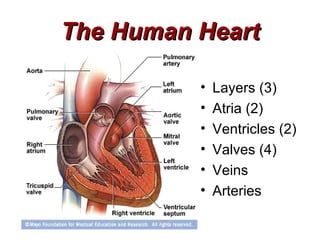
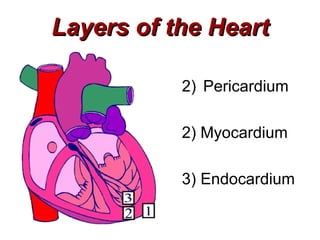
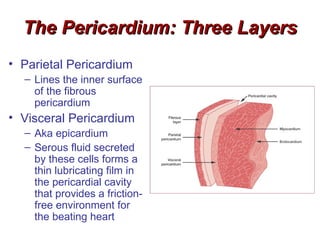
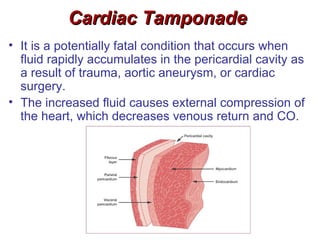
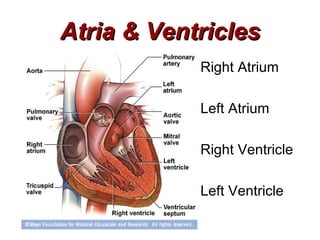
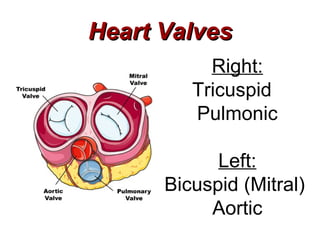
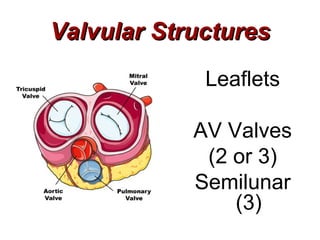
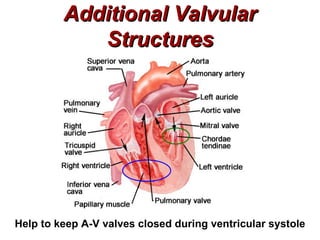
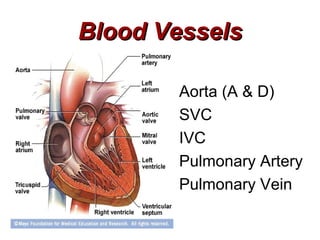
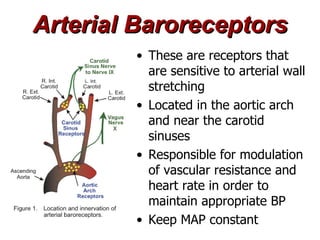
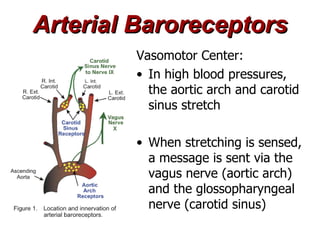
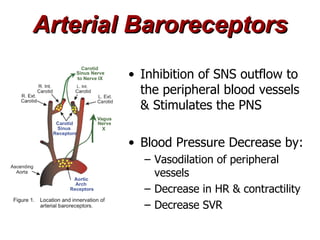
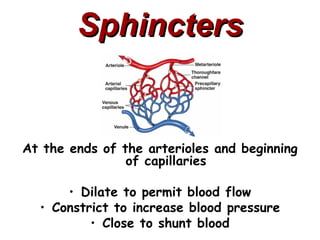
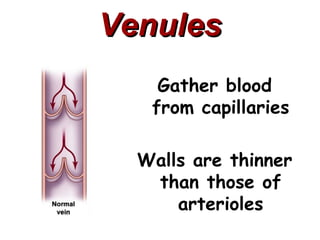
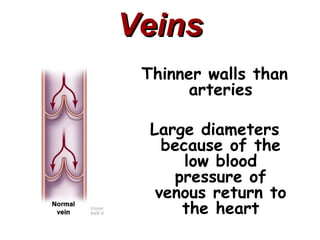
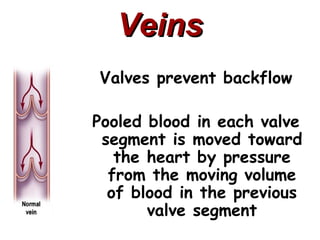
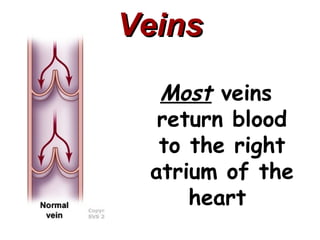
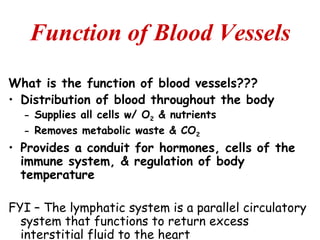
(1) The document provides an overview of cardiac anatomy and physiology, including the layers of the heart, chambers, valves, blood vessels, and the pumping action.
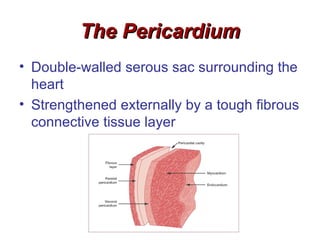
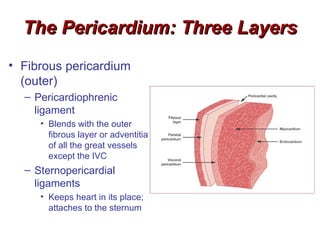
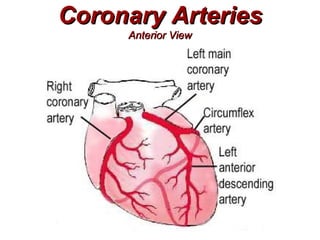
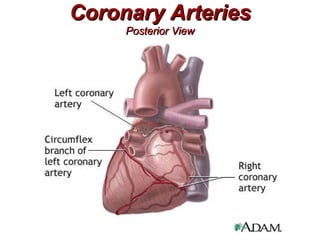
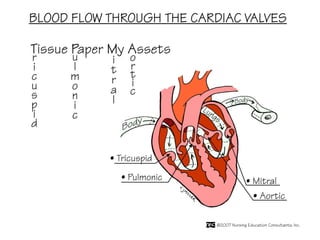
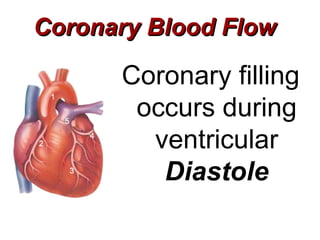
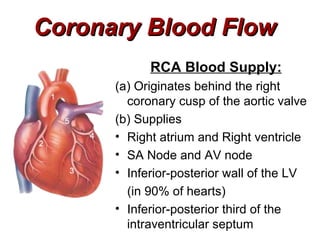
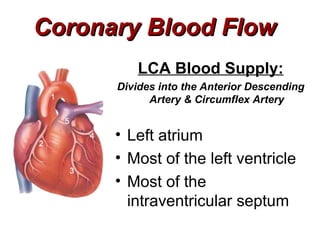
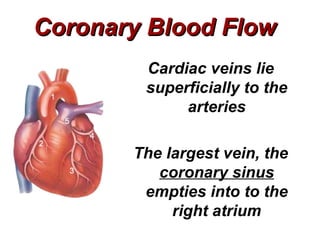
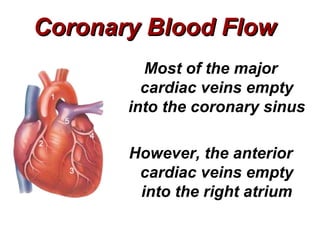
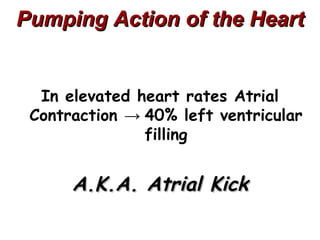
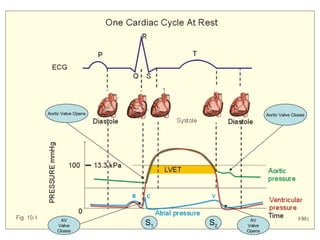
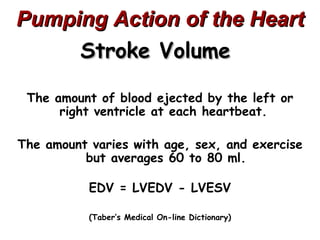
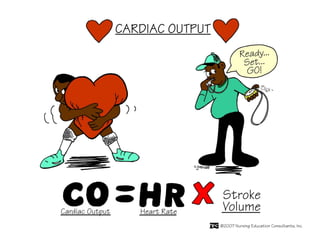
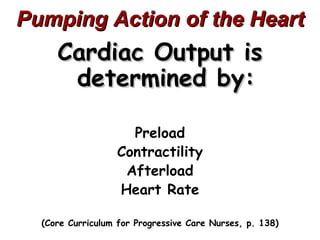
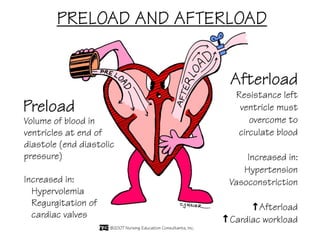
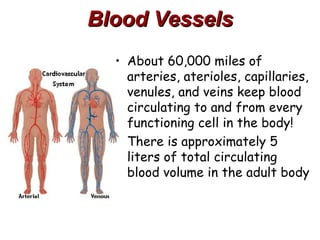
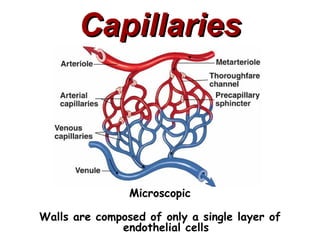
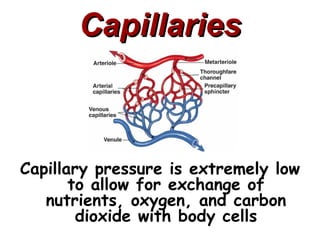
(2) It describes the pericardium, myocardium, endocardium, atria, ventricles, valves, coronary arteries and veins, and how preload, contractility, afterload, and heart rate impact cardiac output.
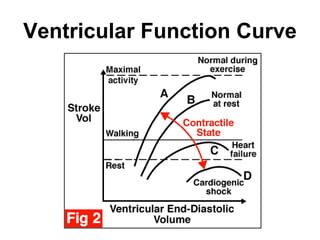
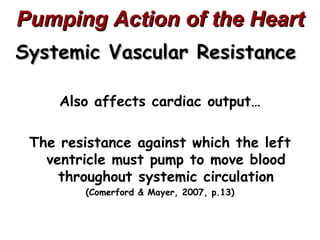
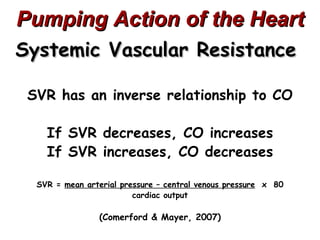
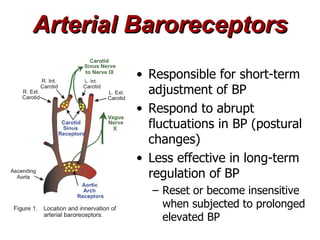
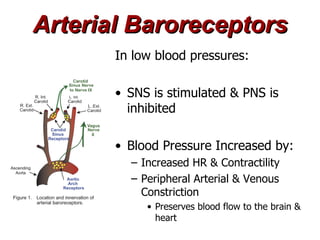
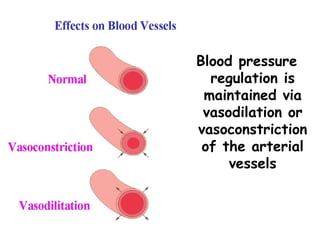
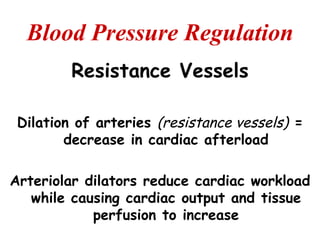
(3) Key concepts covered are the Frank-Starling mechanism, factors that increase or decrease preload, contractility, and afterload, and how systemic vascular resistance impacts cardiac output.