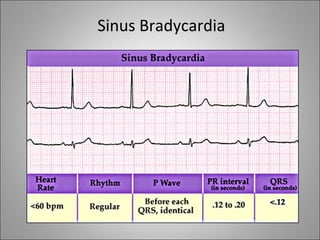
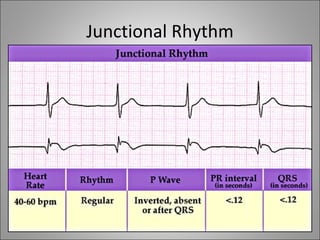
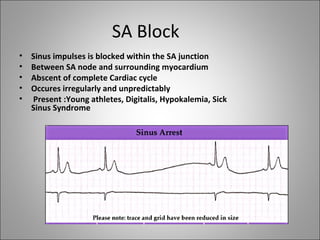
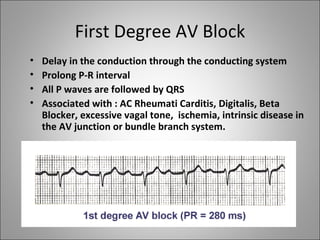
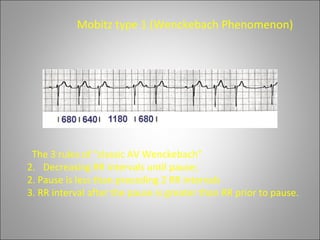
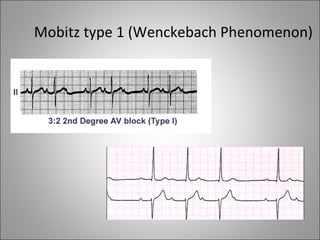
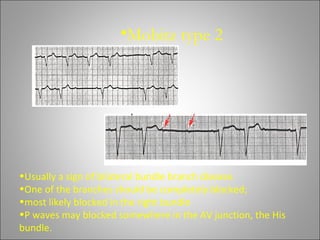
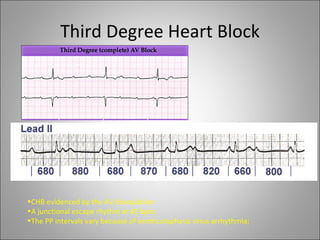
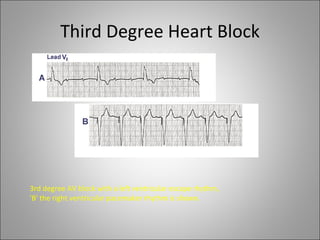
1) Bradyarrhythmias include sinus bradycardia, junctional rhythm, sinoatrial block, and atrioventricular block which can be first, second, or third degree.
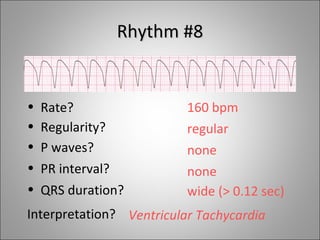
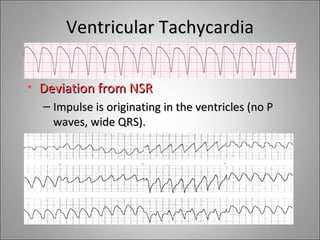
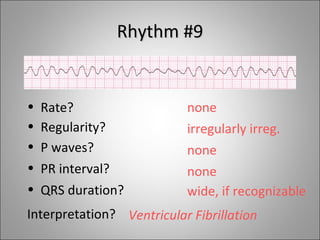
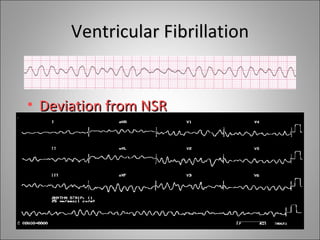
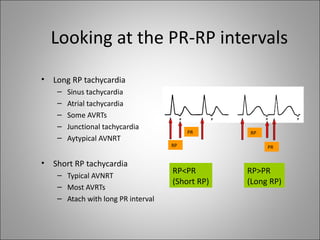
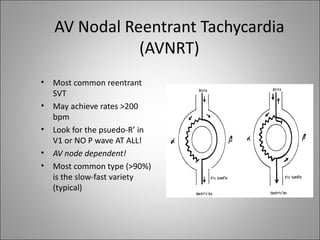
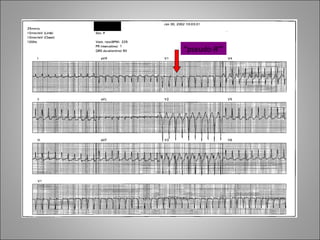
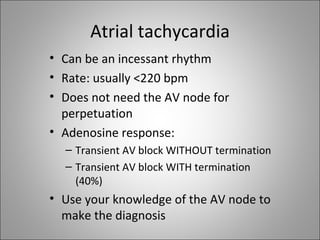
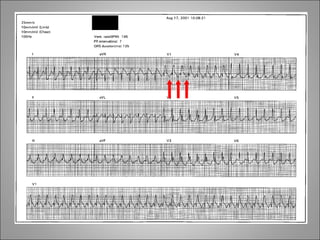
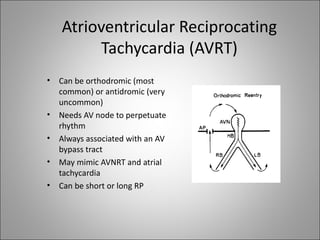
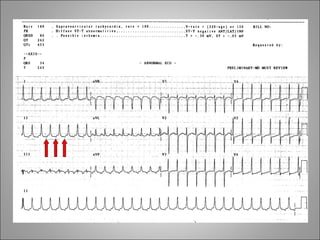
2) Tachyarrhythmias include ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, atrial fibrillation, AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, and atrial tachycardia. Narrow complex tachycardias require analyzing the P waves and PR and RP intervals to determine the mechanism.
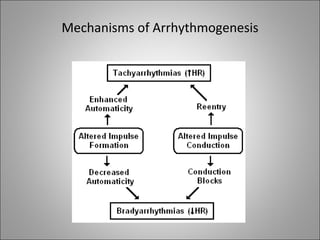
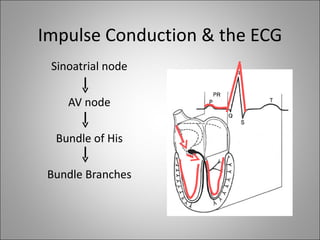
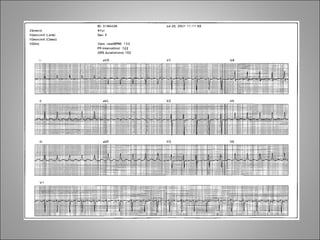
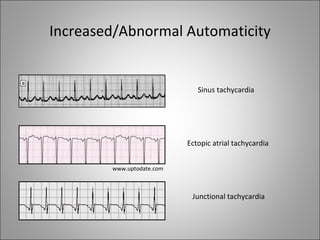
3) Different arrhythmias are caused by abnormalities in impulse conduction through the heart or abnormal automaticity in the sinoatrial node or elsewhere. Diagnosis requires interpreting the rhythm on