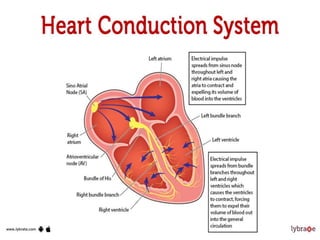
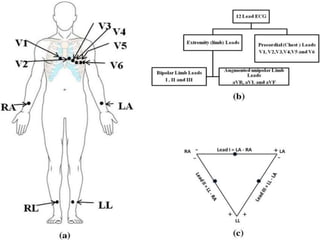
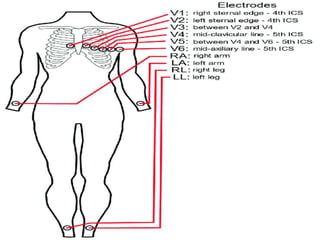
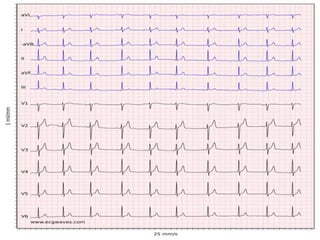
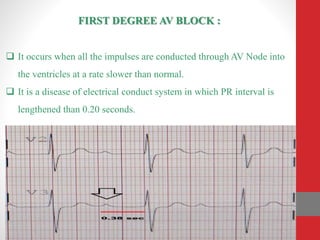
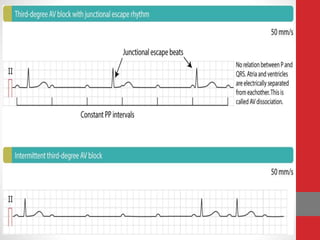
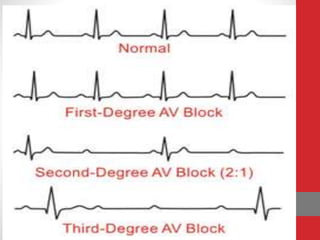
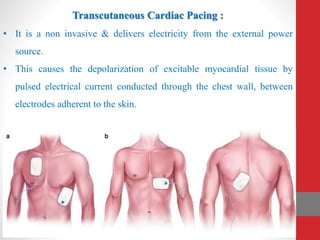
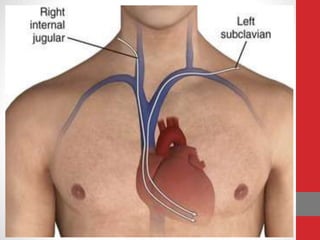
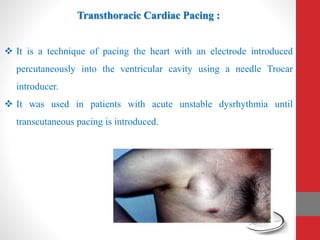
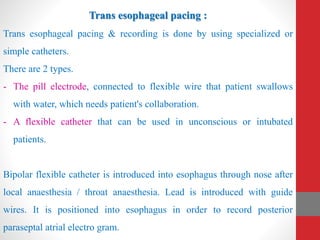
Heart block is a condition where the heart beats more slowly or irregularly due to a disruption in the electrical signals controlling the heartbeat. There are three main types of heart block - first, second, and third degree - which differ based on the level and extent of disruption in electrical signal conduction. Diagnosis involves ECG, echocardiogram, and cardiac monitoring. Treatment ranges from medication and pacemaker implantation depending on symptoms and severity of block. Temporary pacemakers are used initially, while permanent pacemakers provide long-term treatment for persistent blocks.