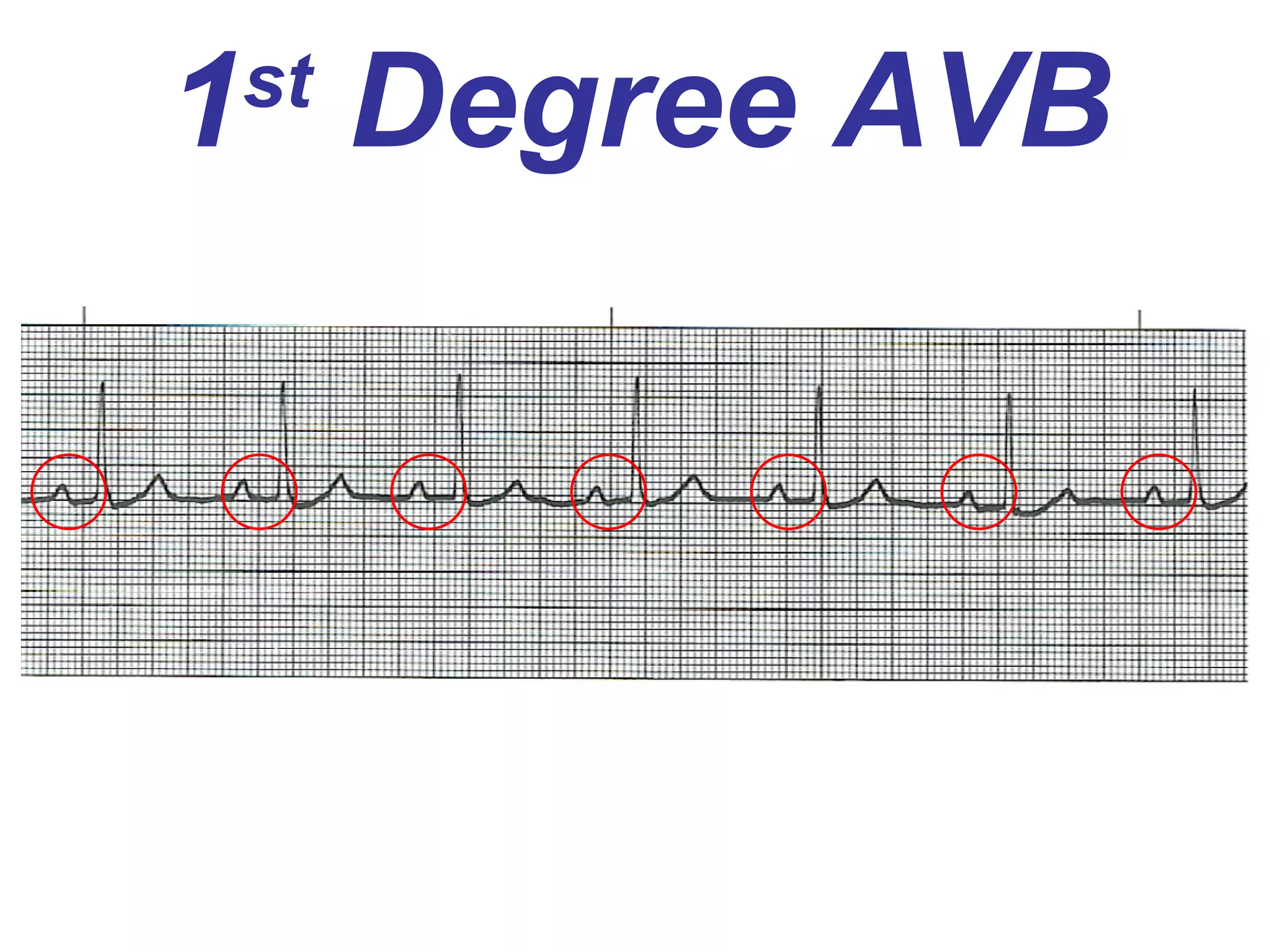
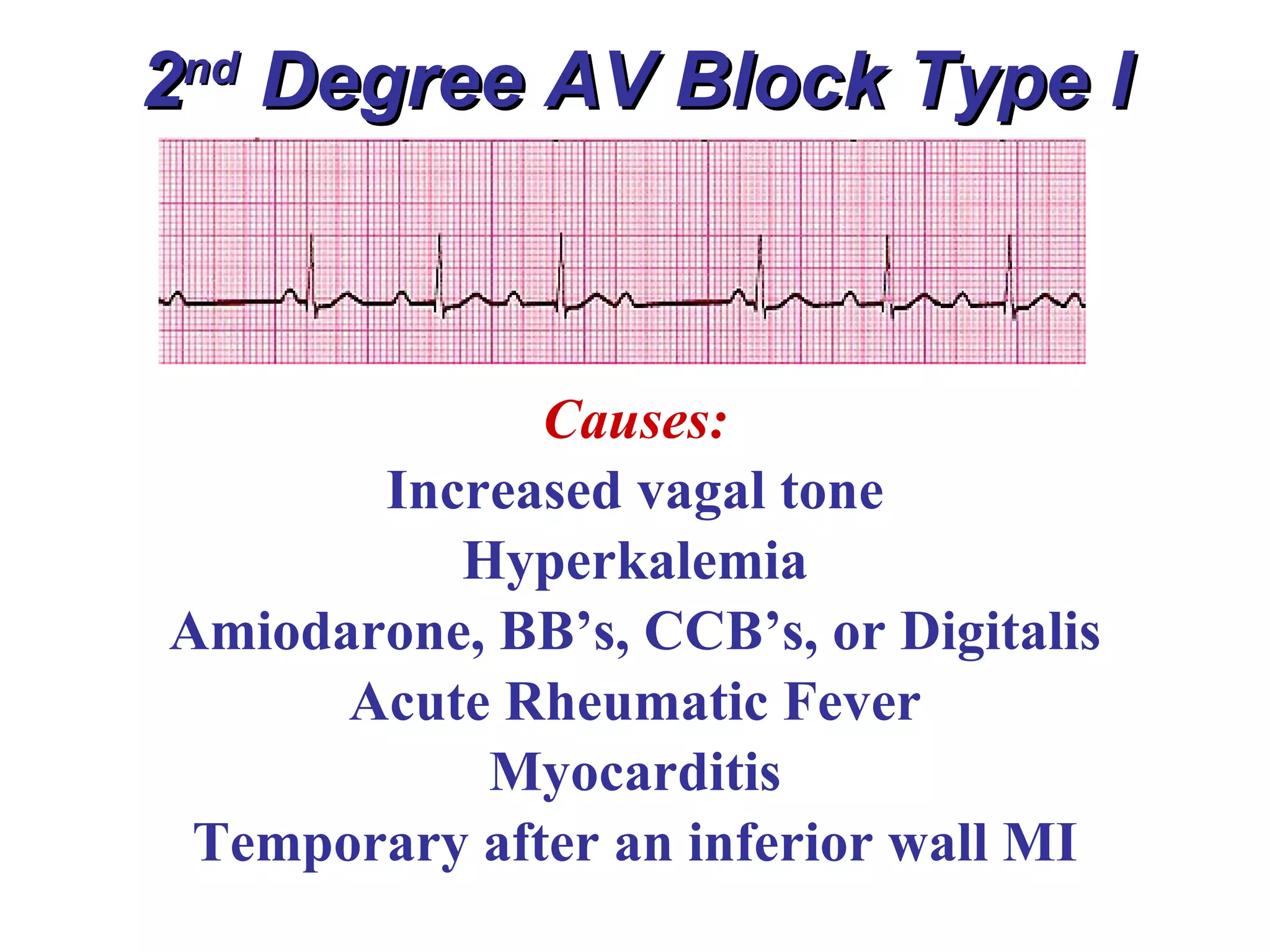
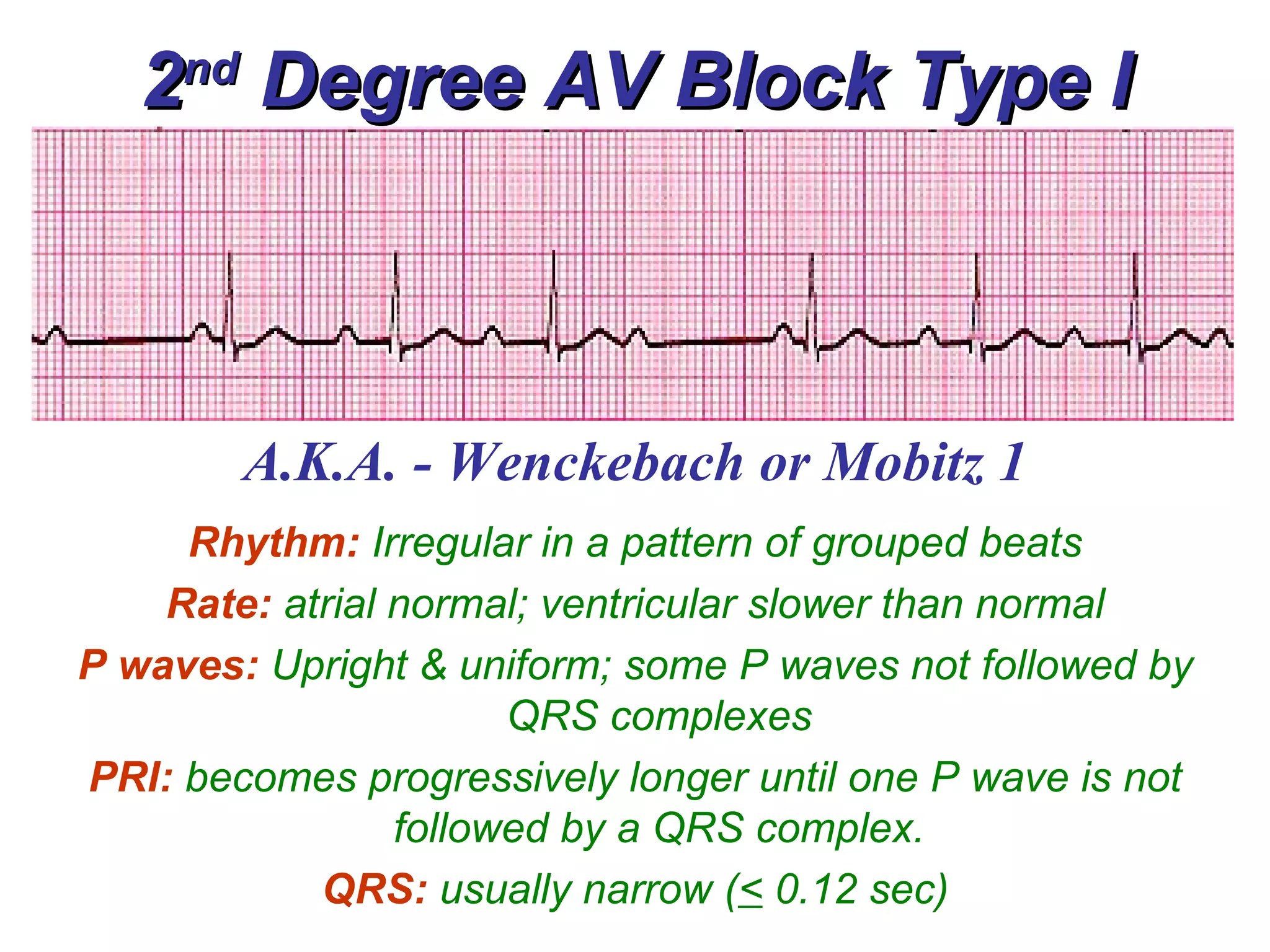
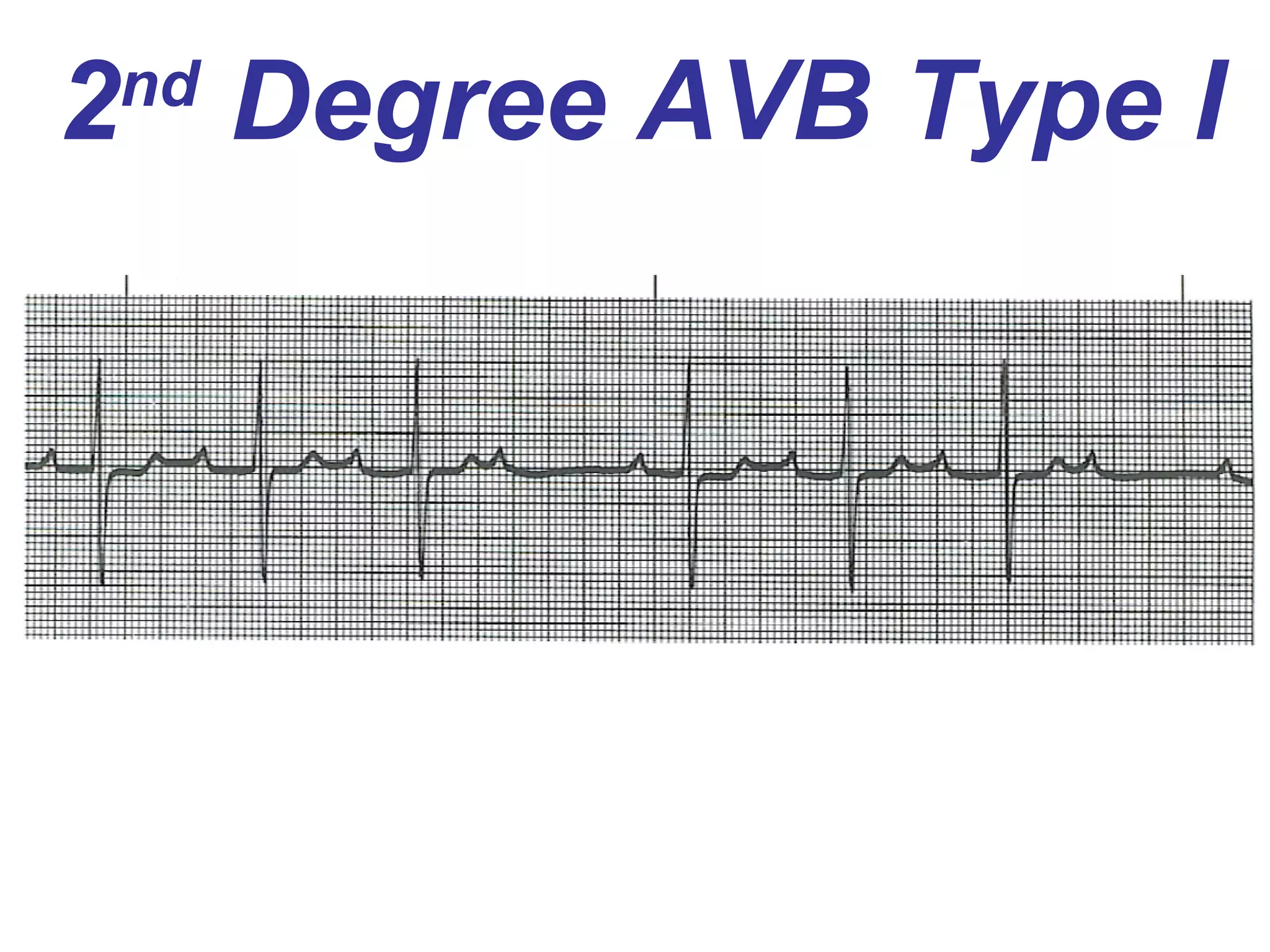
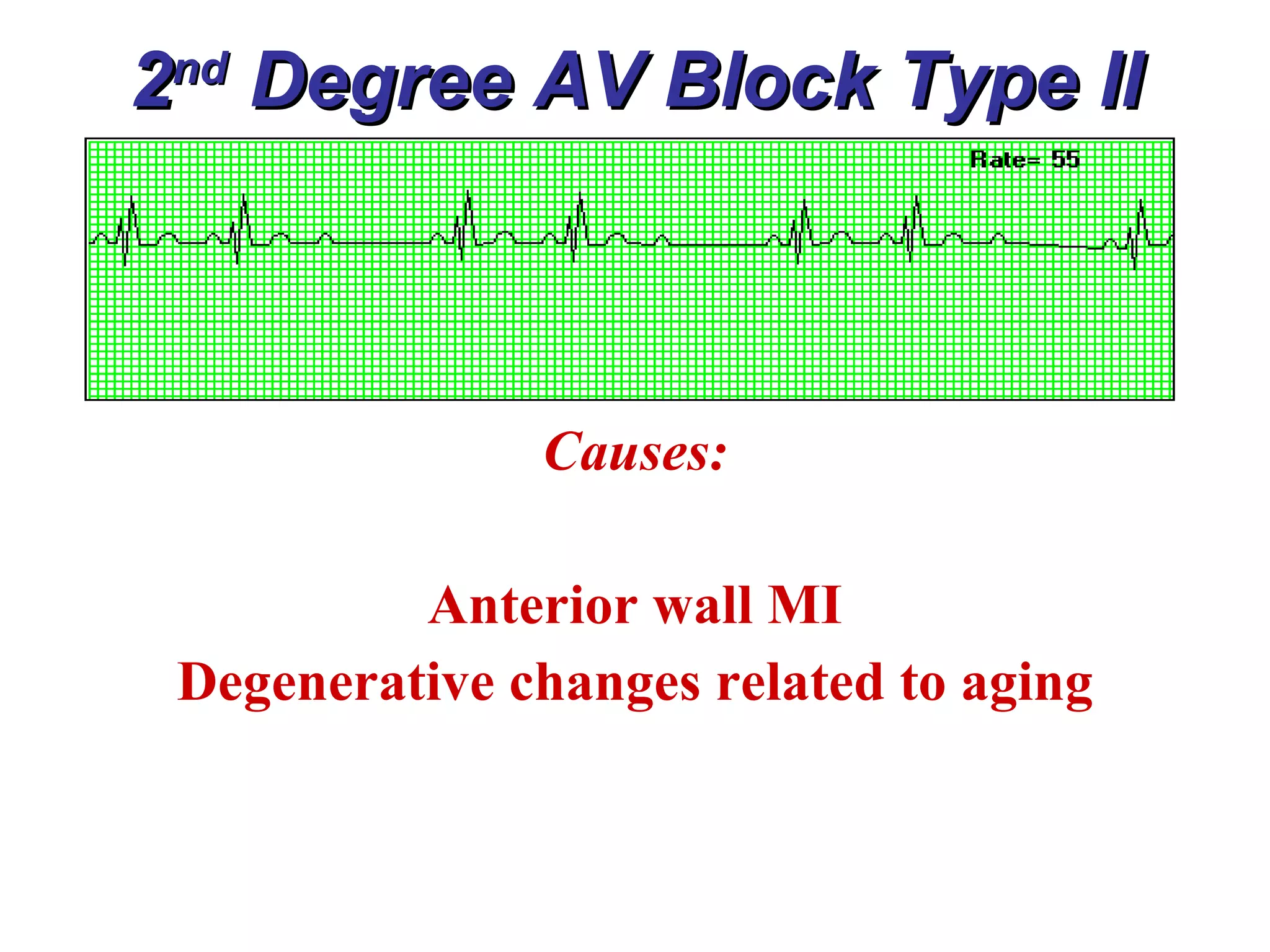
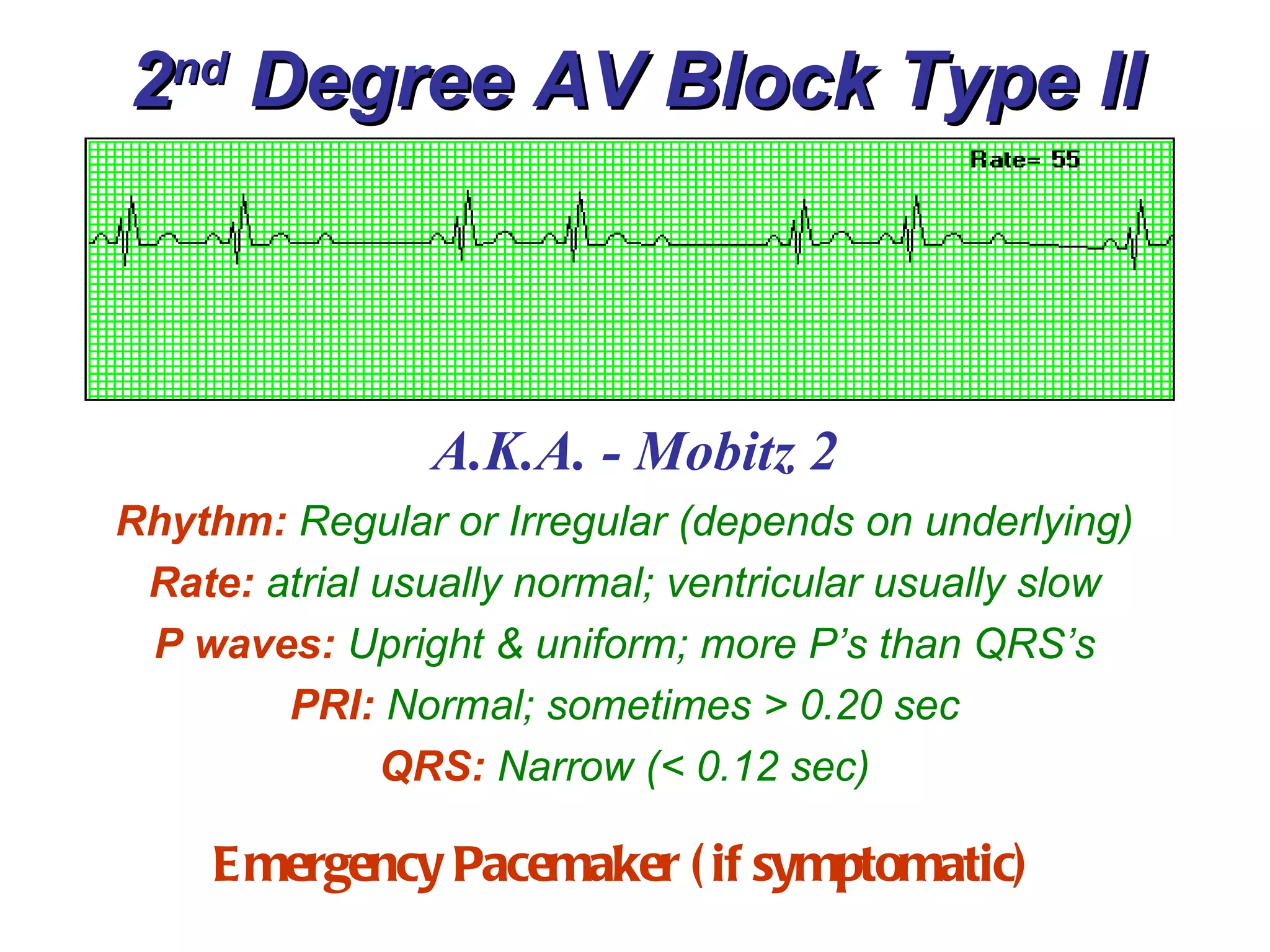
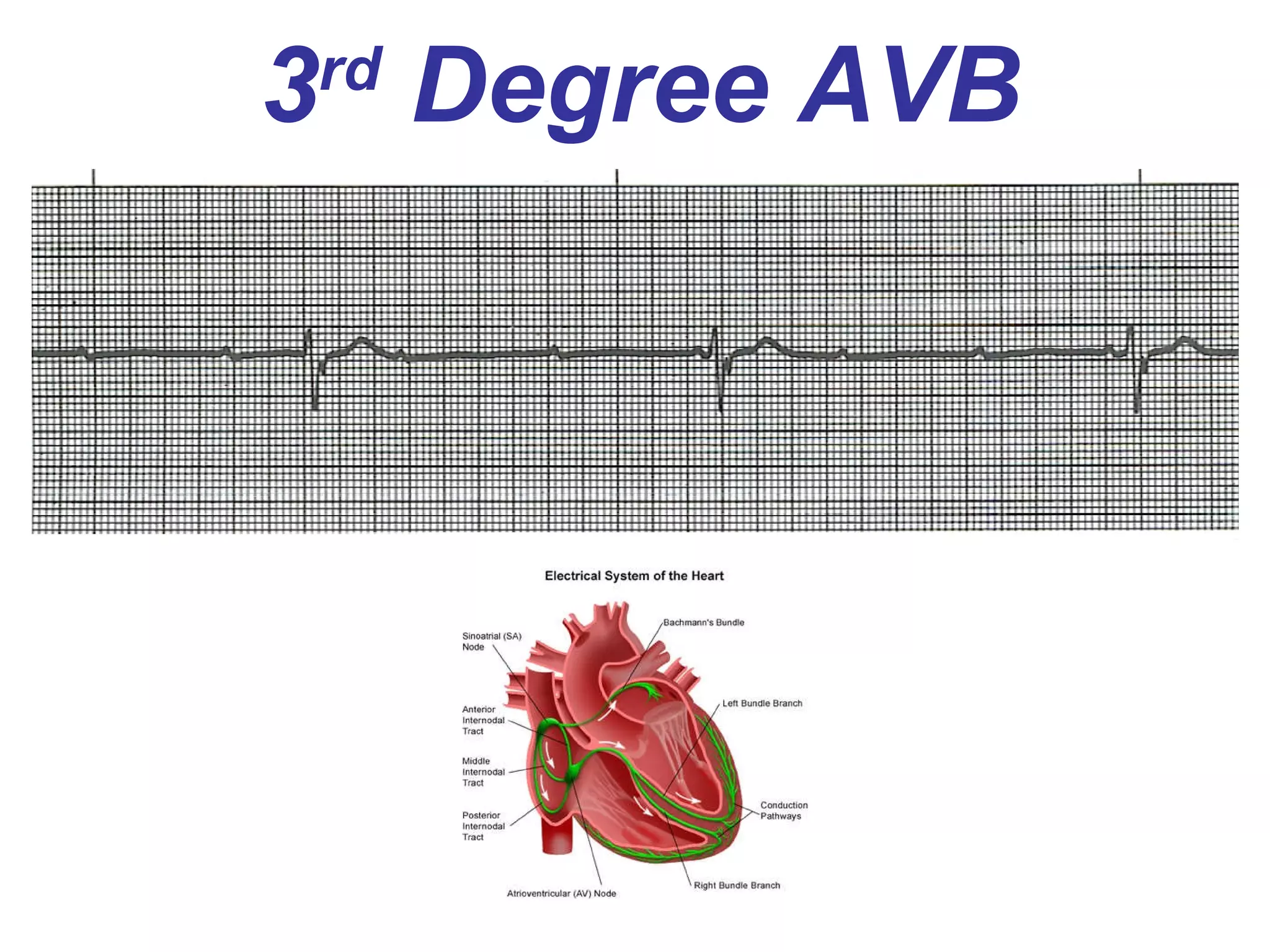
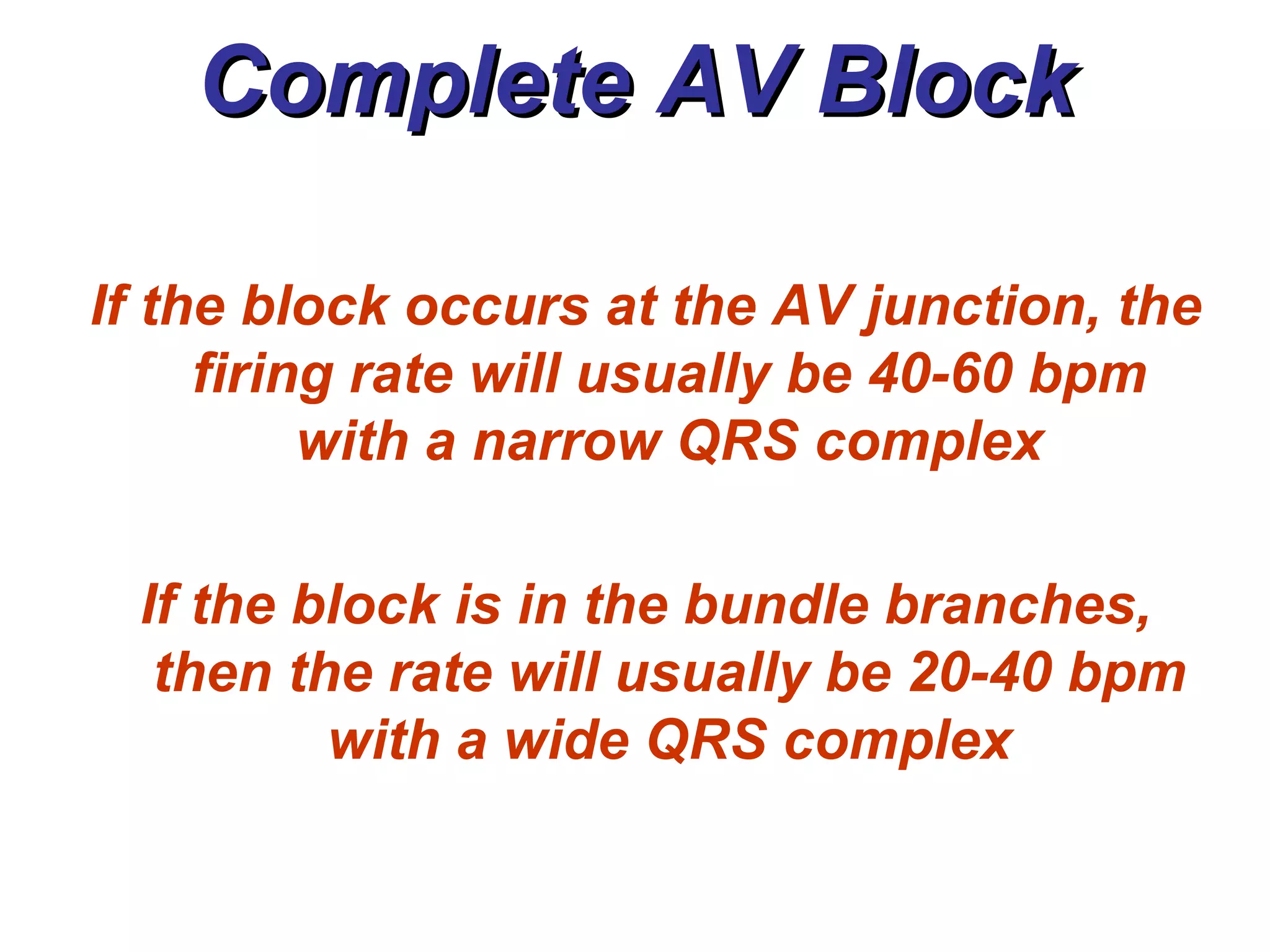
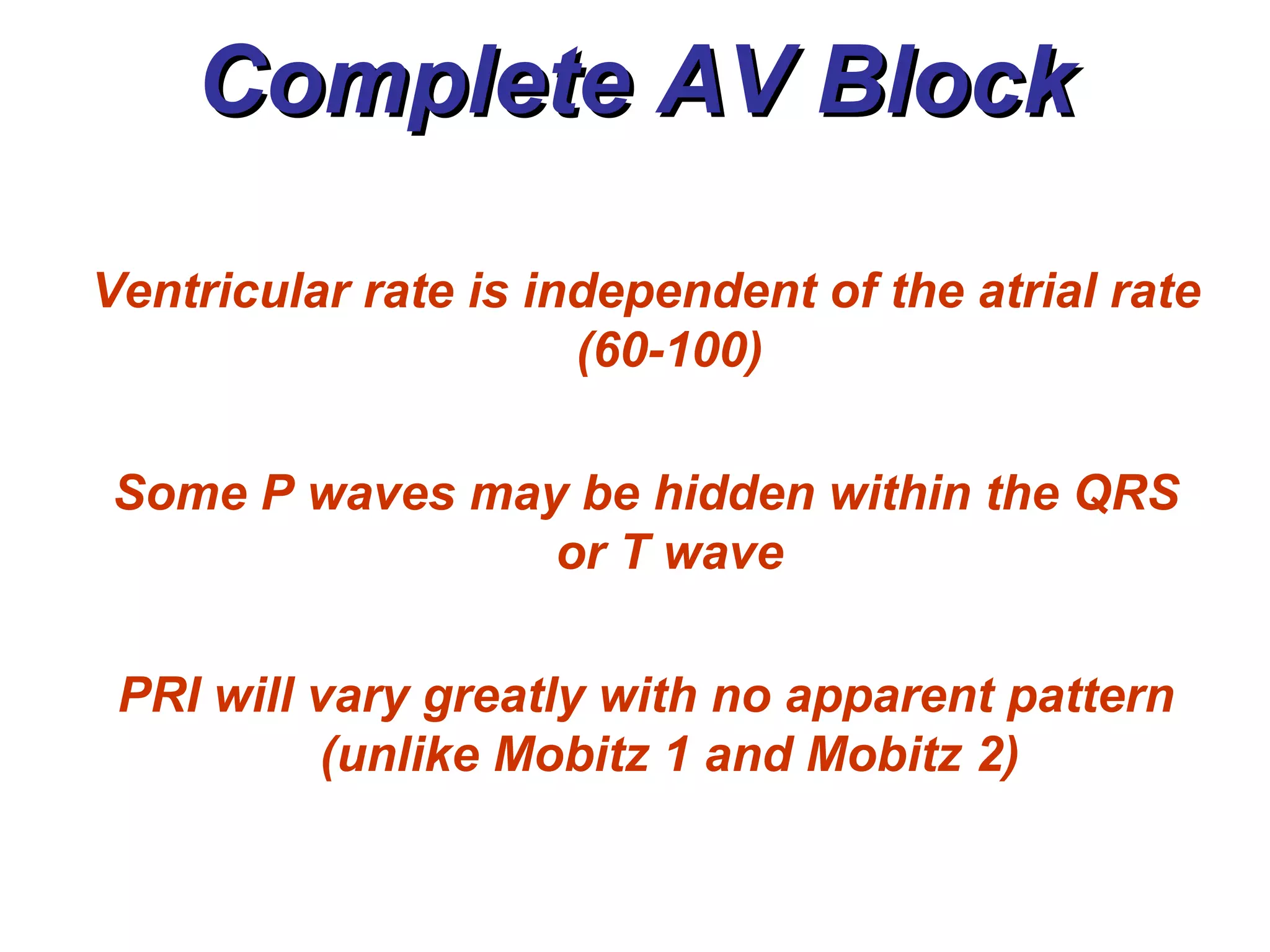
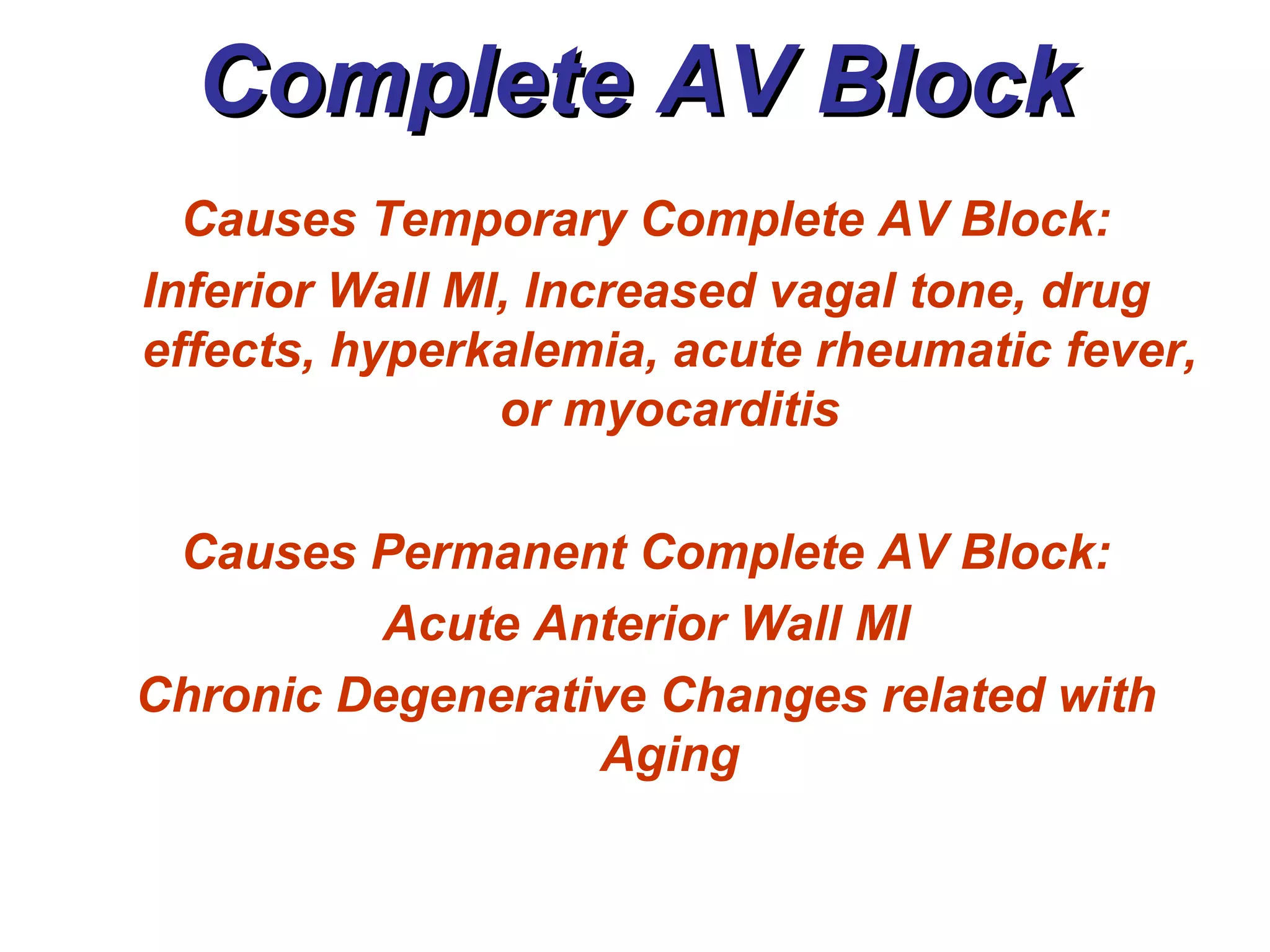
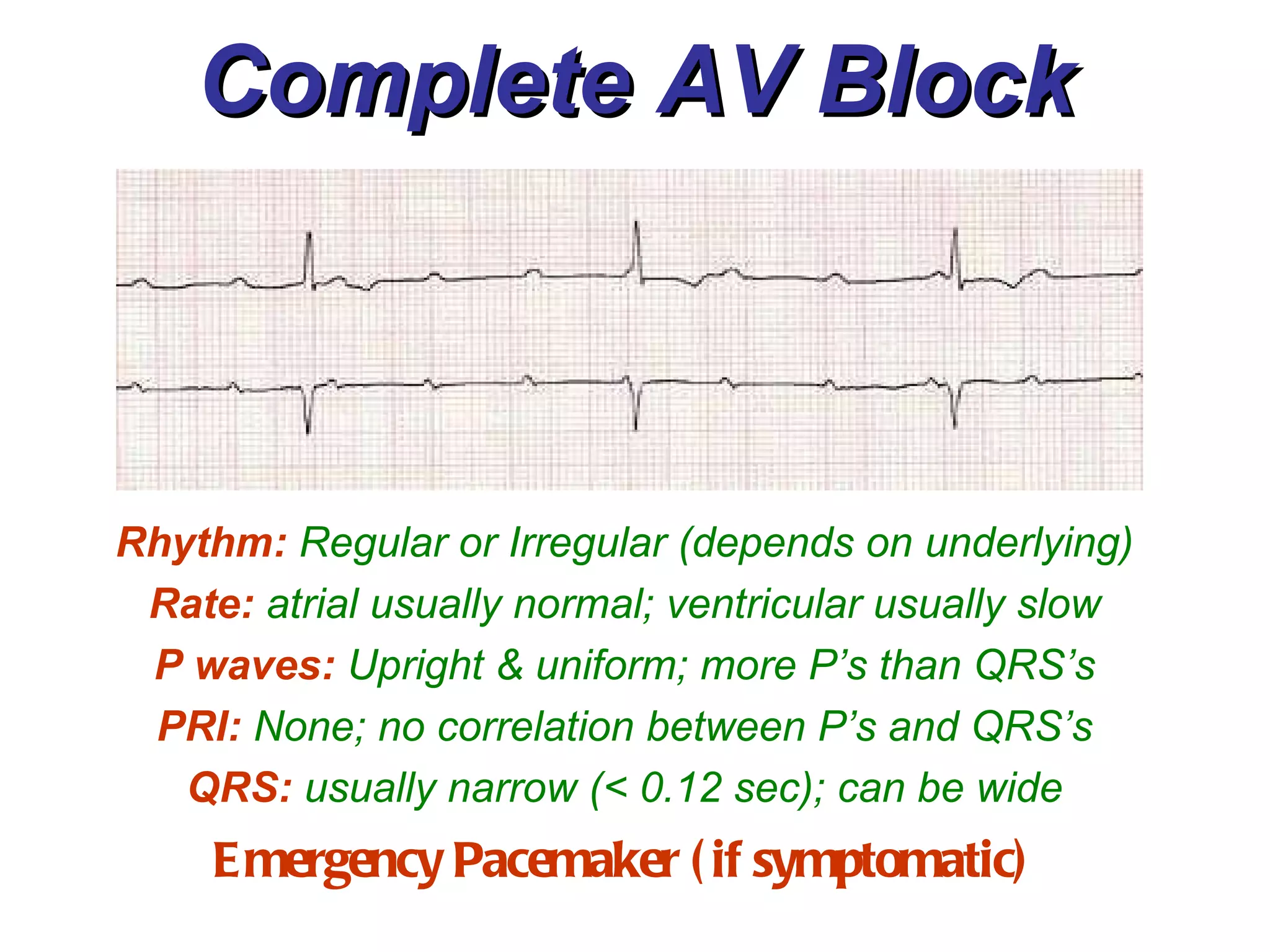
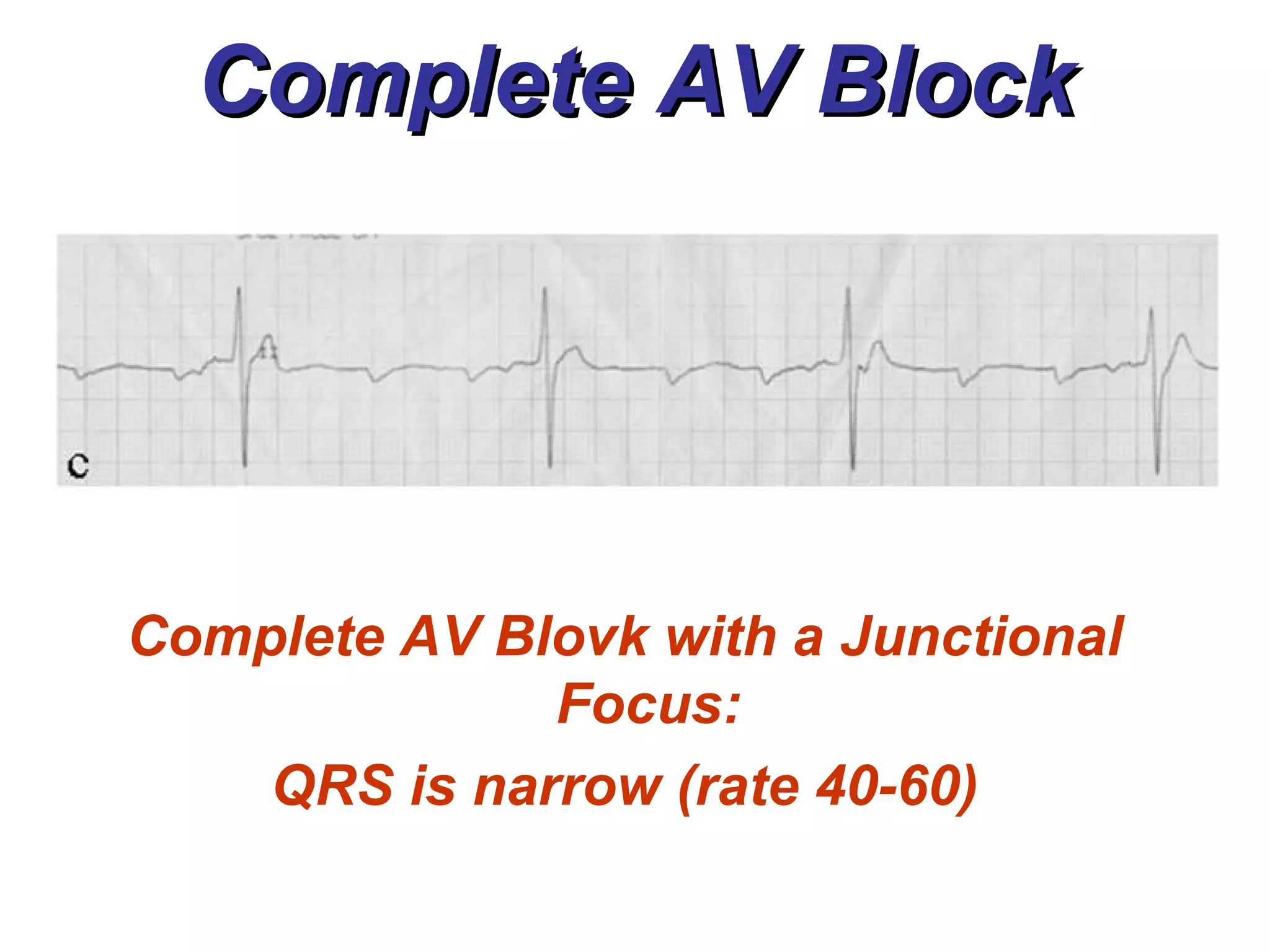
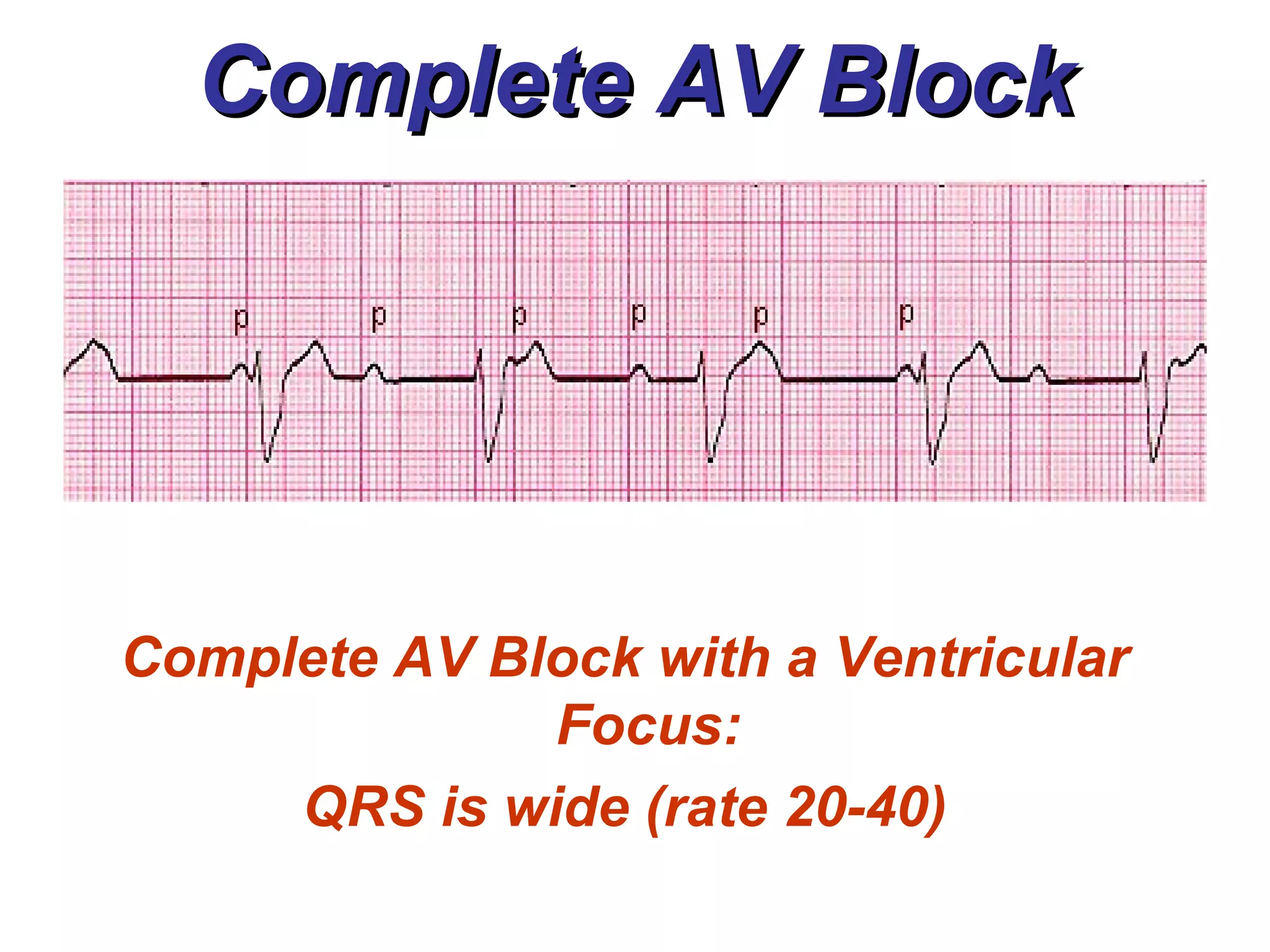
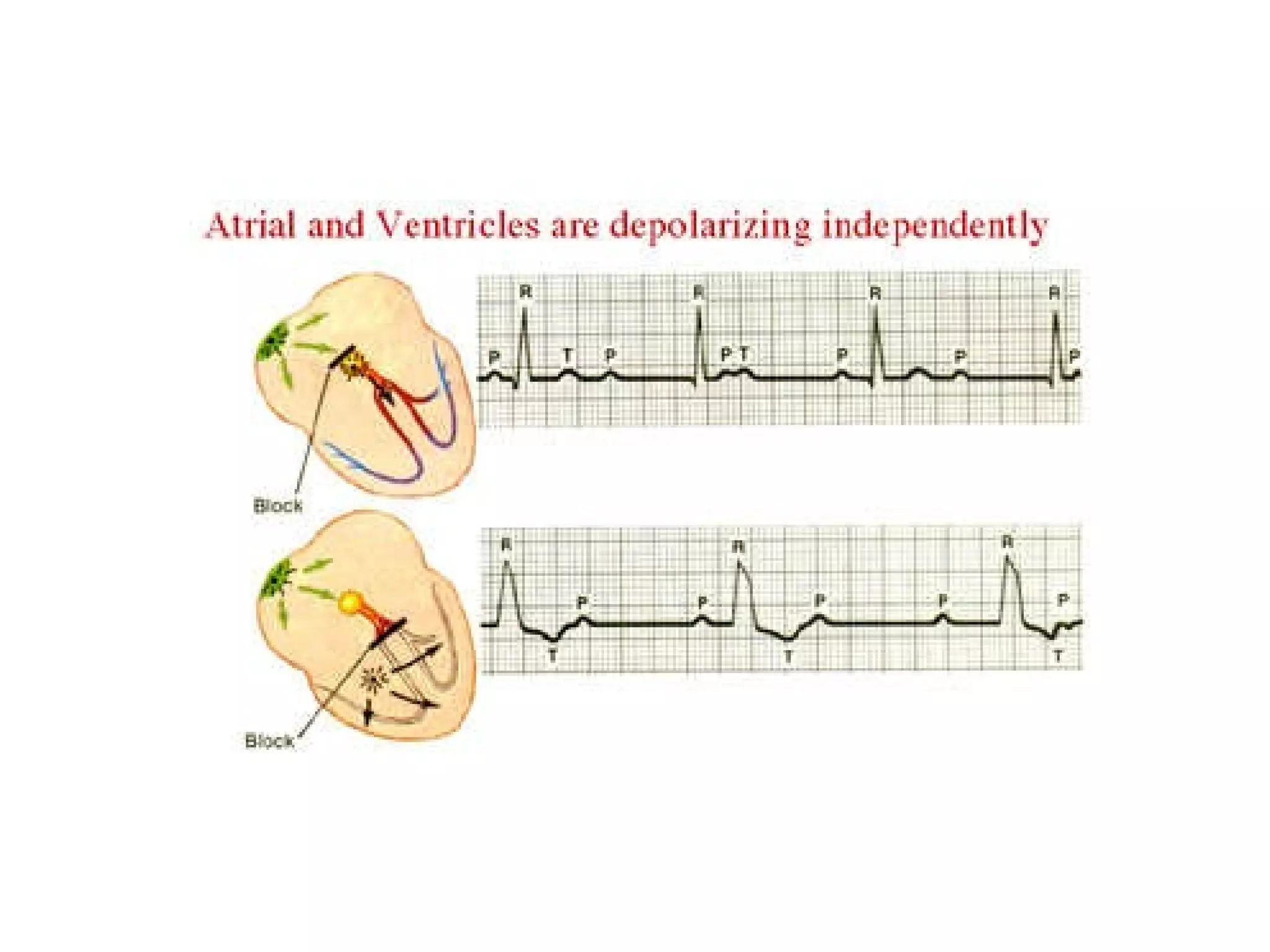
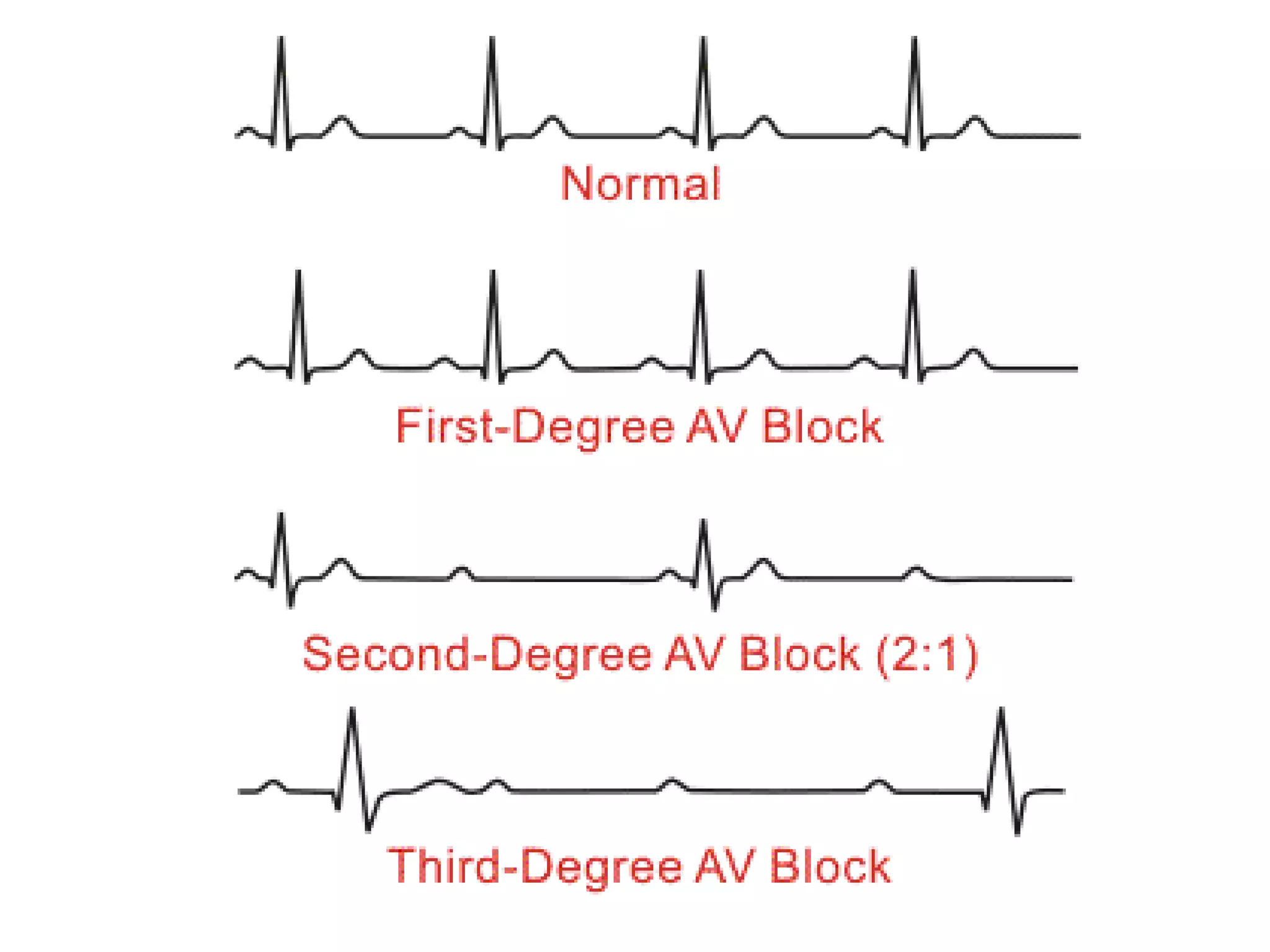
The document discusses different types of atrioventricular blocks (AV blocks), including first-, second-, and third-degree AV blocks. It defines each type of block, describes their characteristic electrocardiogram patterns including rhythm, rate, and P wave and PRI intervals. Causes of temporary and permanent AV blocks are outlined. Management of complete AV block may involve pacemaker placement depending on symptoms and heart rate.