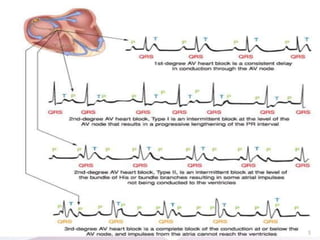
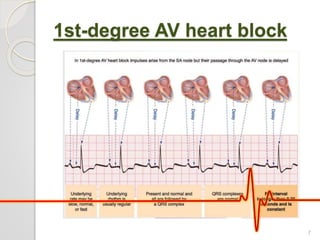
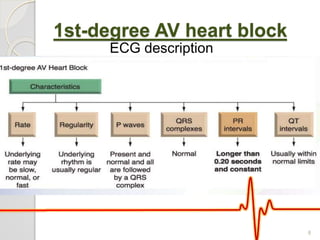
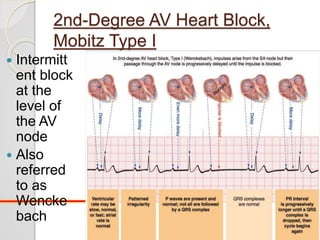
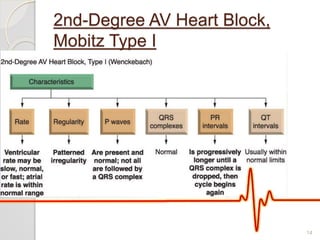
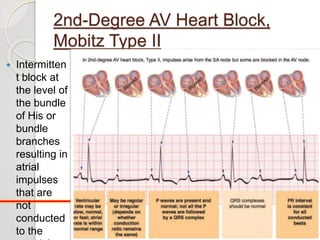
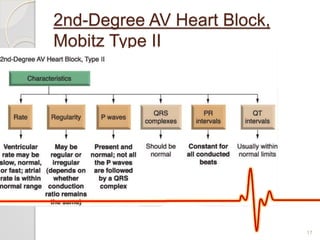
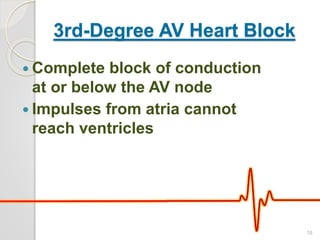
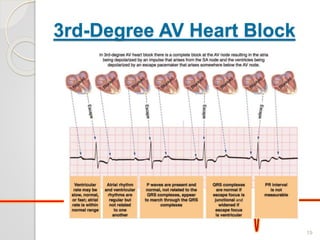
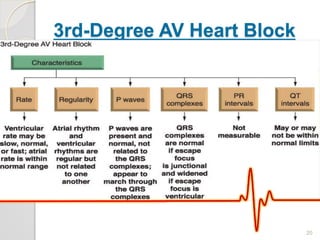
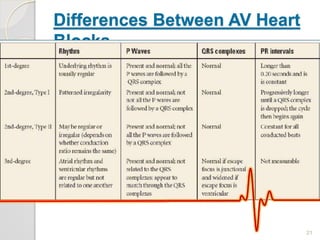
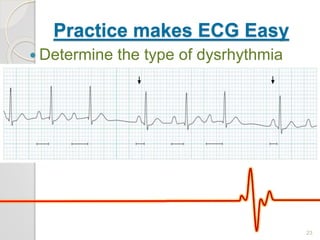
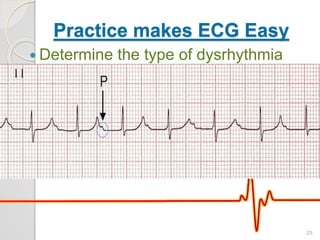
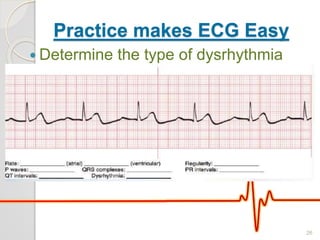
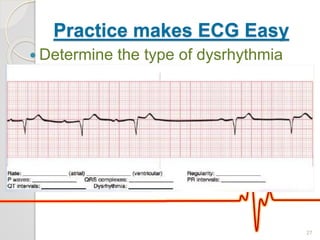
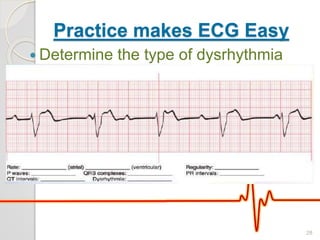
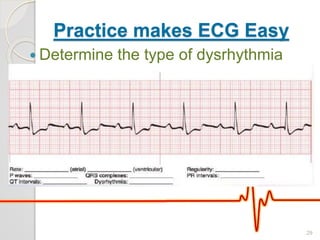
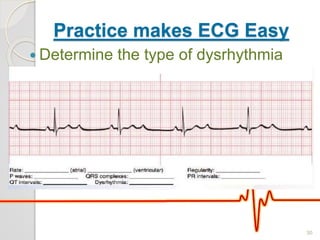
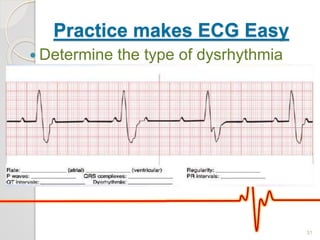
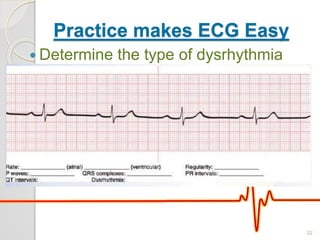
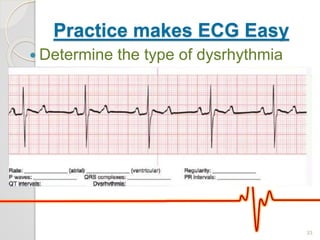
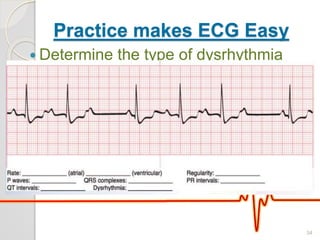
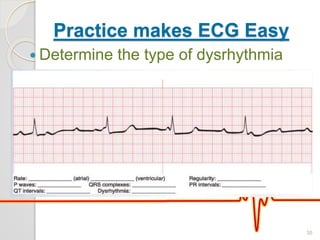
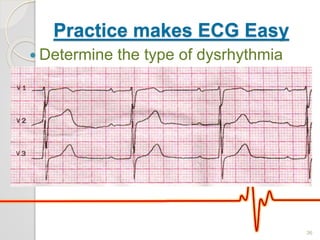
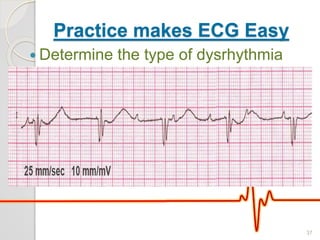
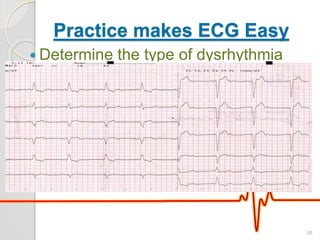
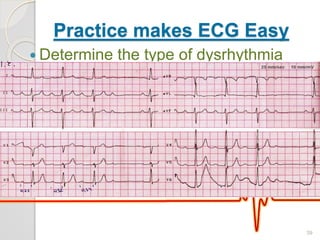
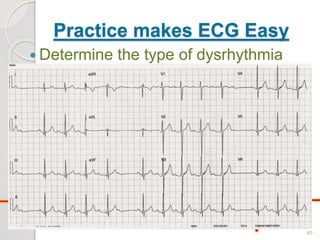
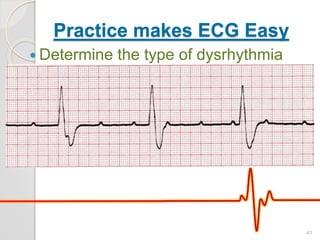
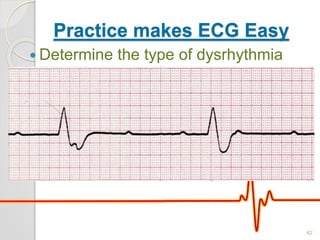
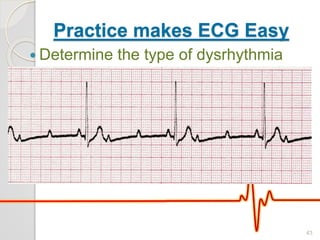
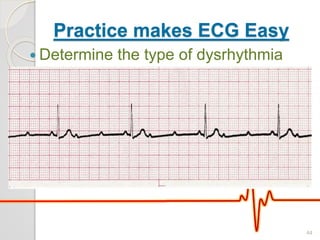
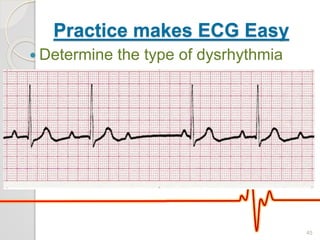
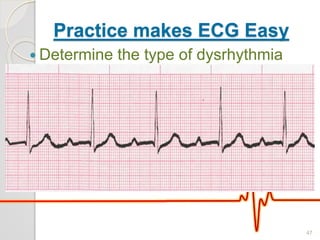
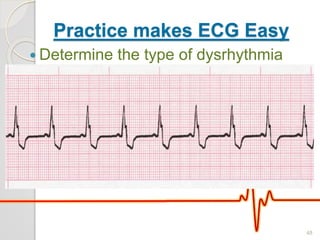
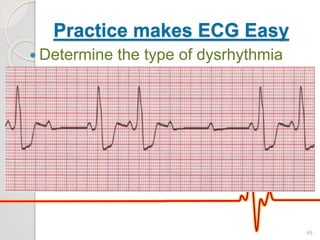
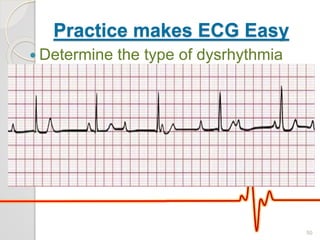
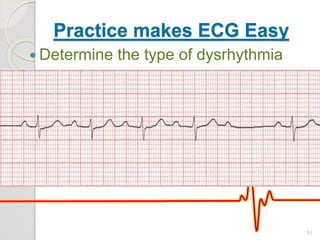
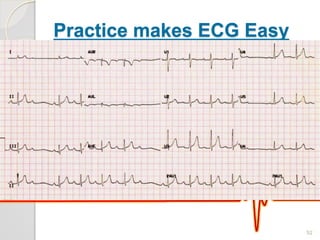
The document discusses atrio-ventricular (AV) block, which refers to delays or interruptions in the conduction pathway between the atria and ventricles of the heart. There are several types of AV block defined by the degree of conduction block, including first-degree, second-degree Mobitz types I and II, and third-degree AV block. The causes, ECG characteristics, and descriptions of each type of AV block are provided. The document emphasizes practicing ECG interpretation to determine the type of cardiac dysrhythmia.