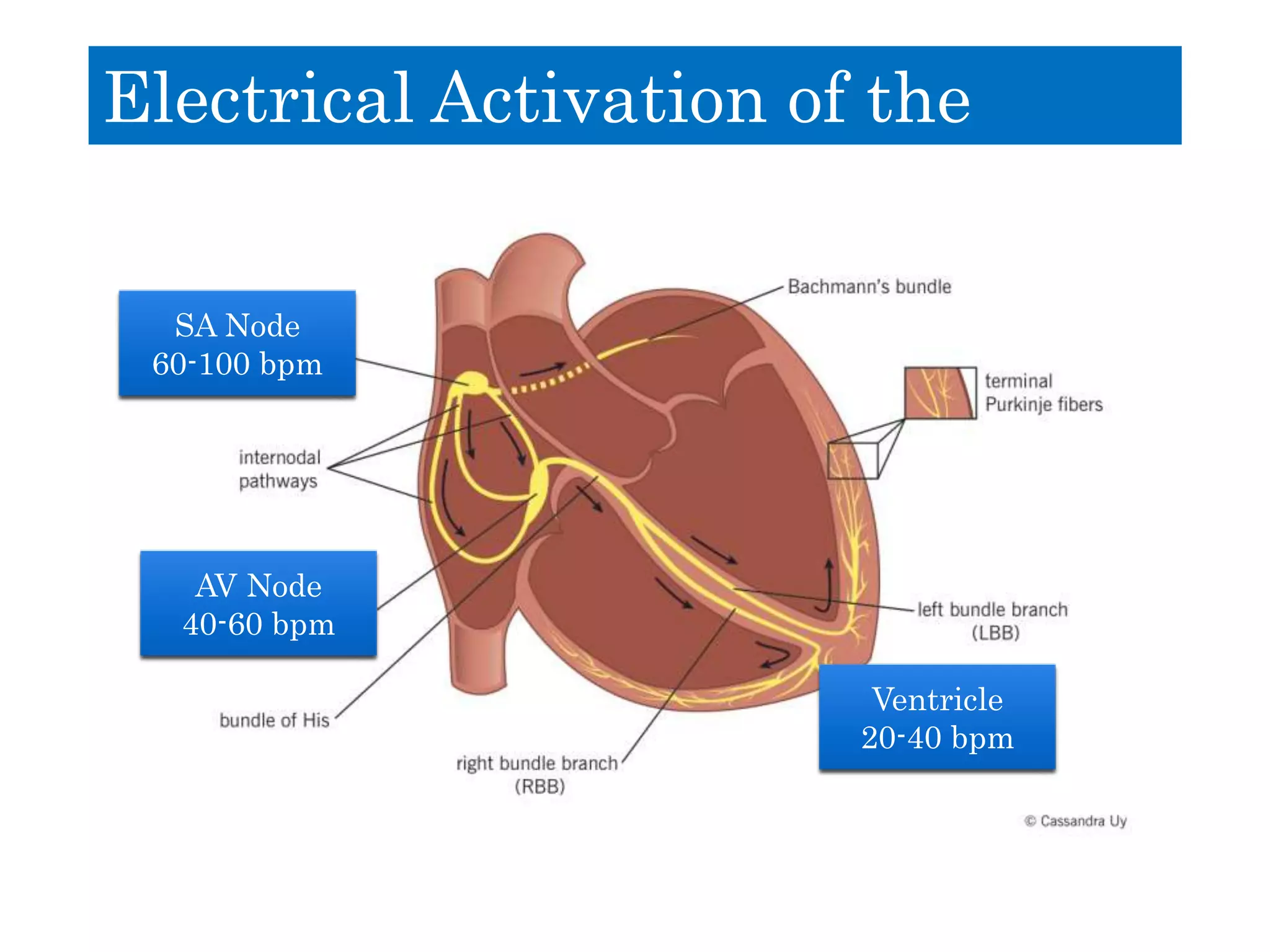
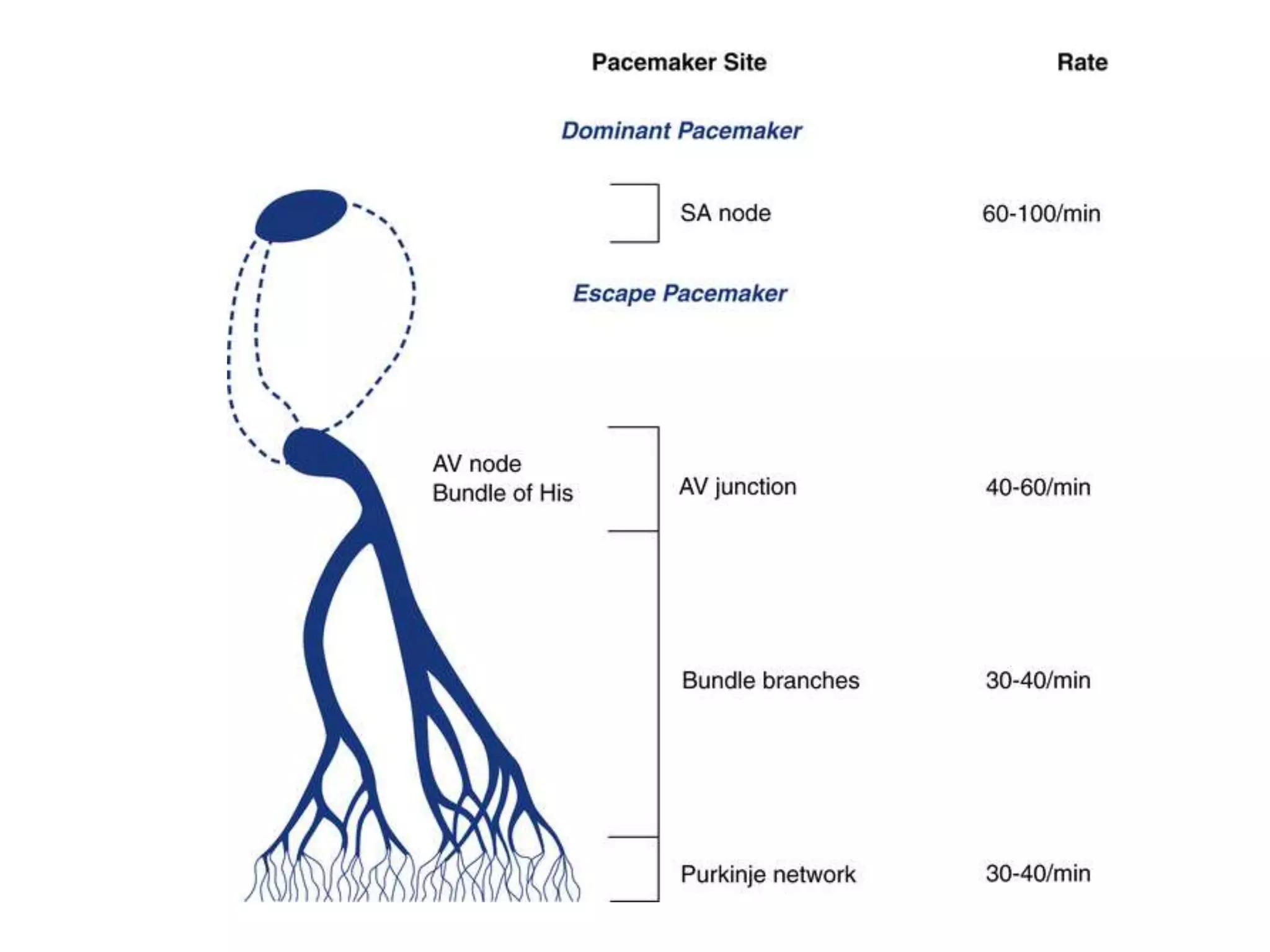
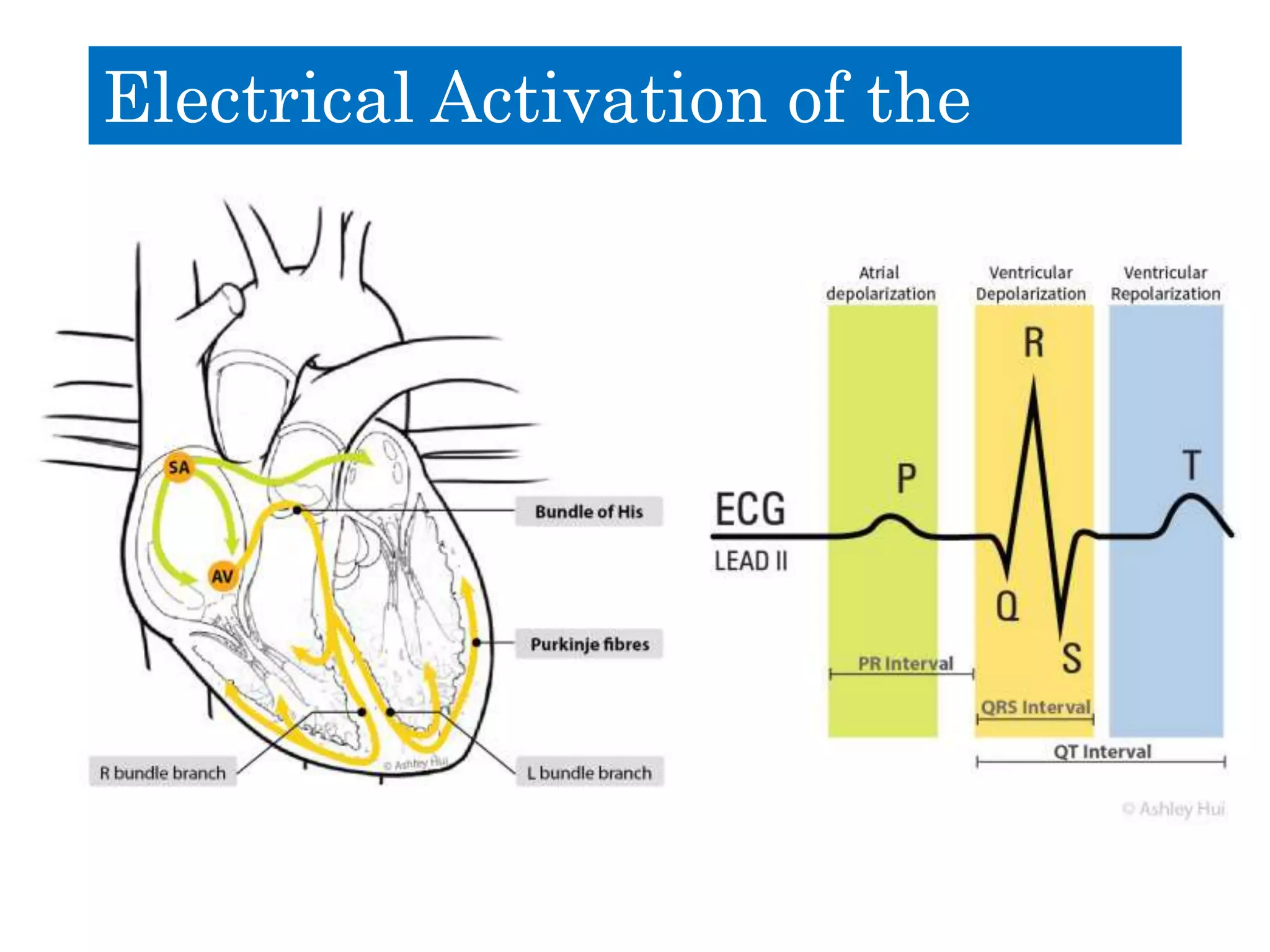
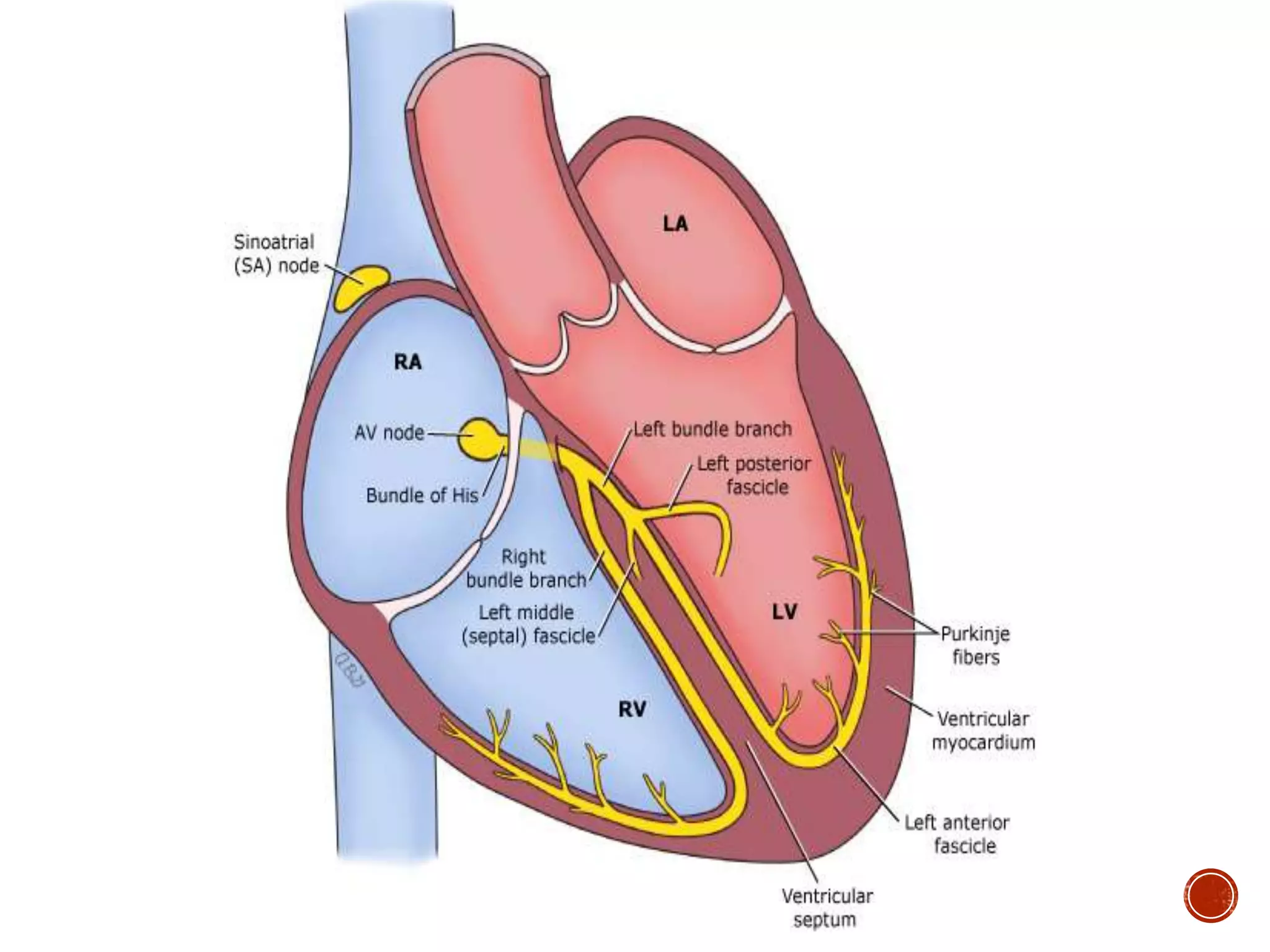
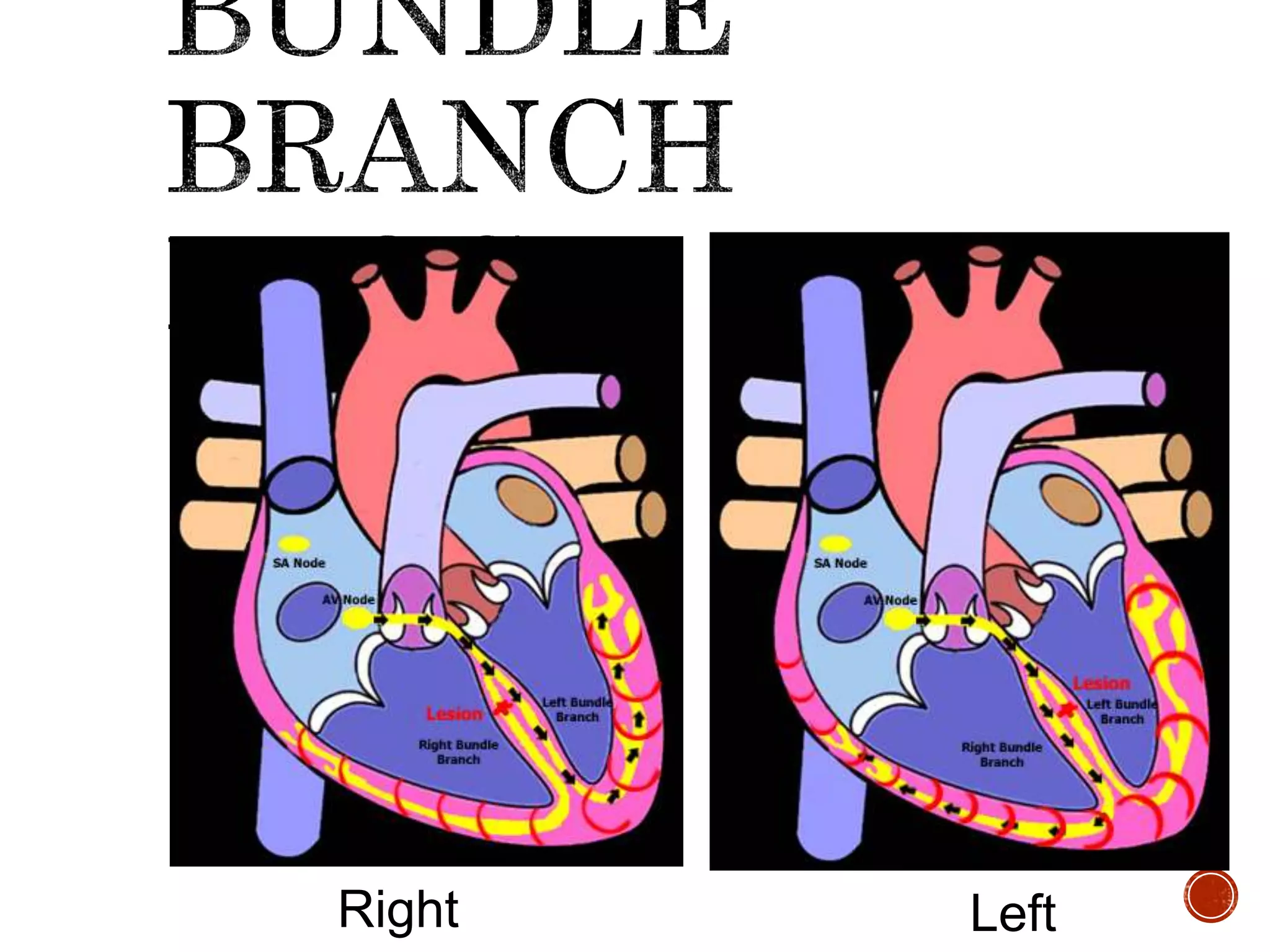
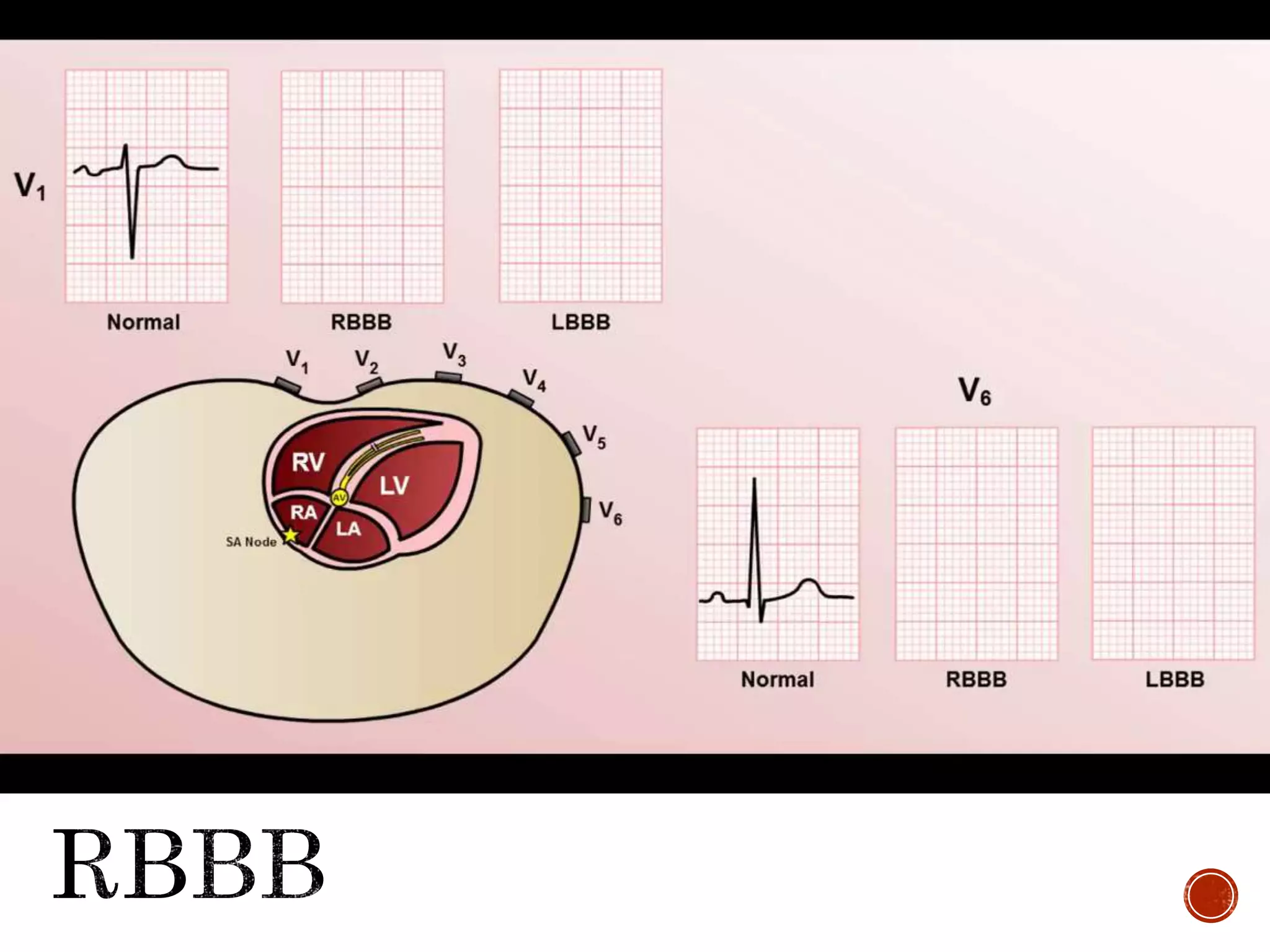
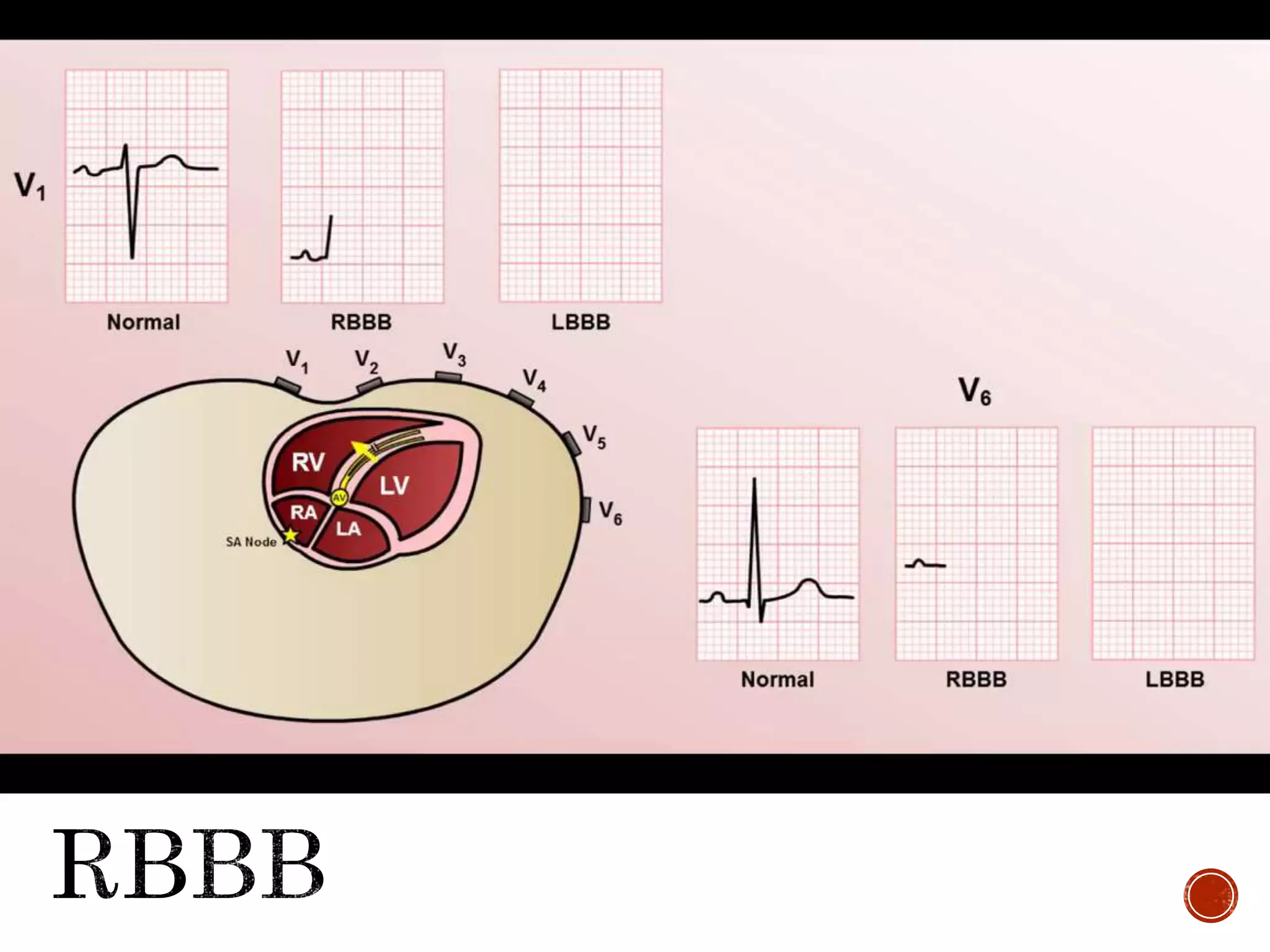
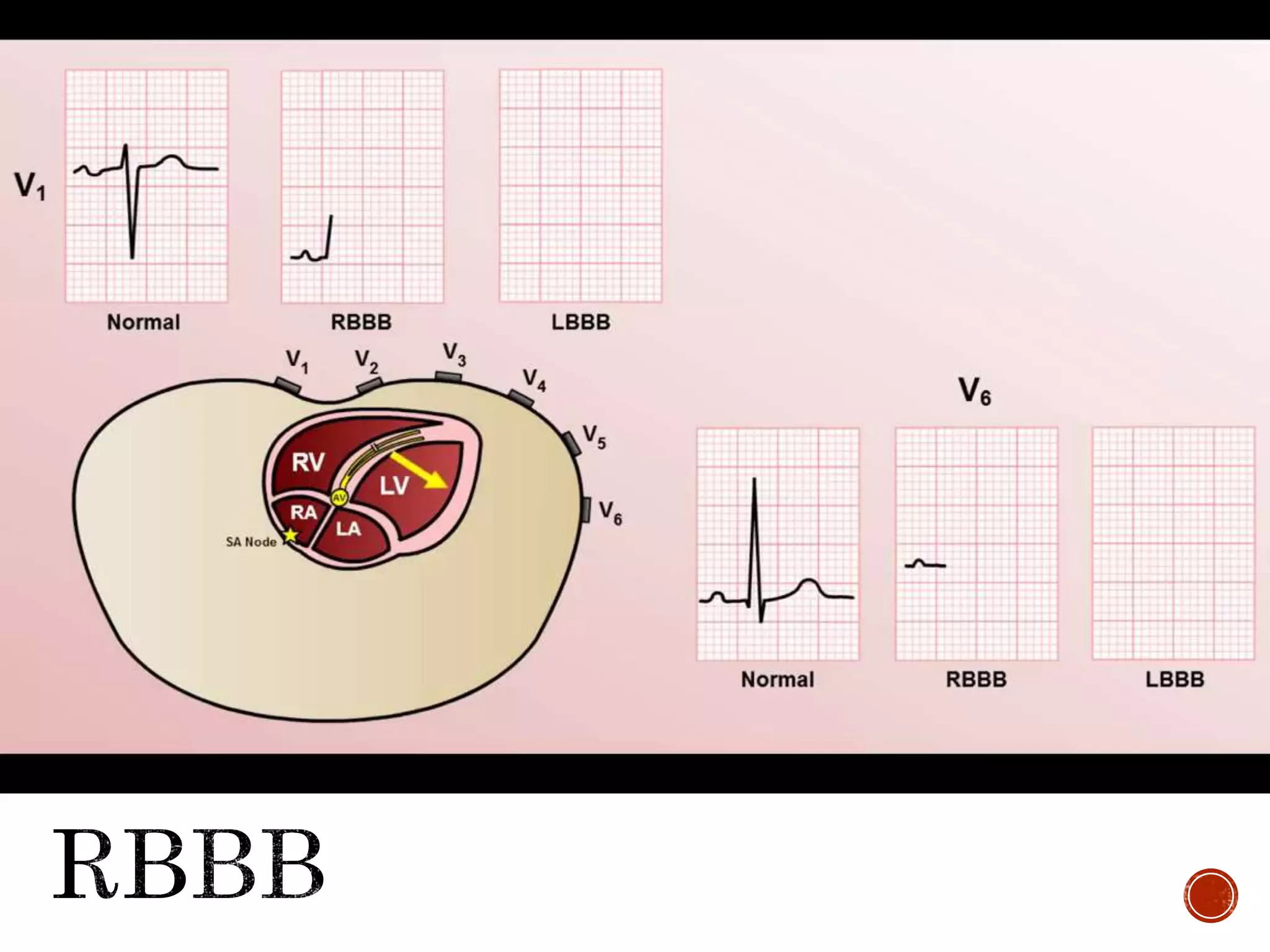
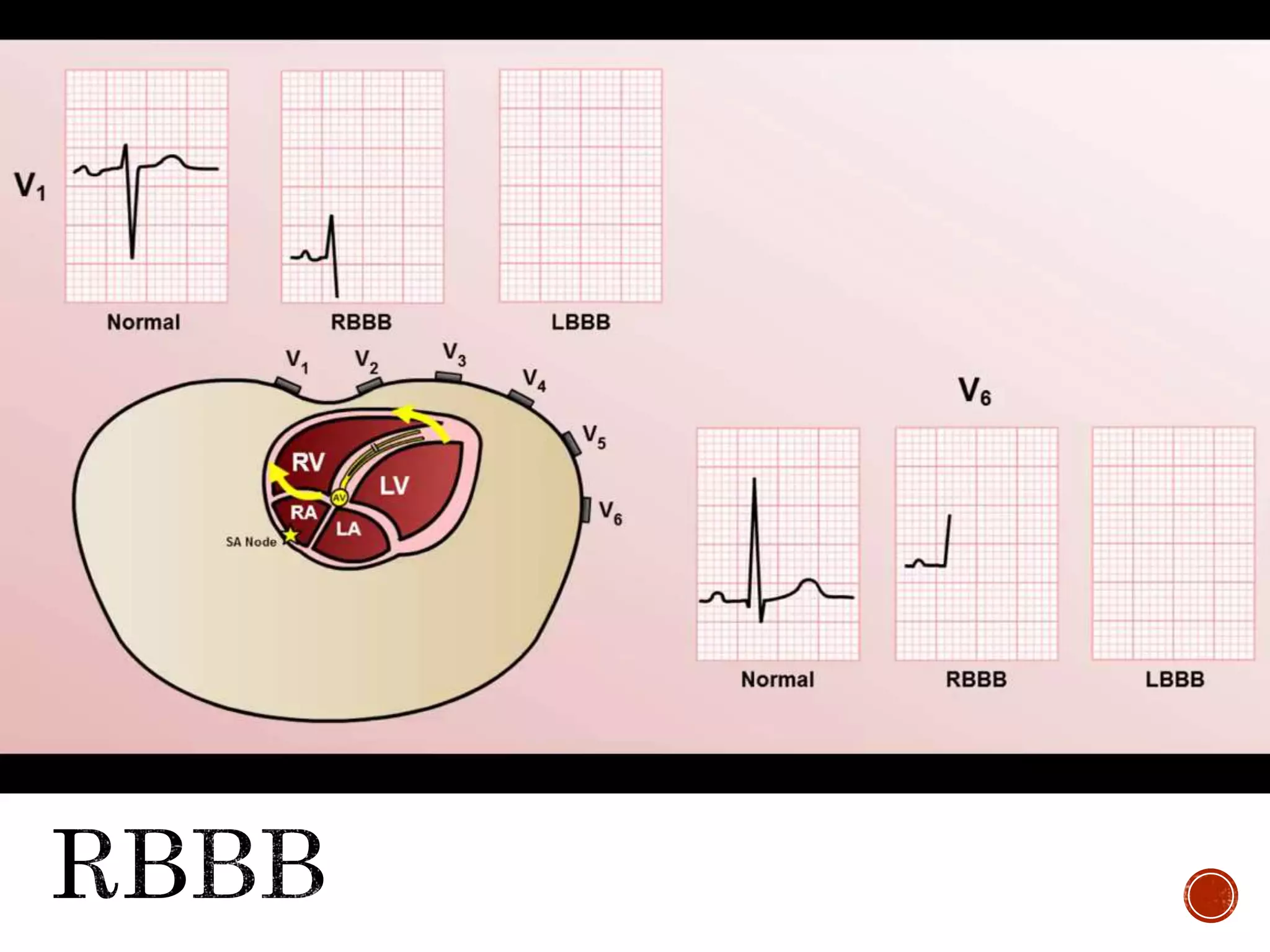
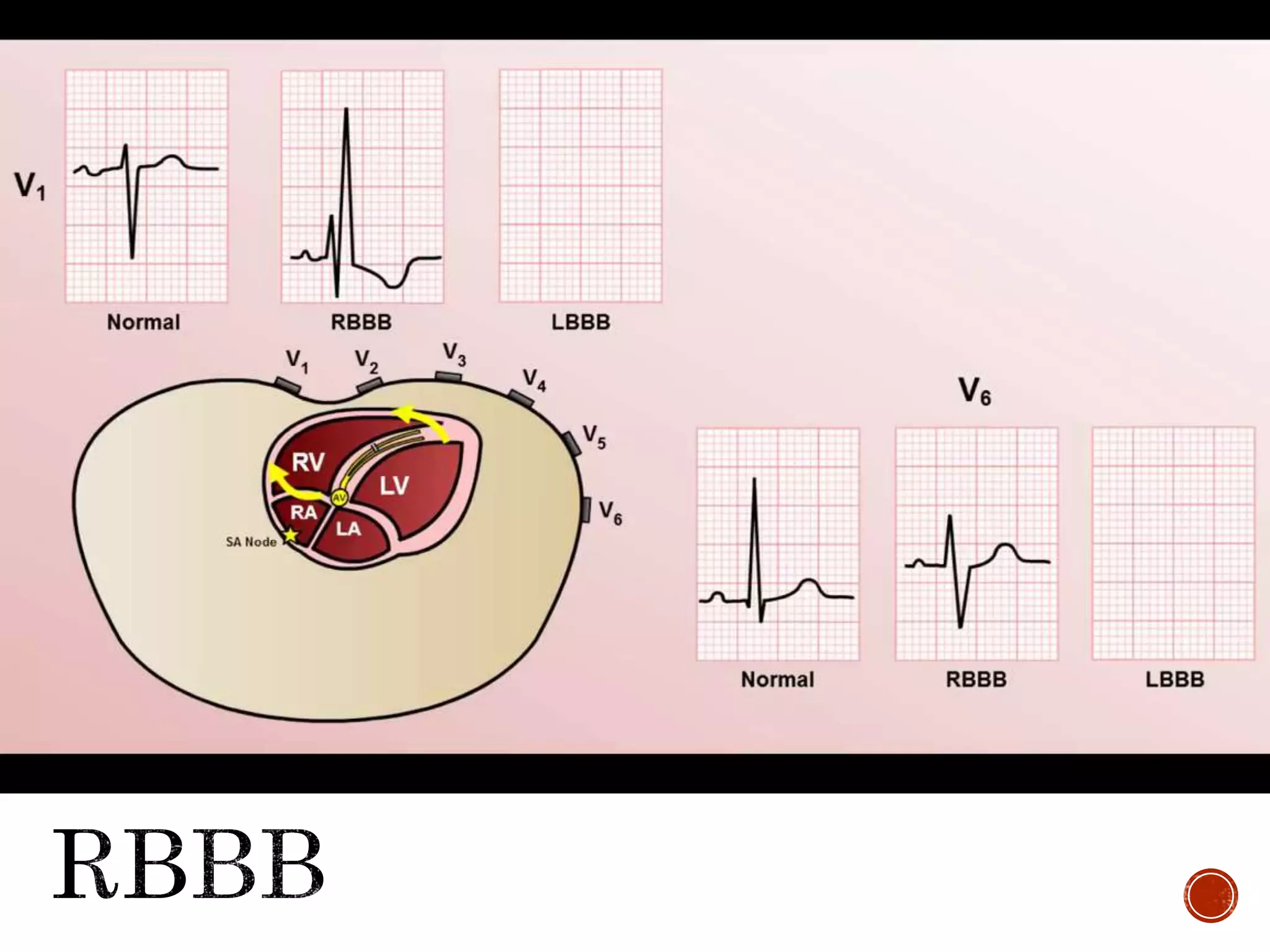
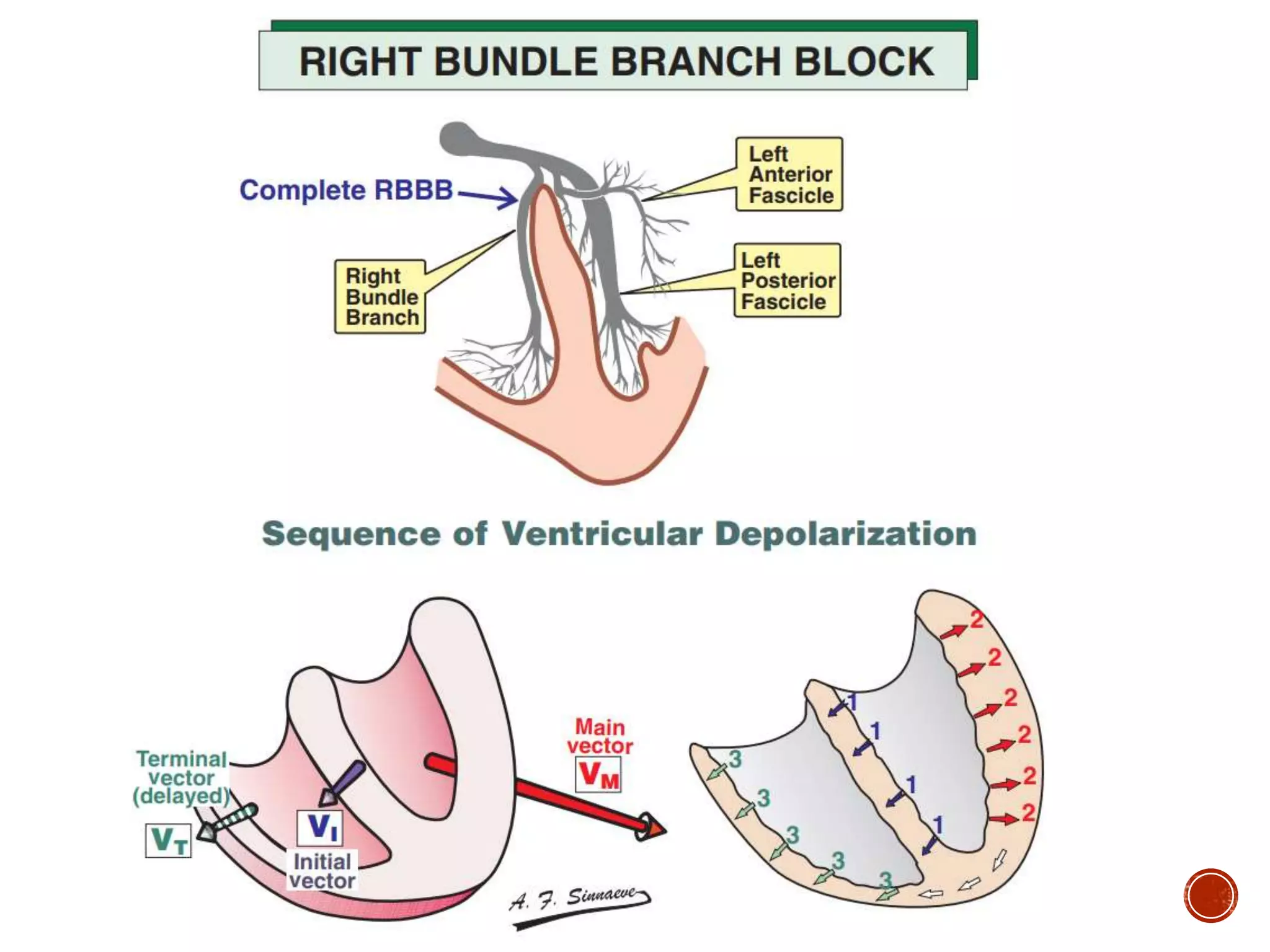
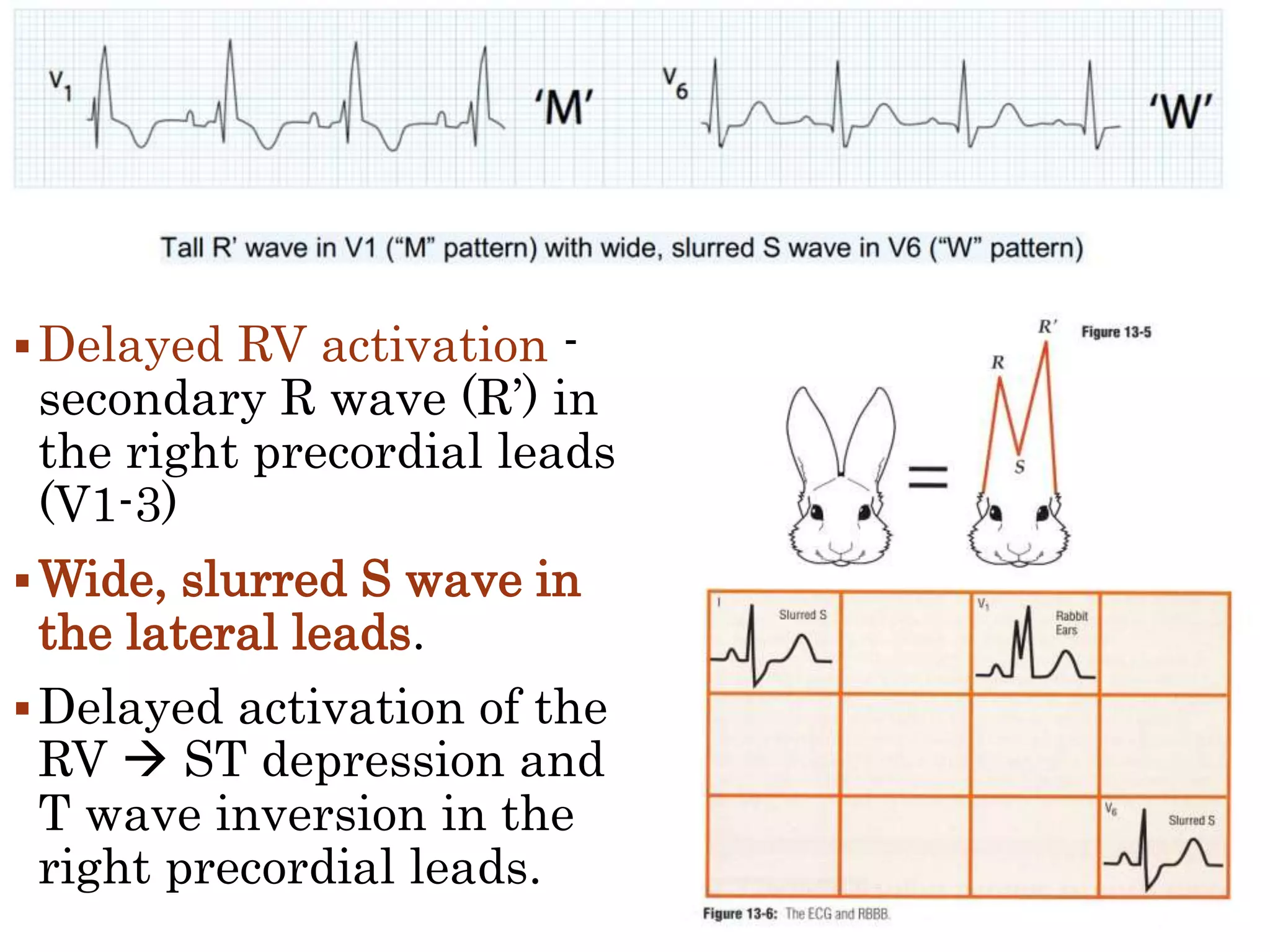
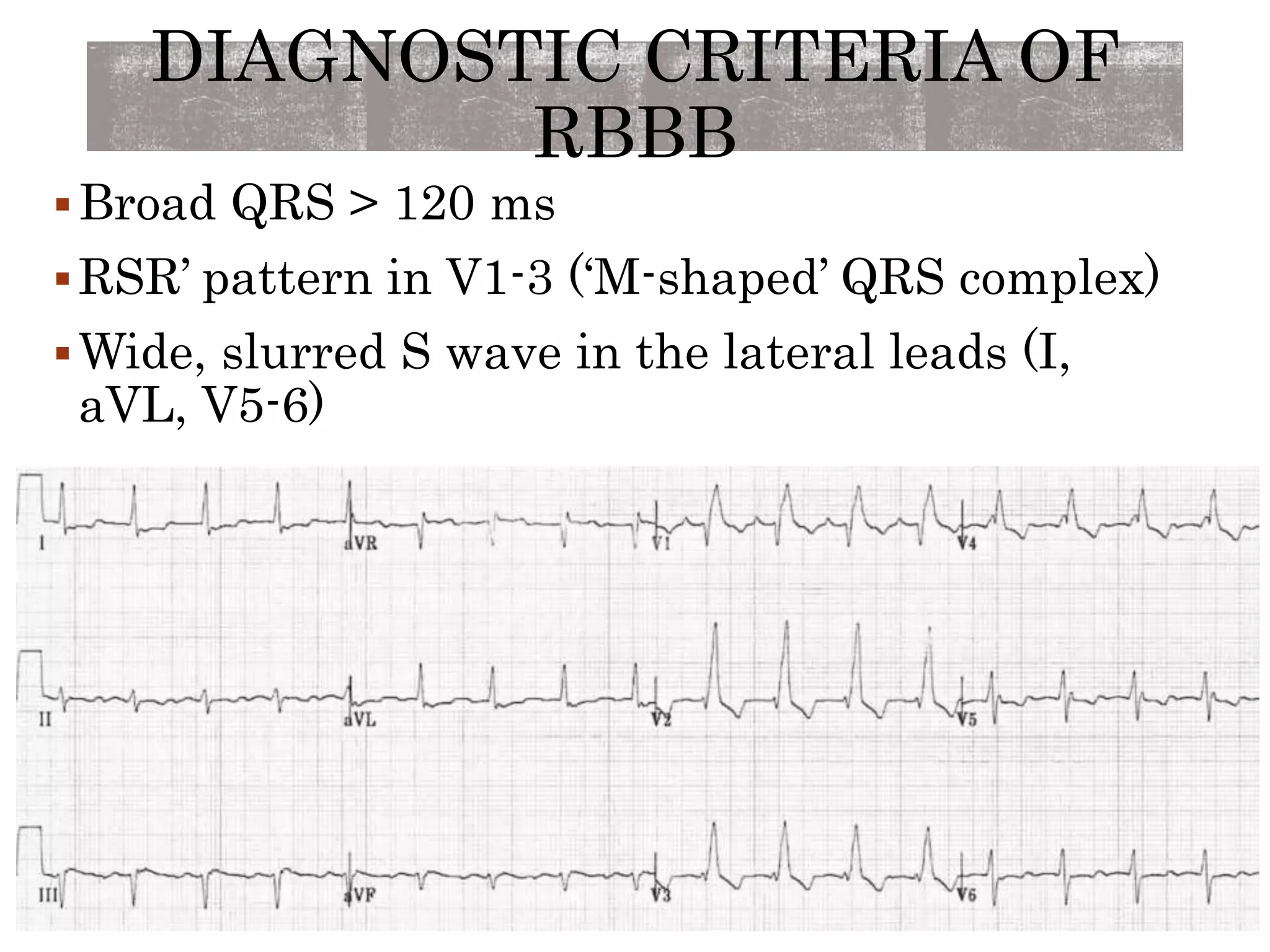
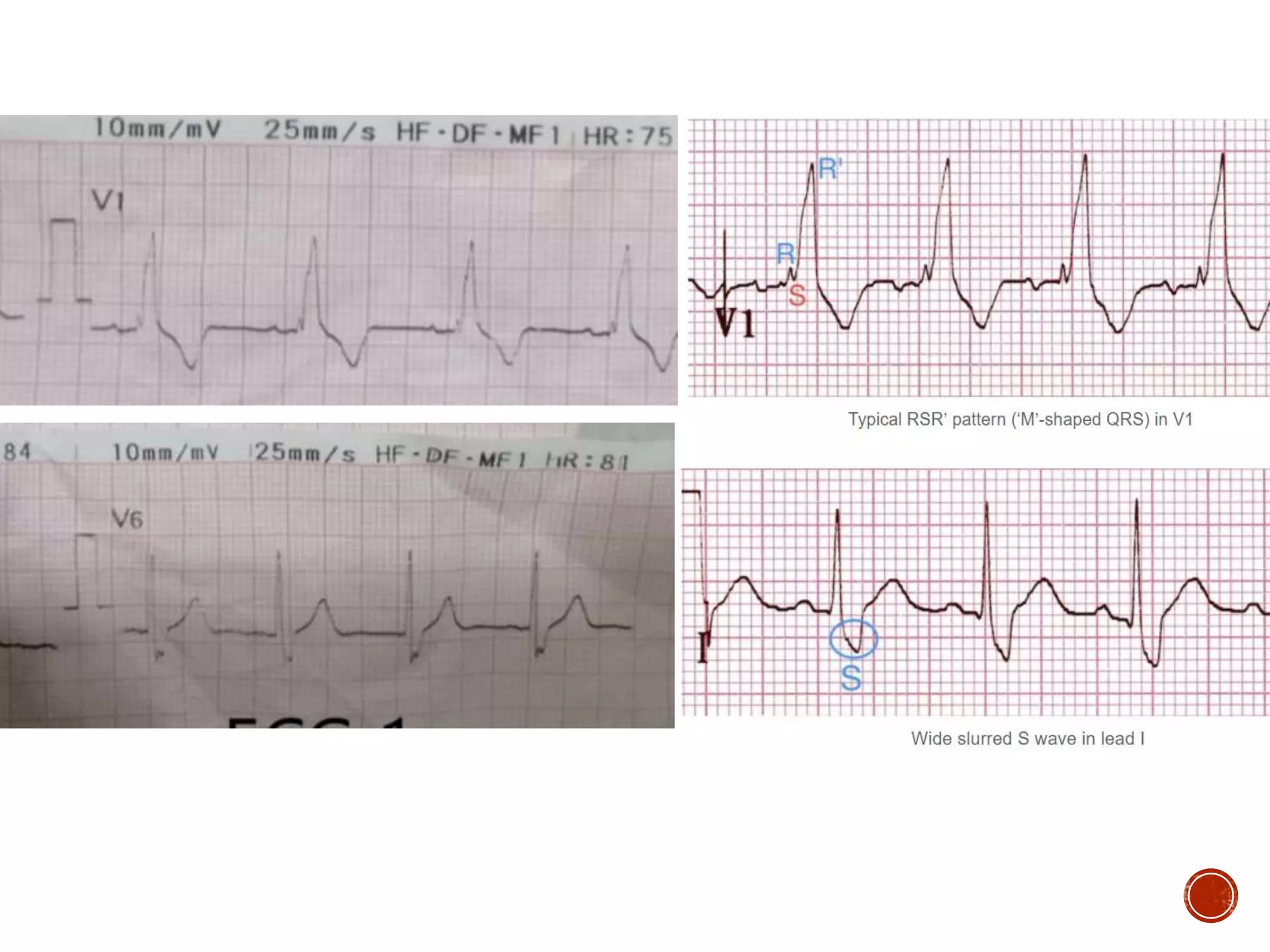
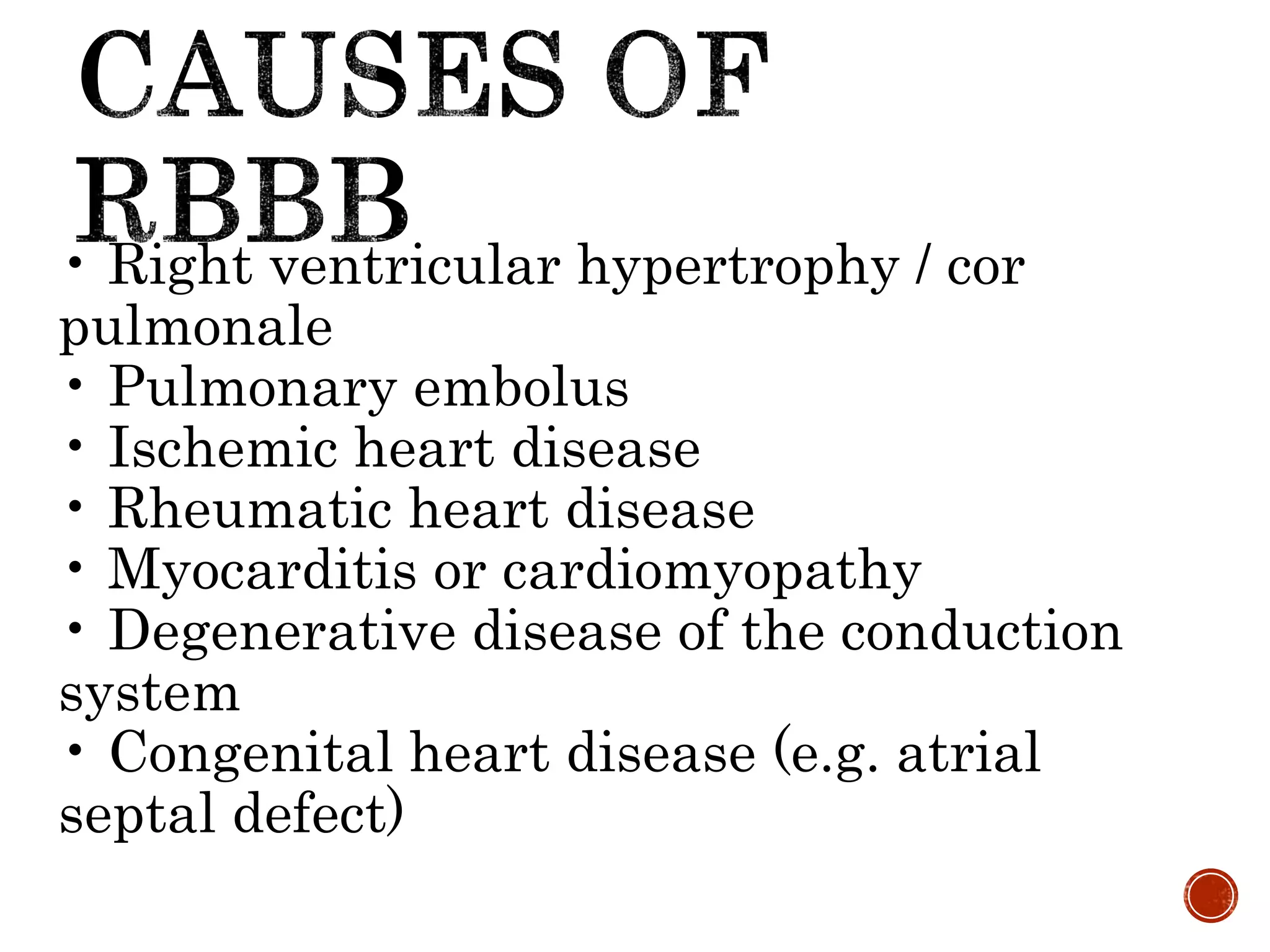
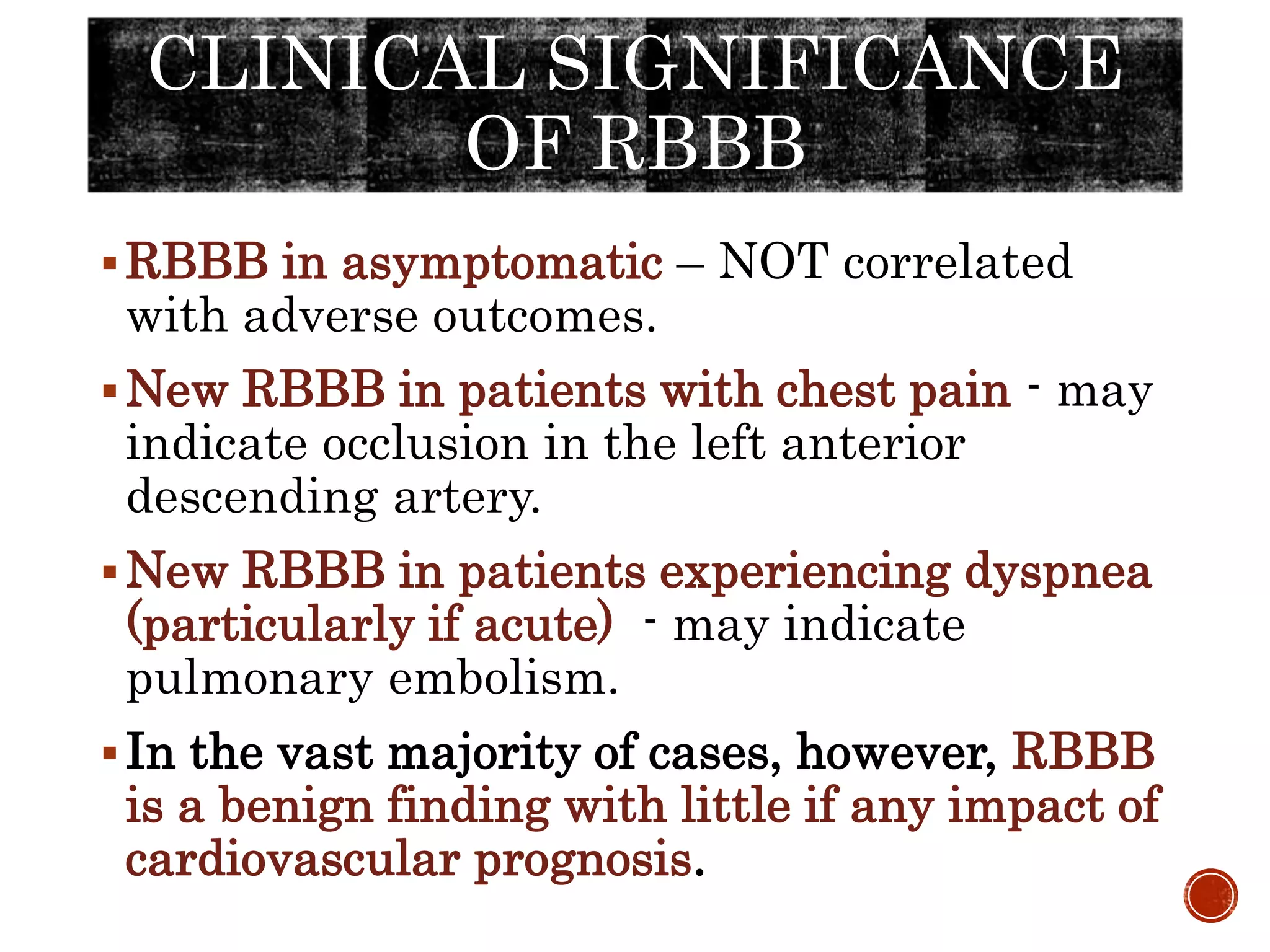
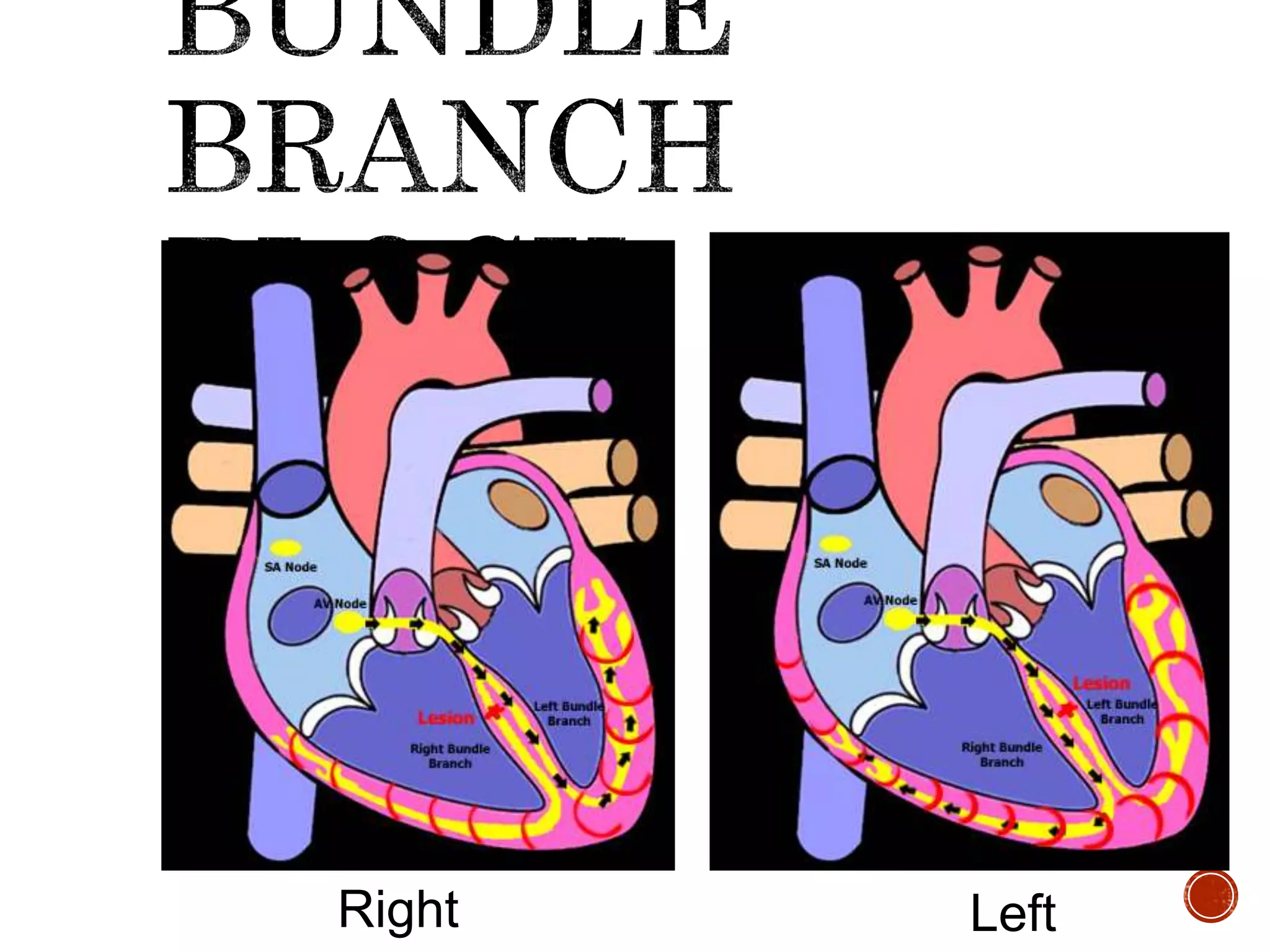
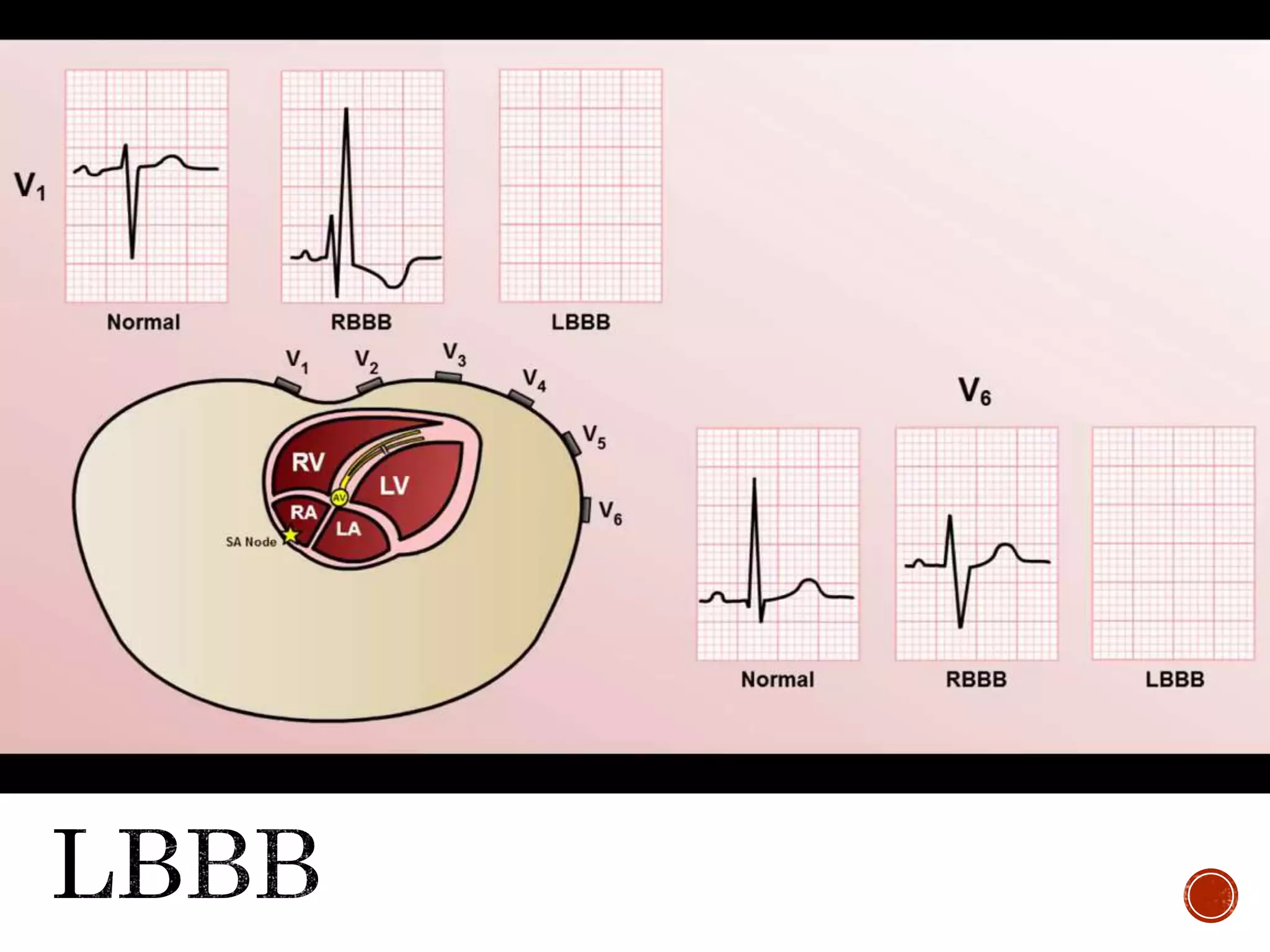
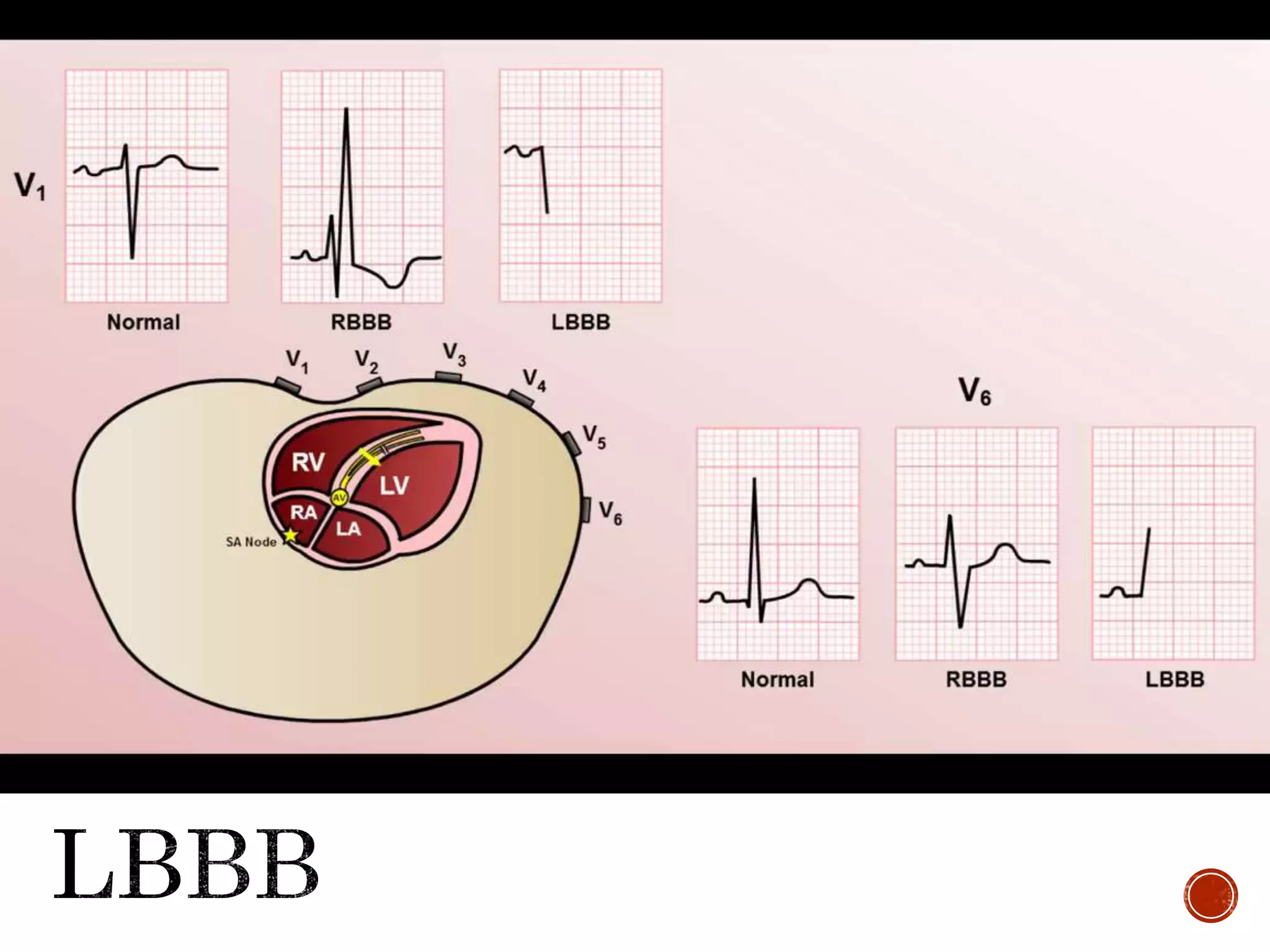
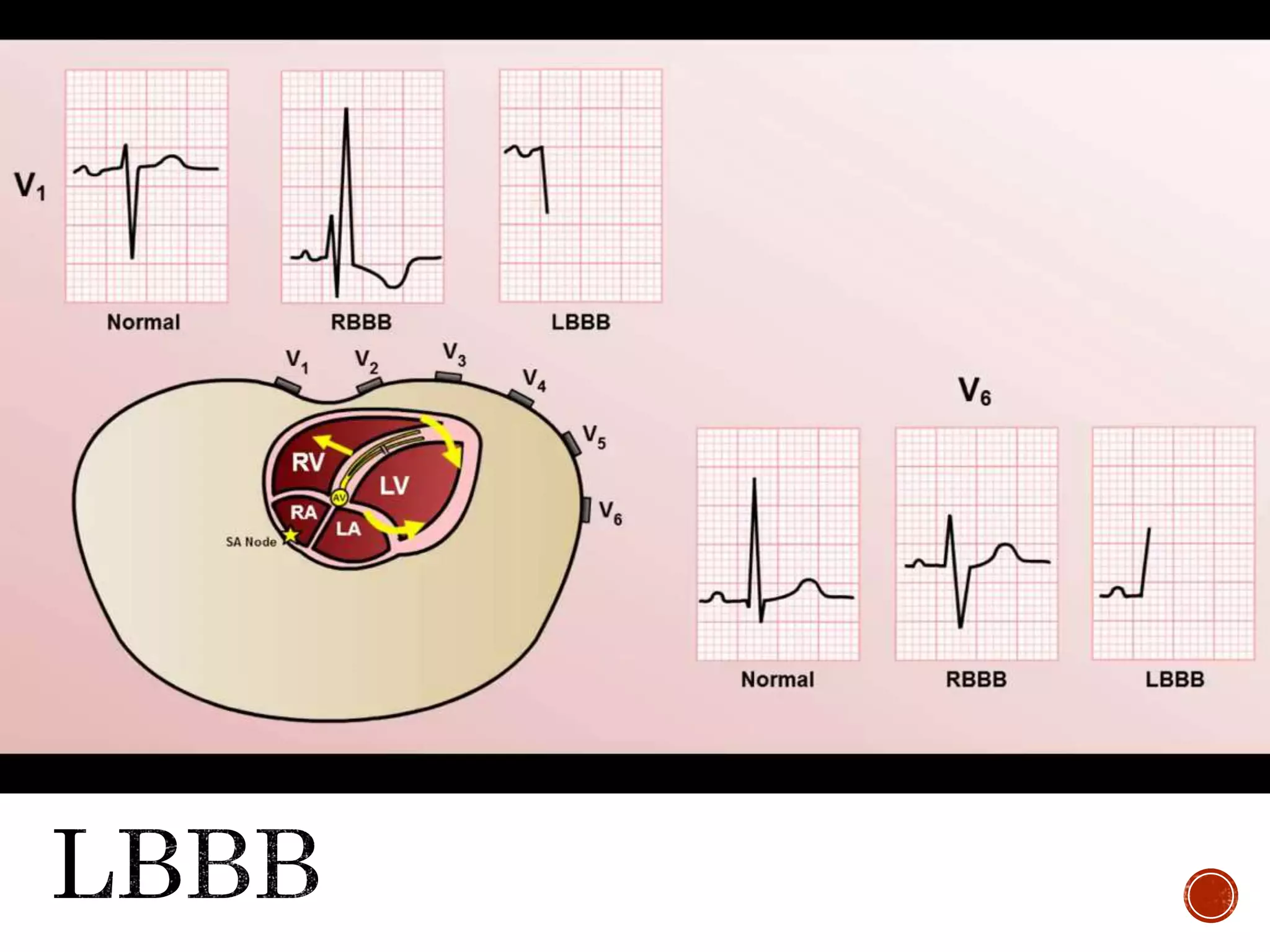
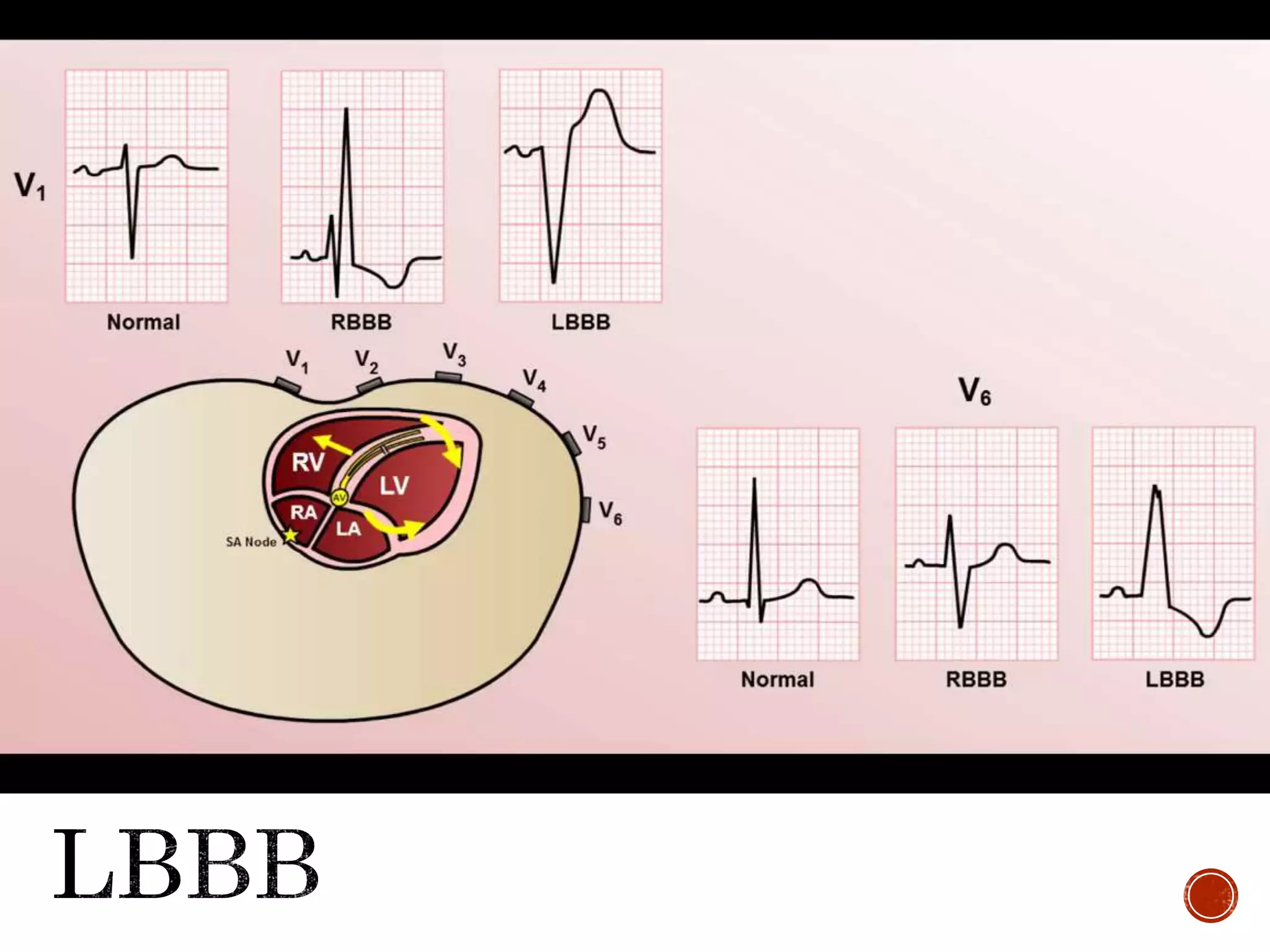
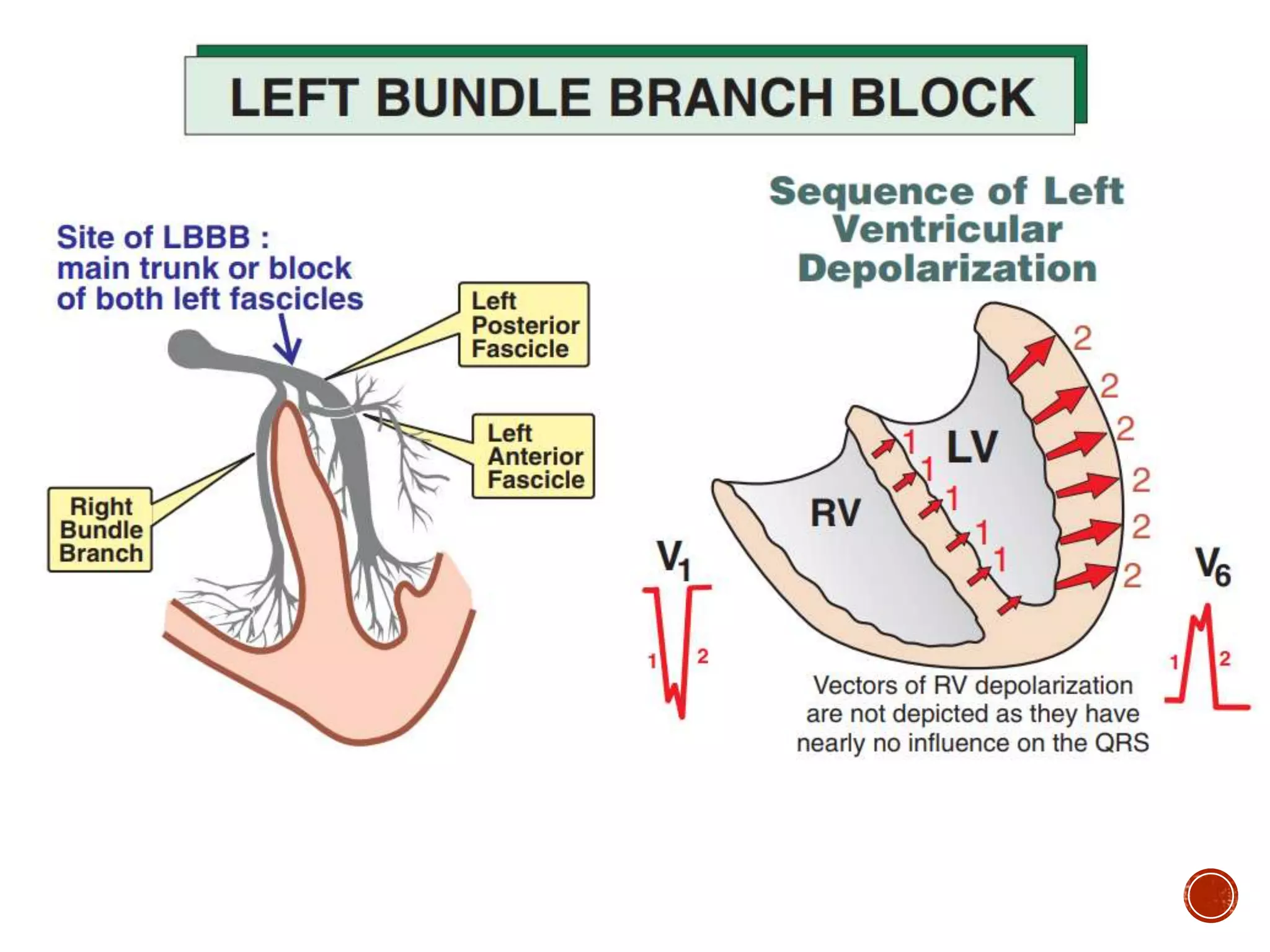
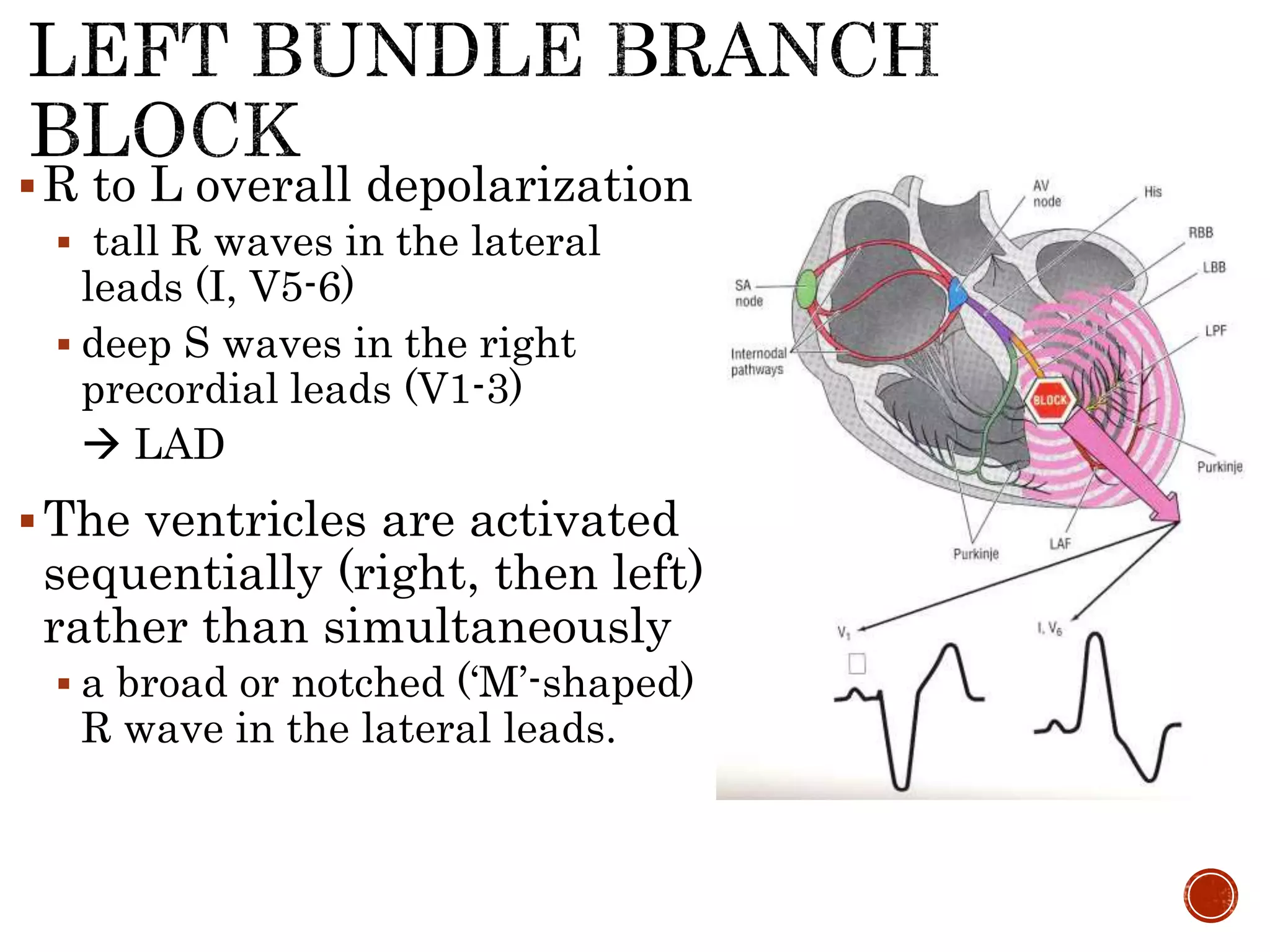
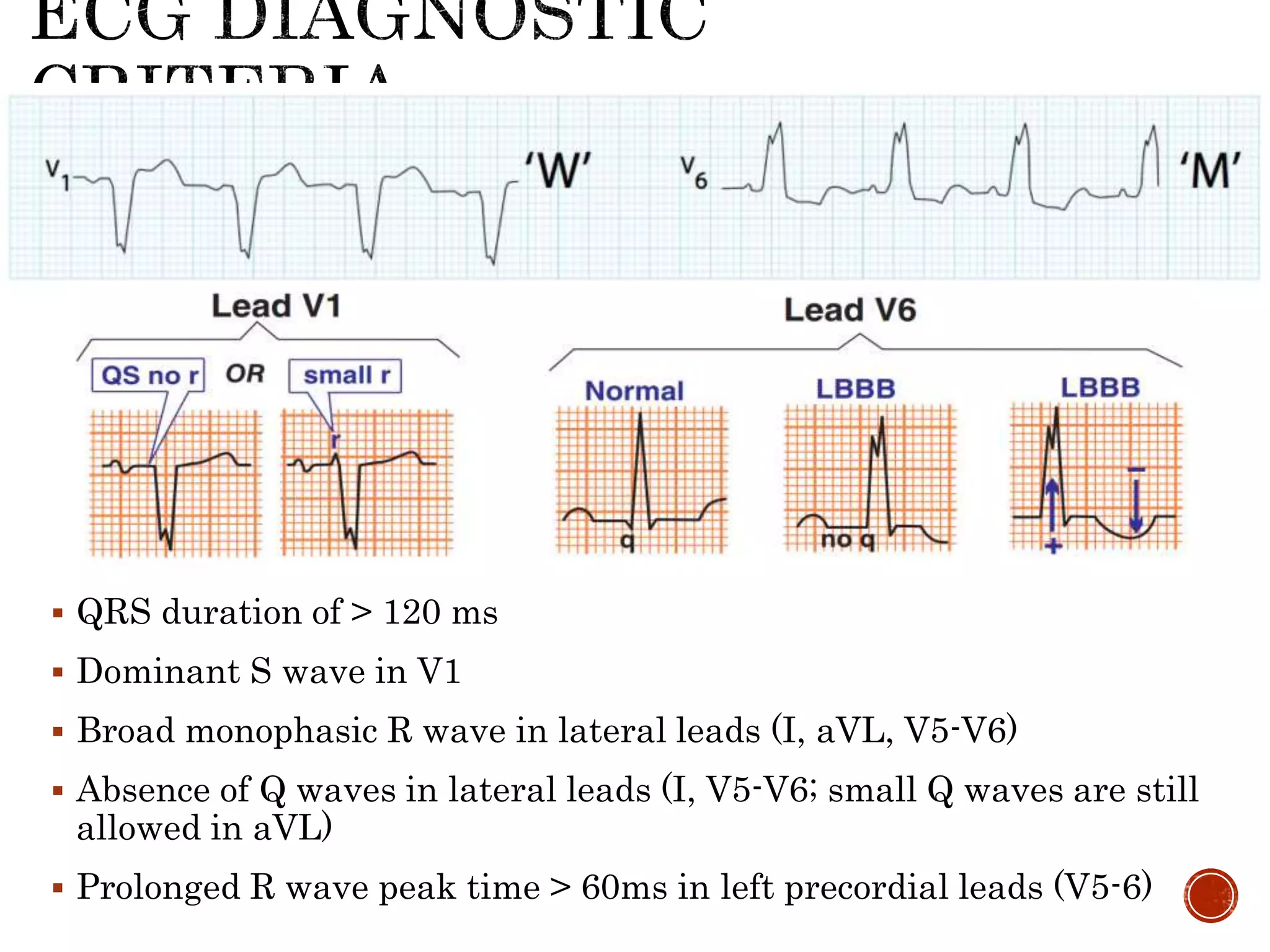
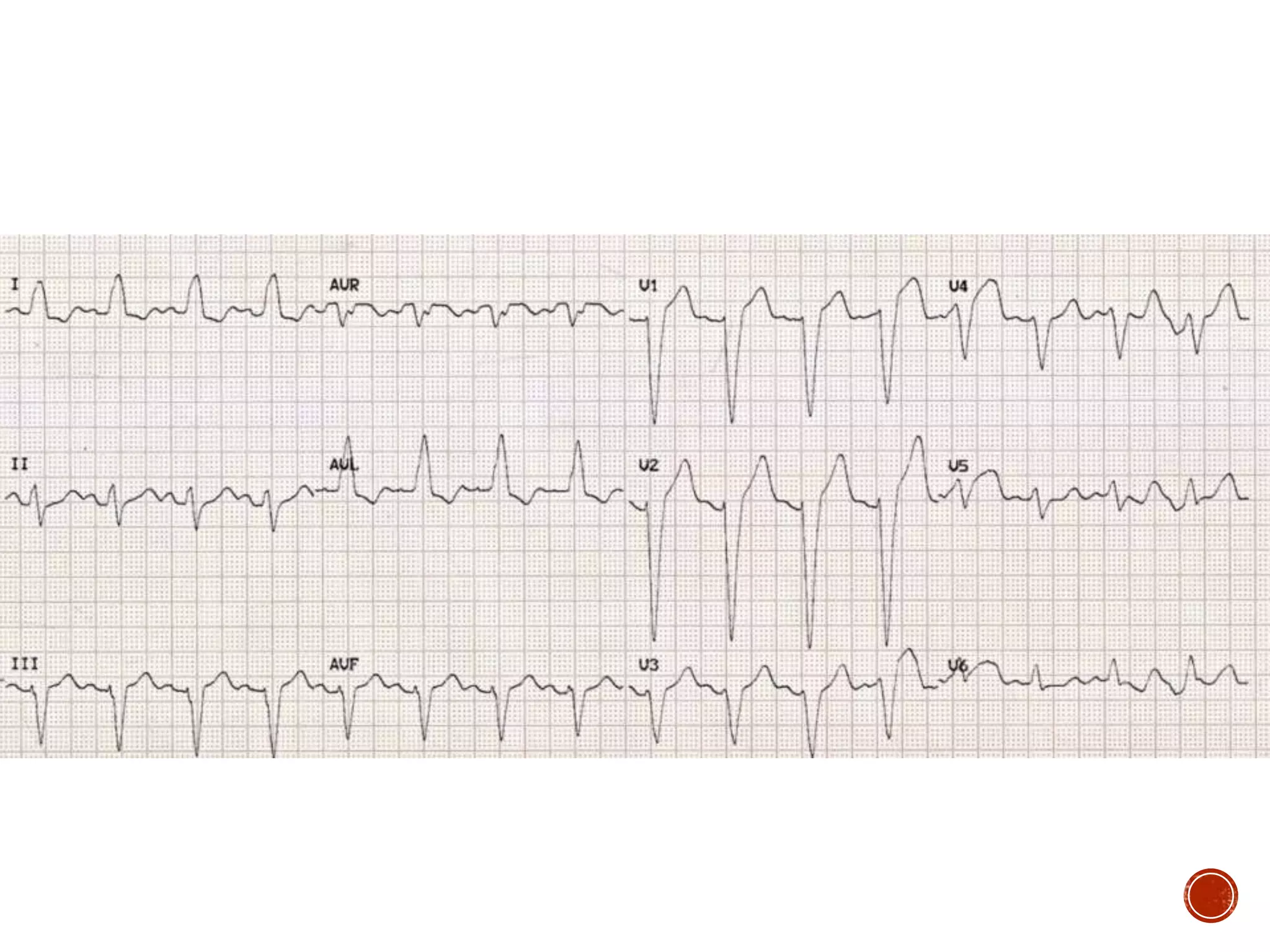
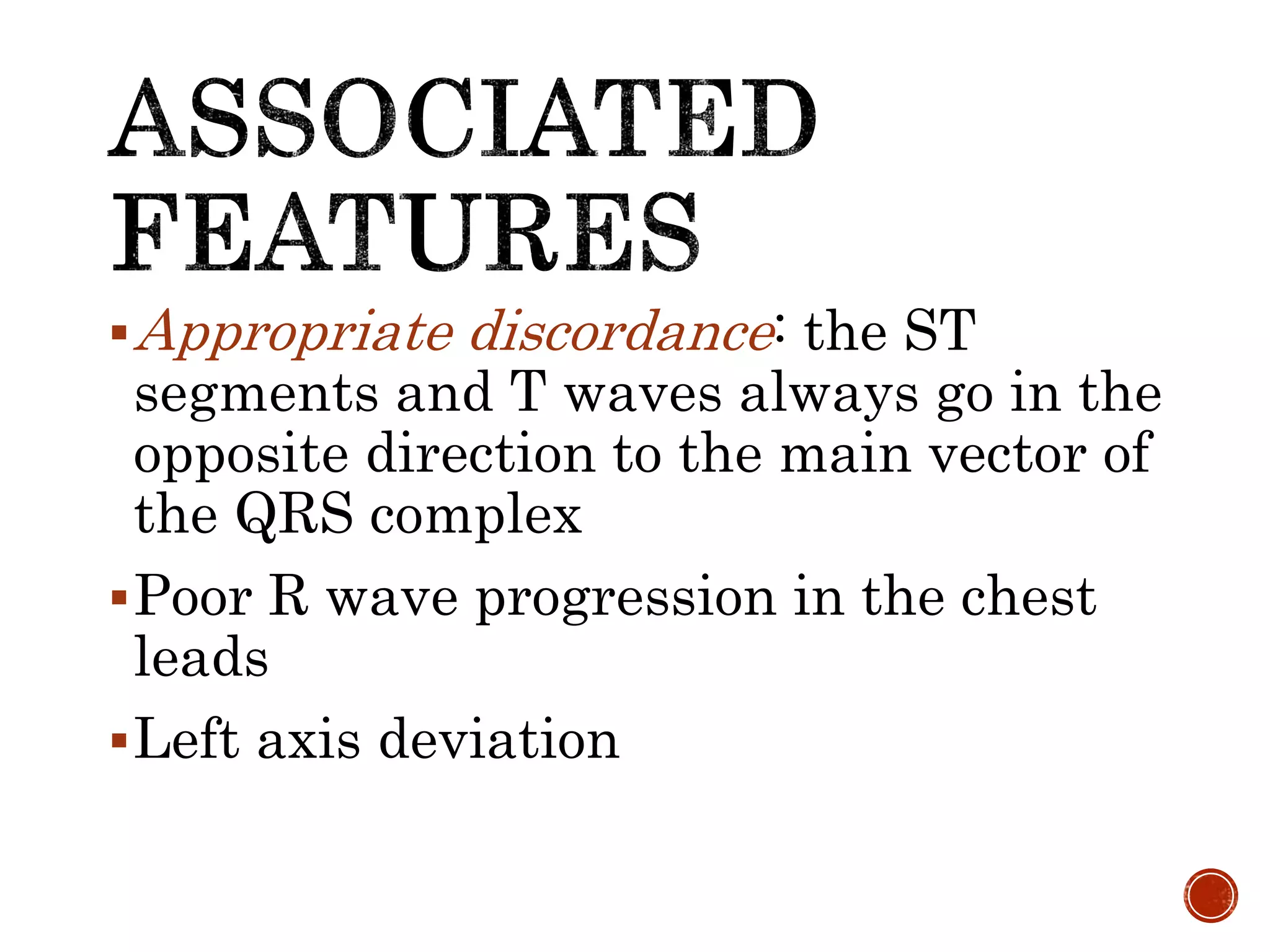
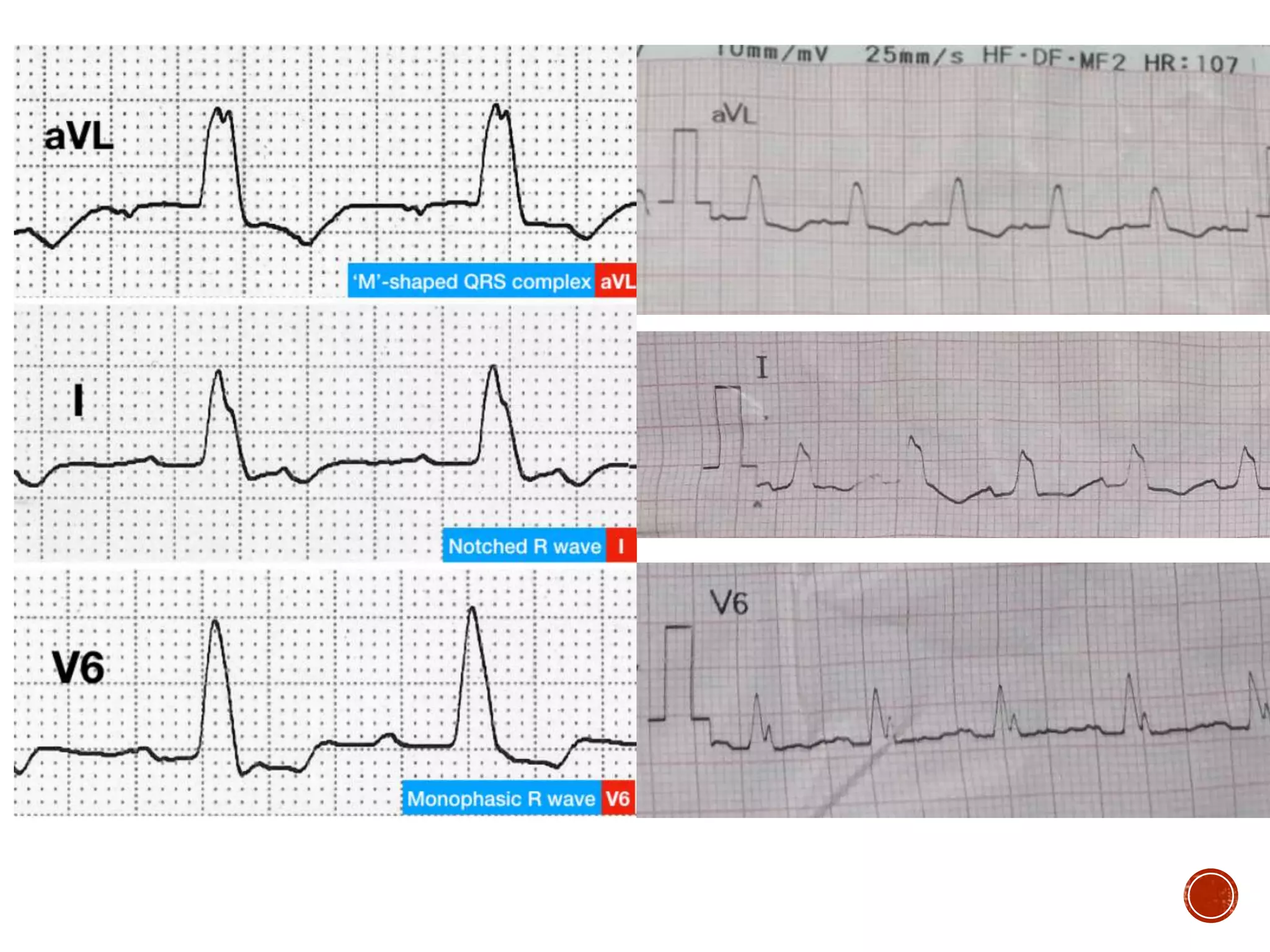
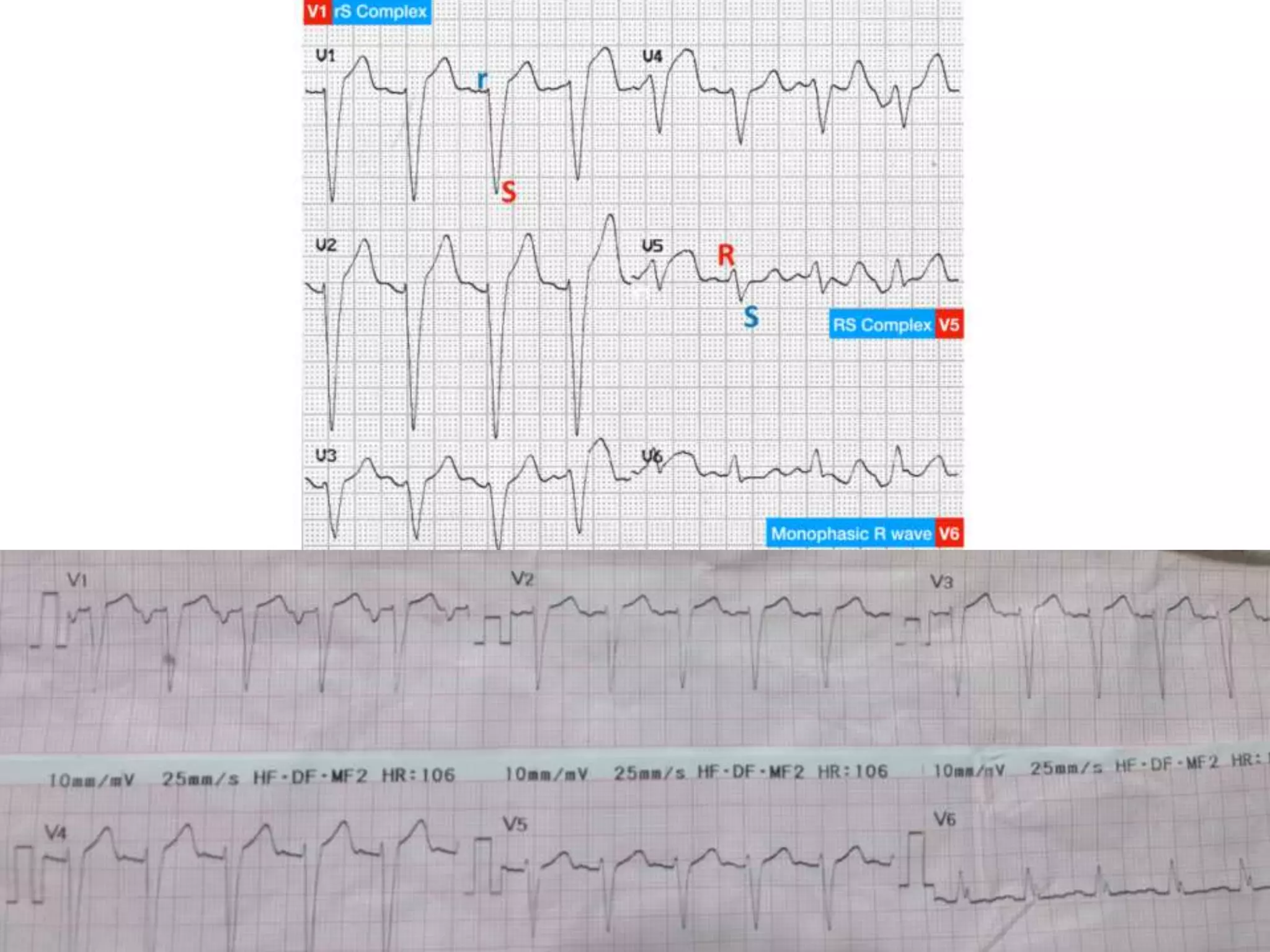
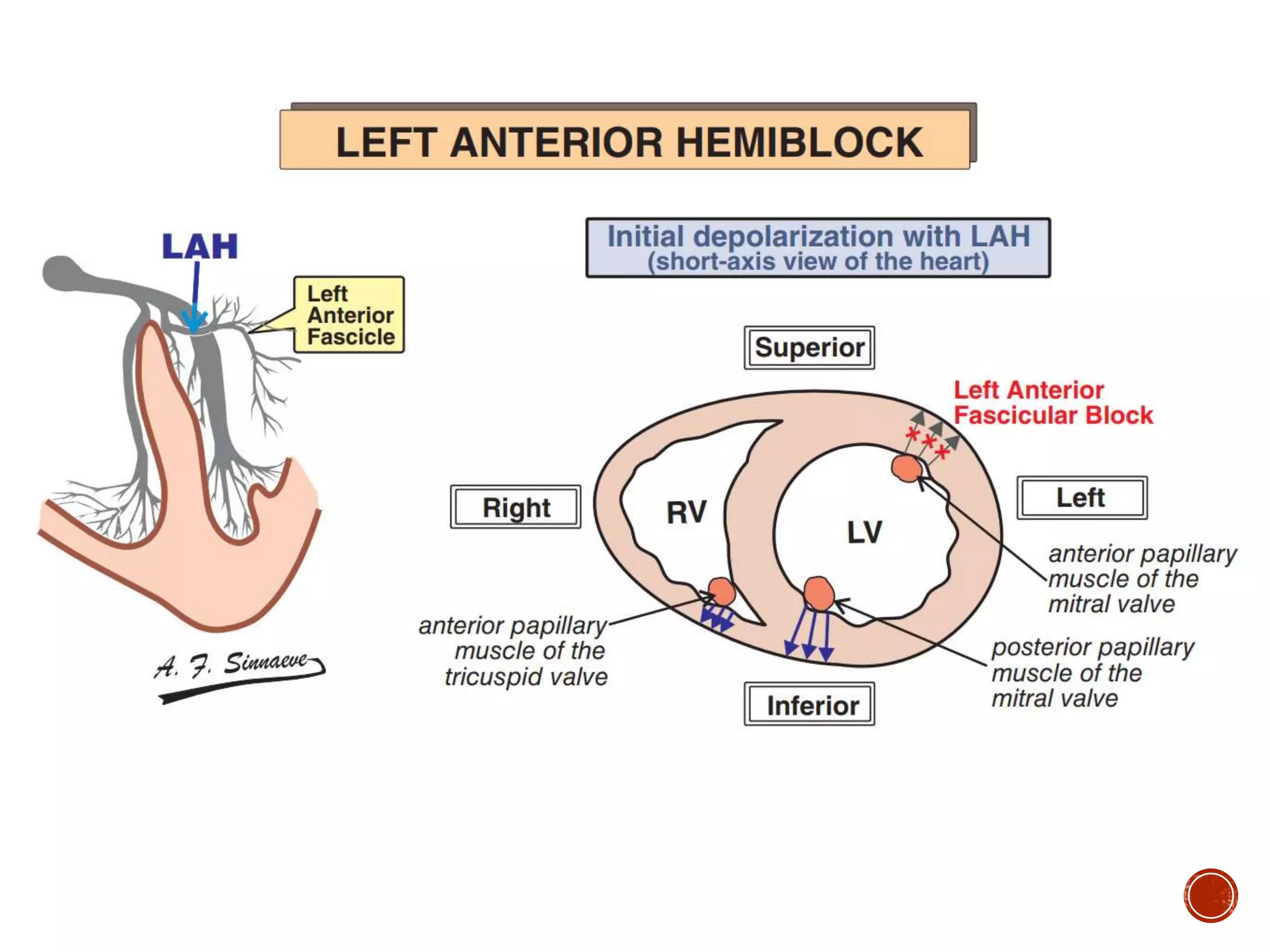
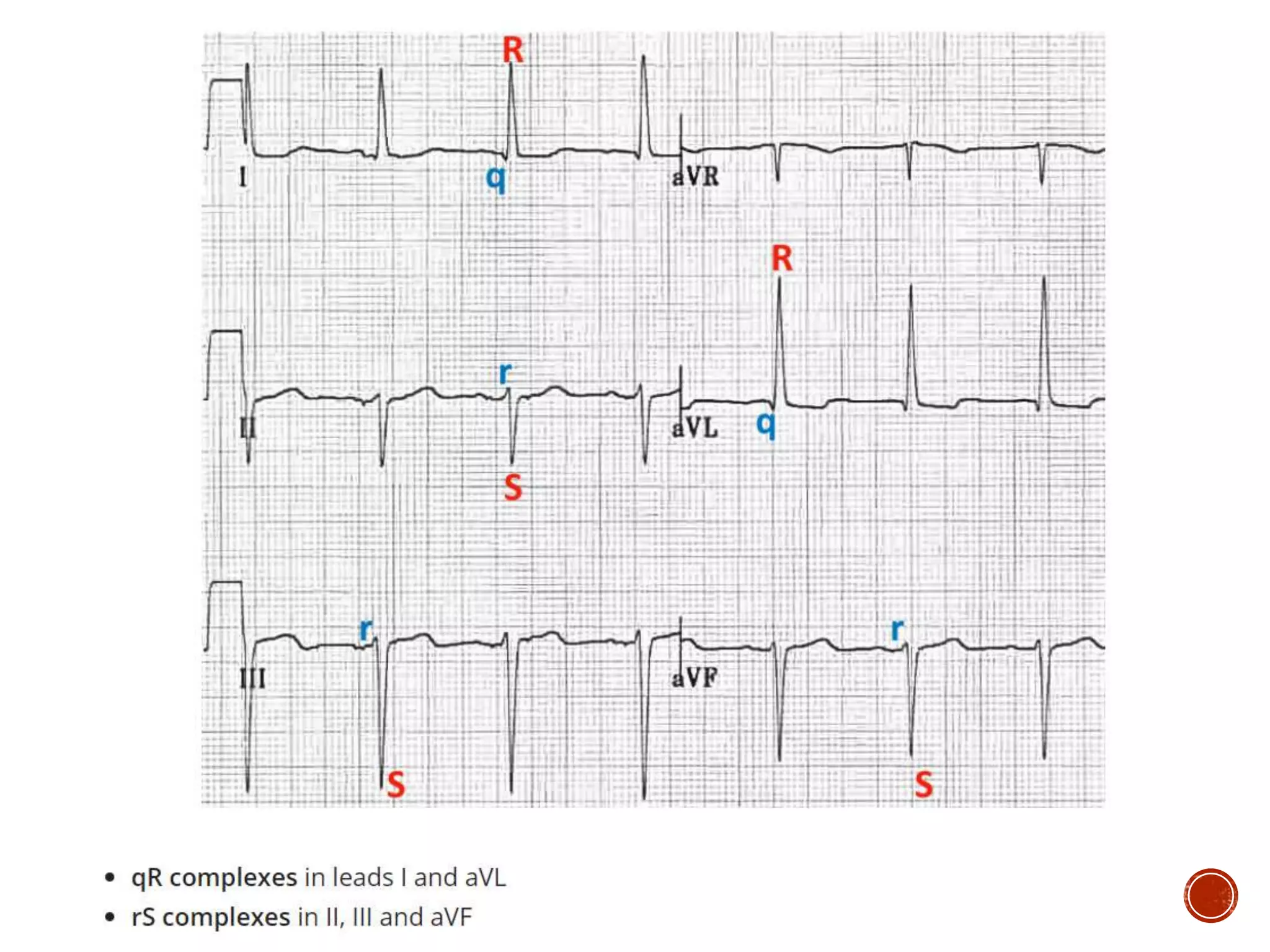
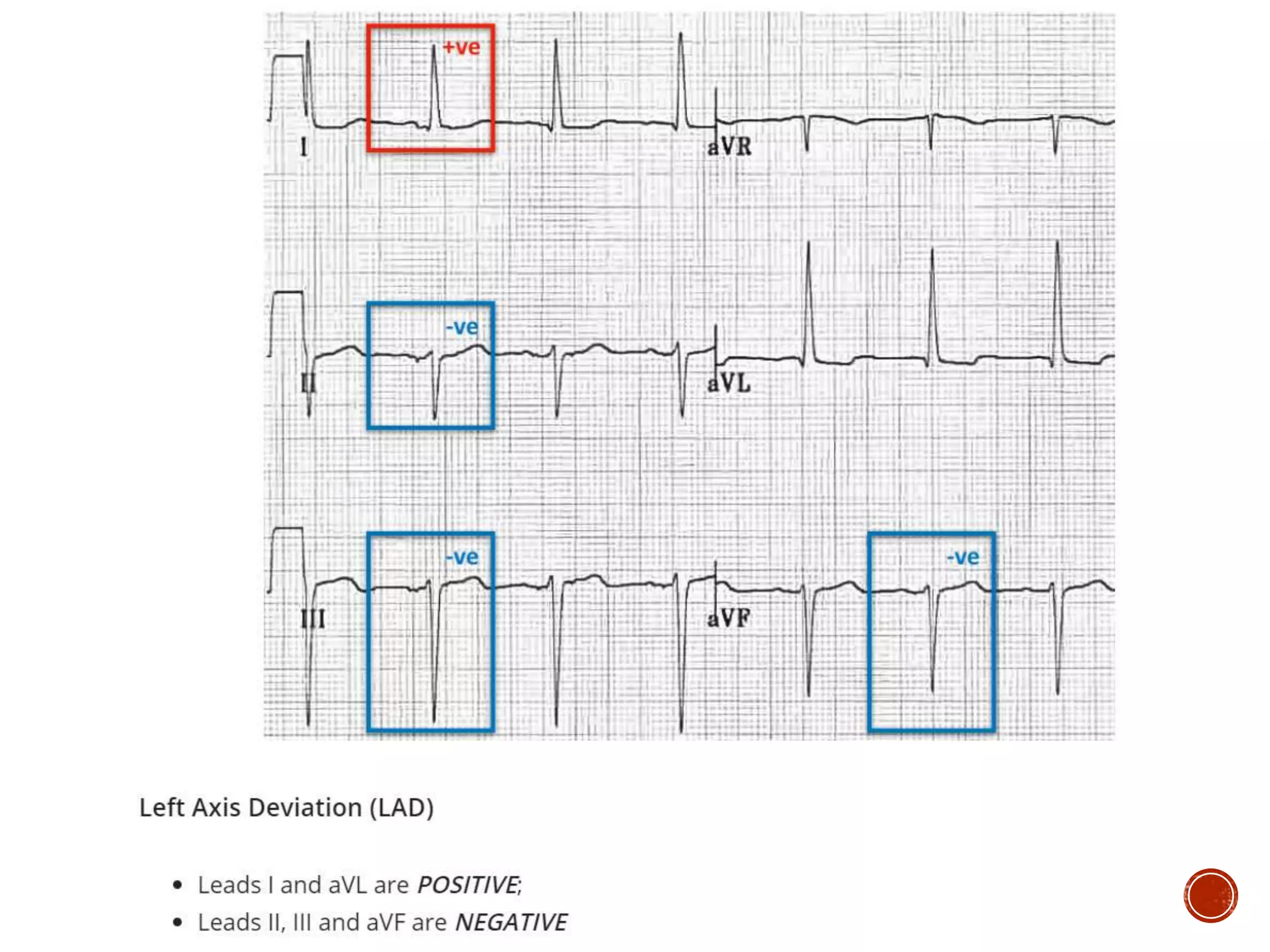
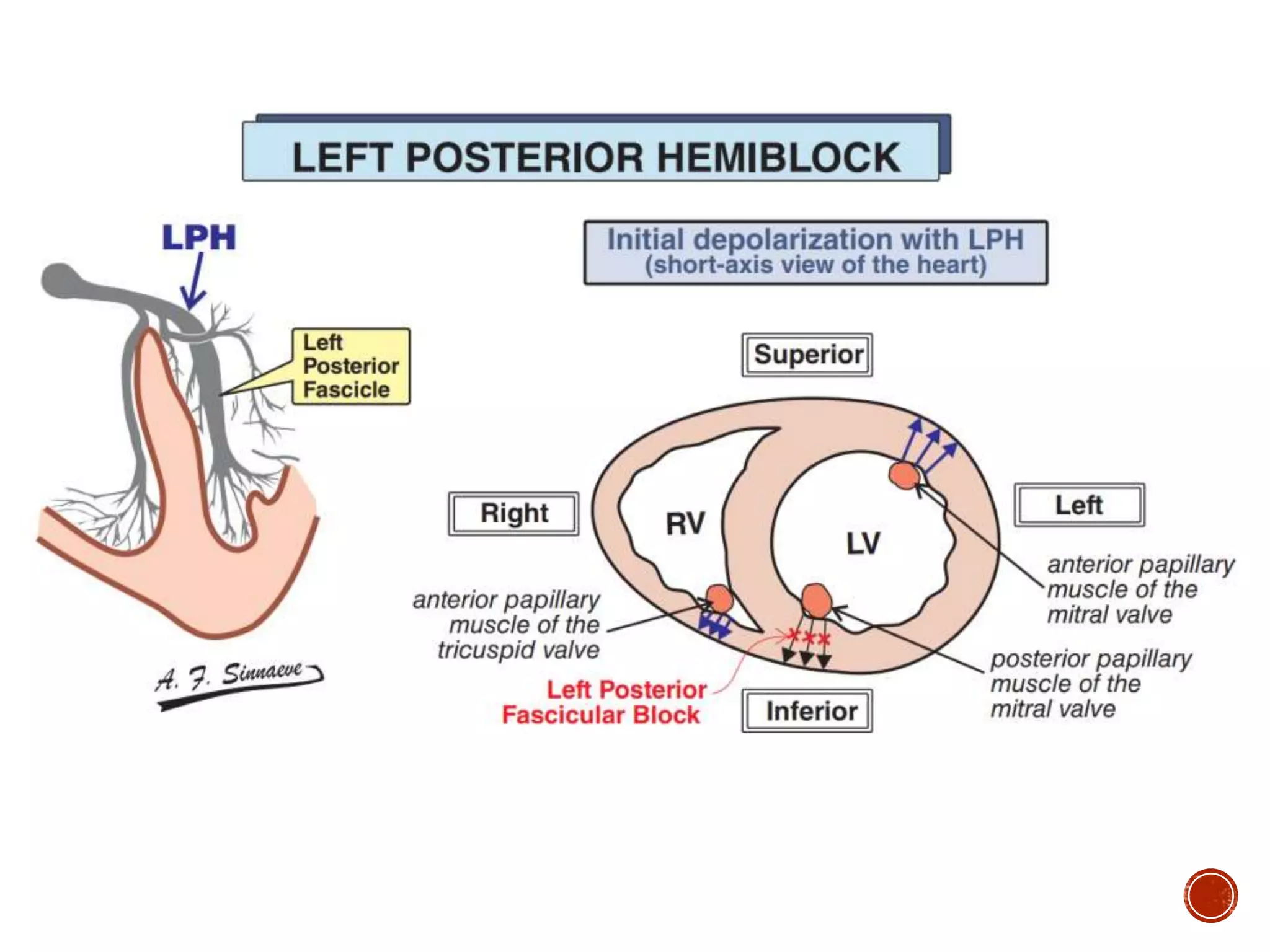
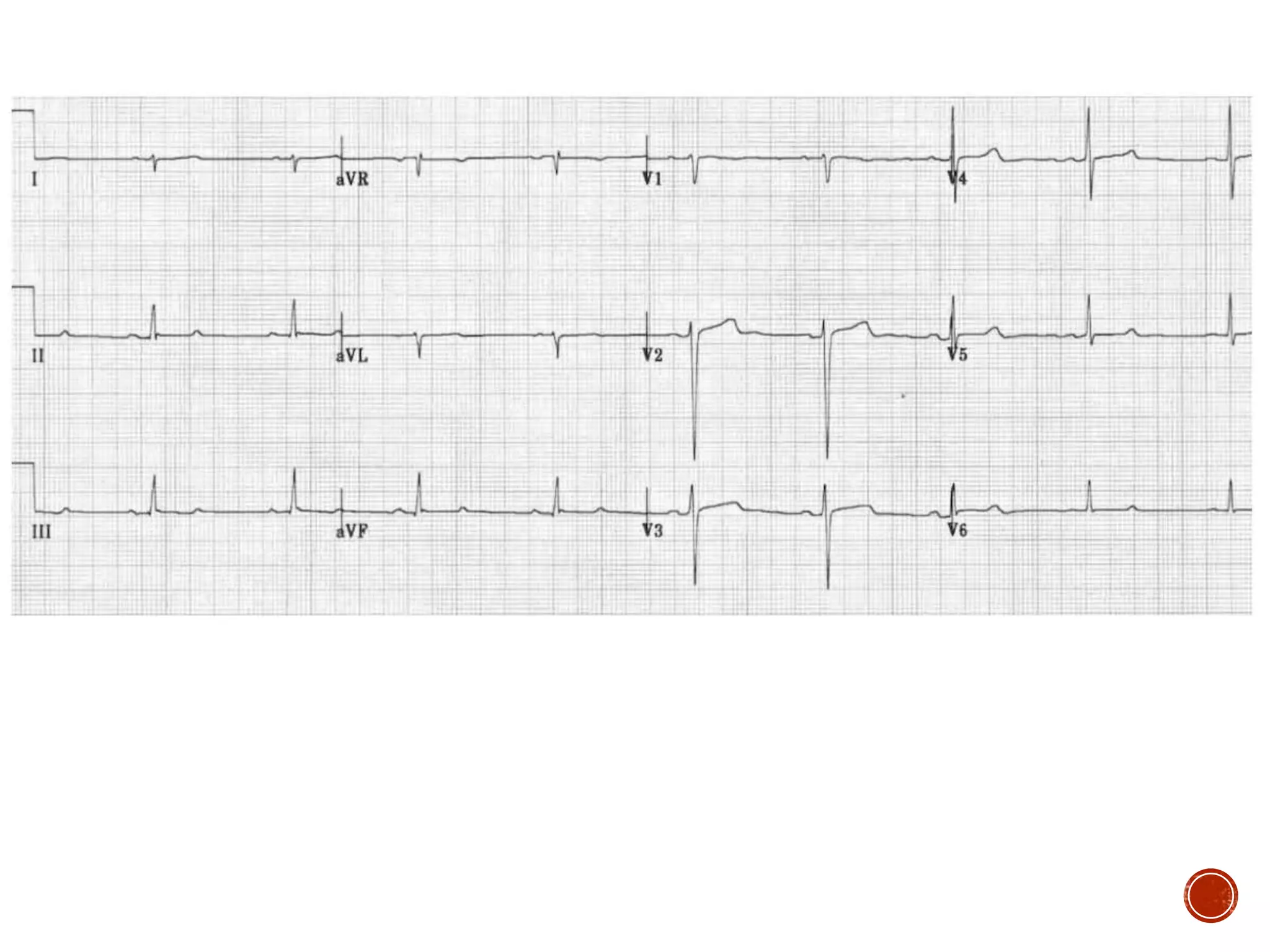
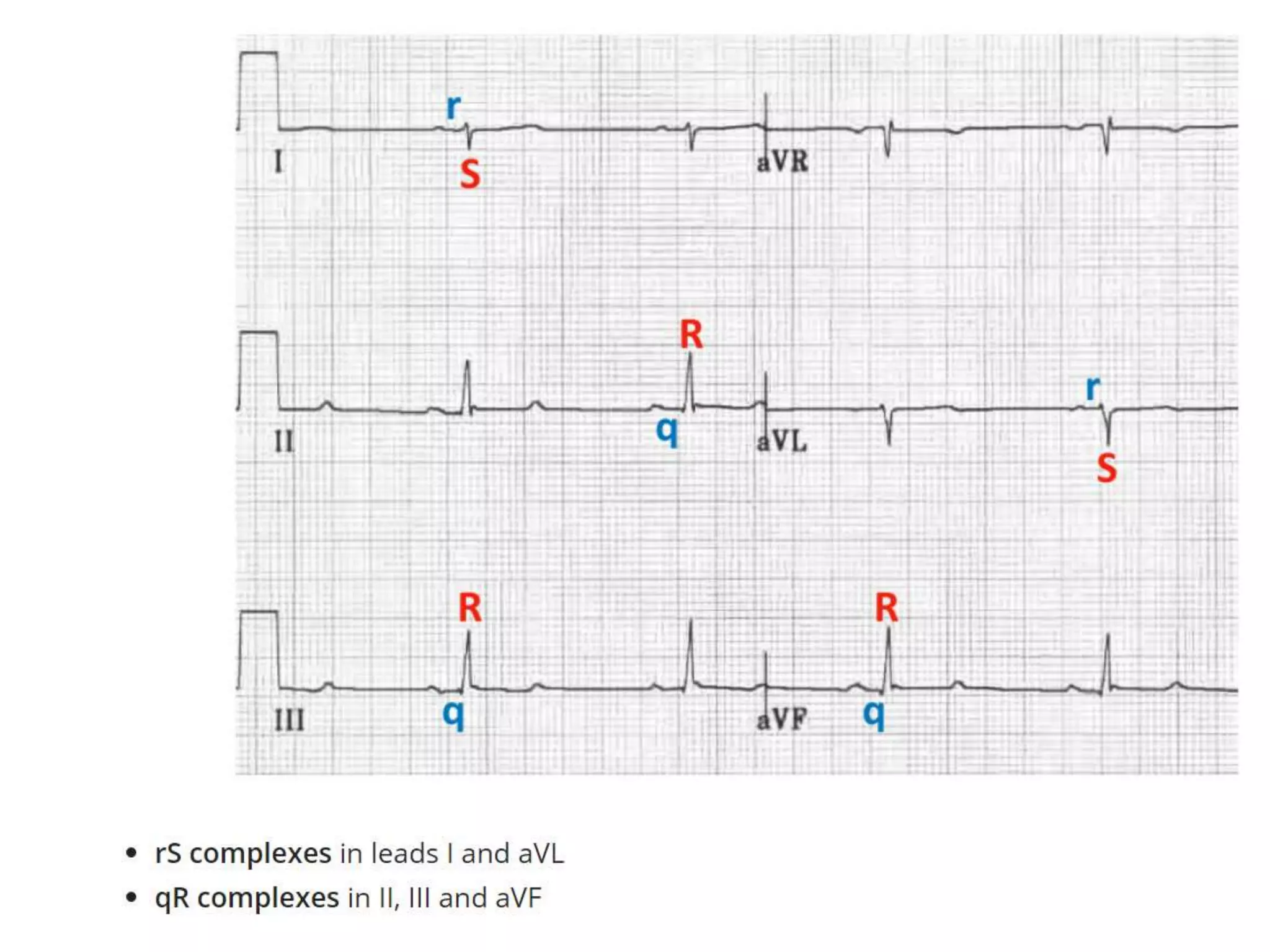
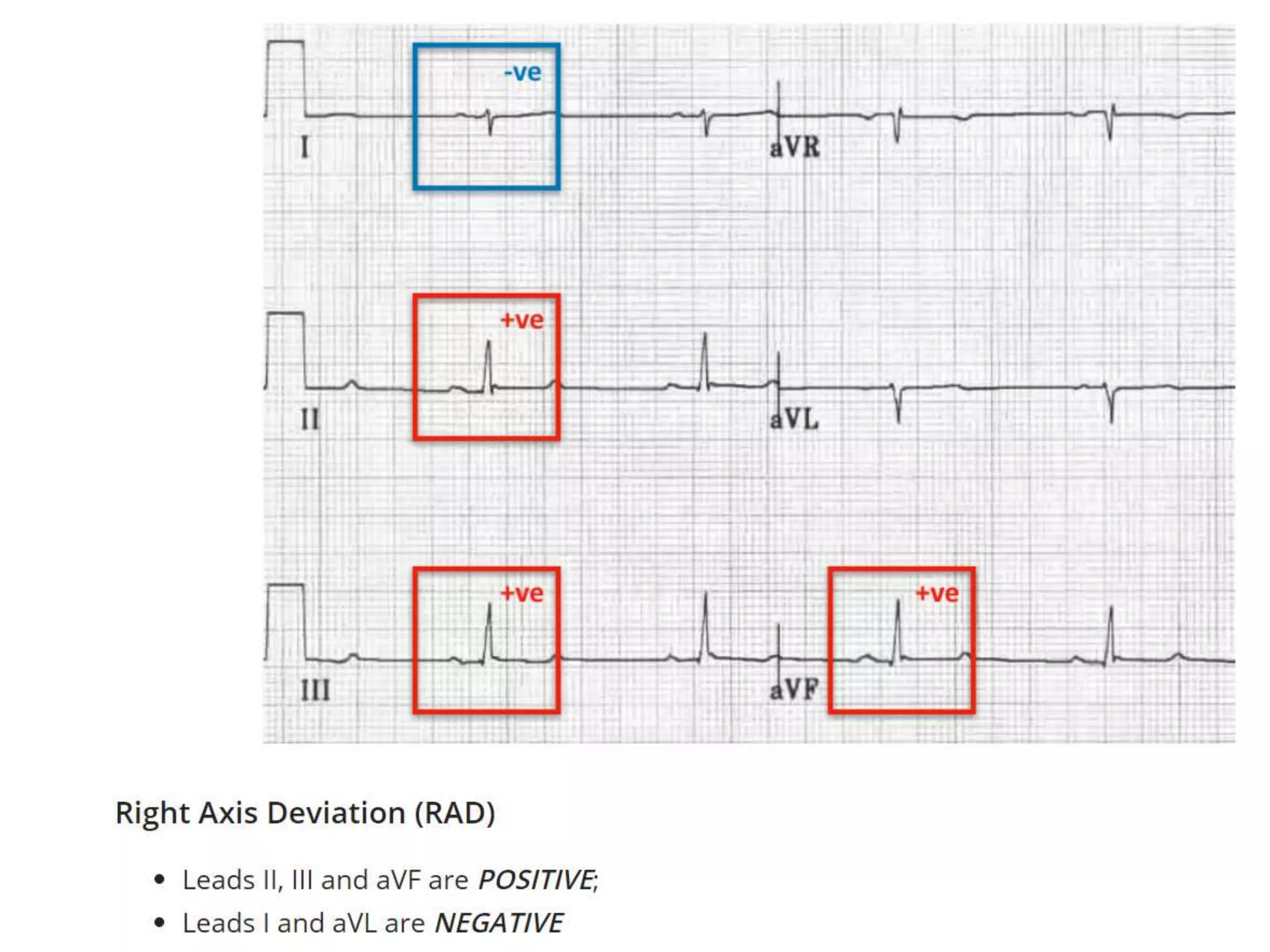
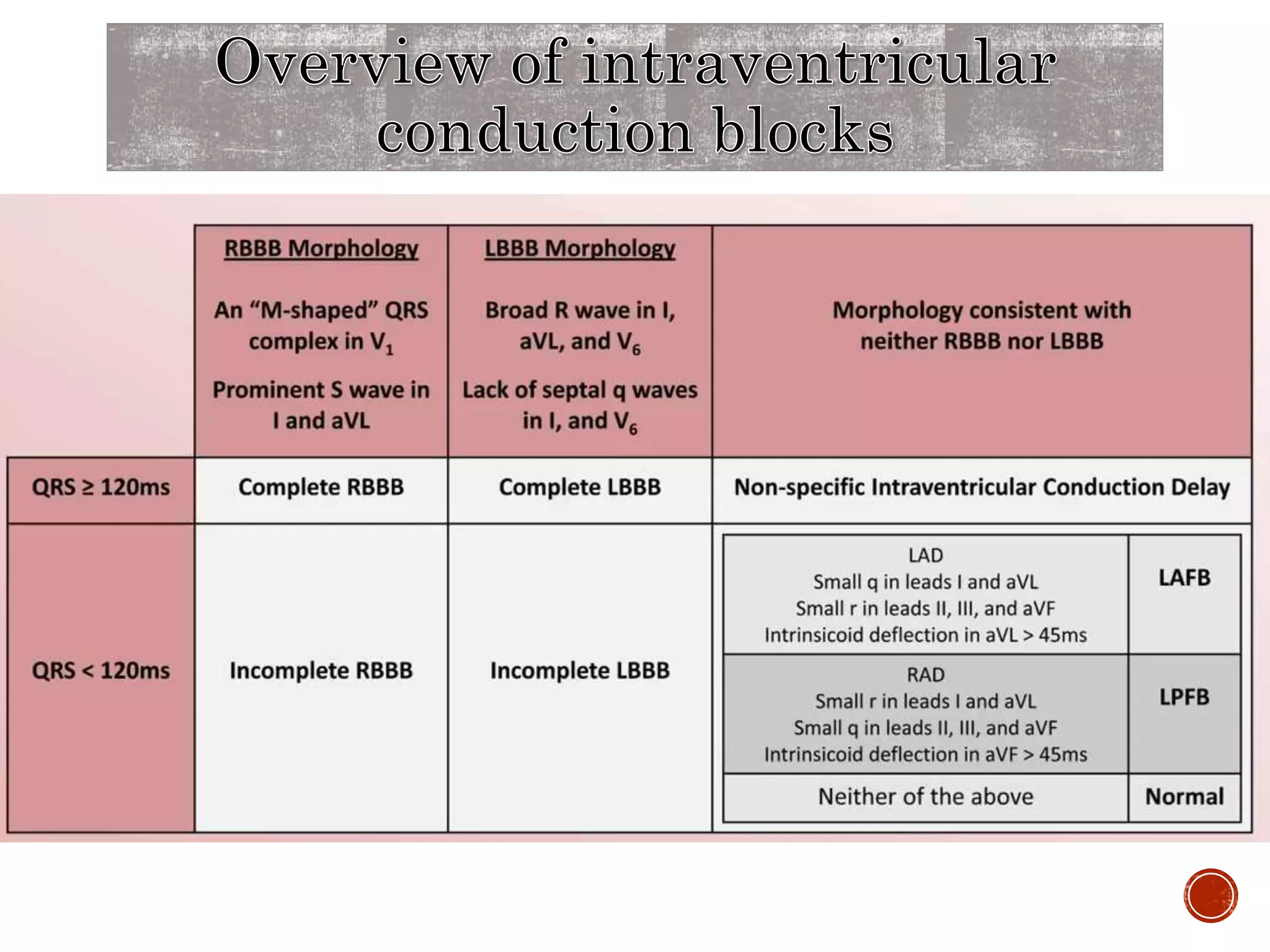
This document discusses right bundle branch block (RBBB). It defines RBBB and its diagnostic criteria. Potential causes of RBBB are listed, including pulmonary embolism and ischemic heart disease. The document notes that RBBB is generally not clinically significant in asymptomatic patients and has little impact on prognosis, though it can indicate issues in patients with symptoms like chest pain or dyspnea. Large studies have found no association between RBBB and increased mortality in otherwise healthy individuals.