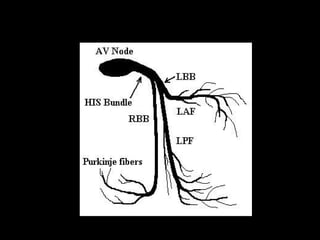
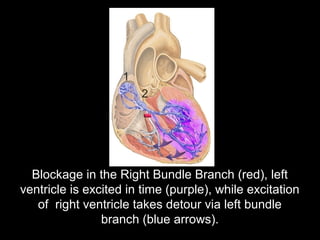
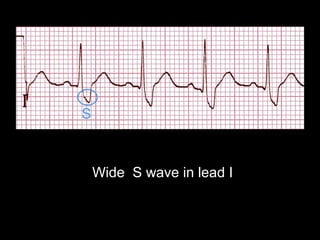
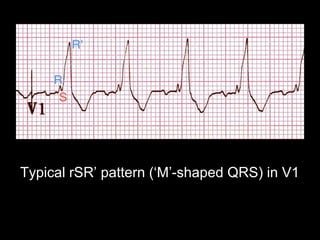
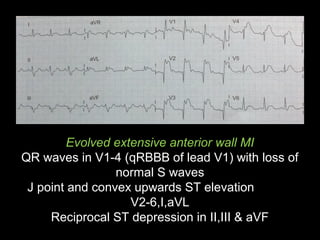
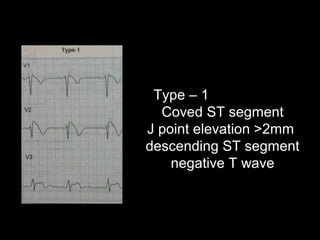
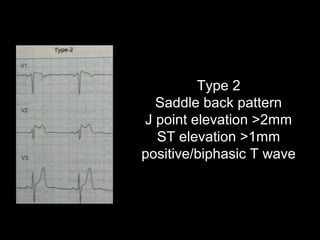
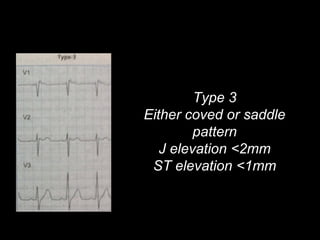
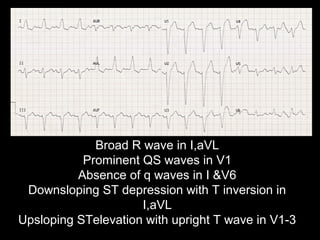
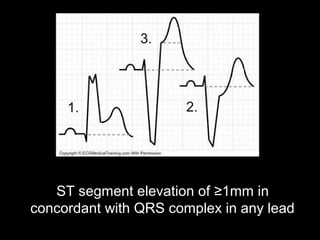
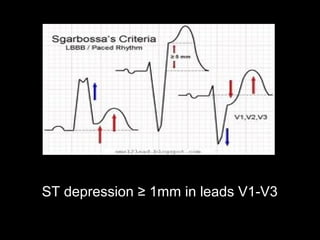
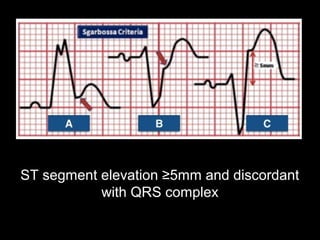
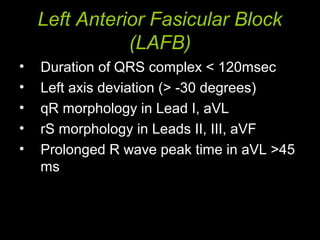
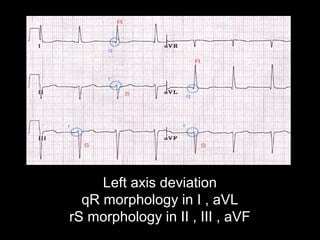
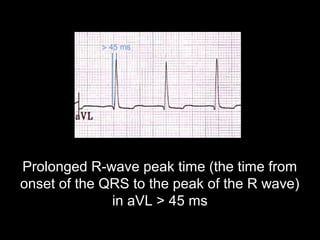
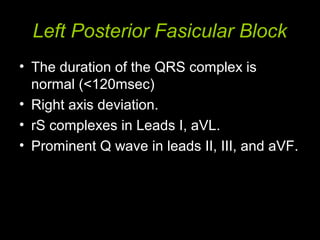
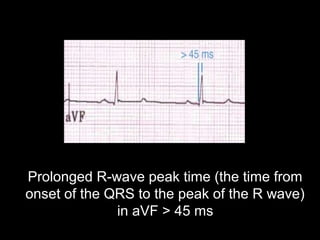
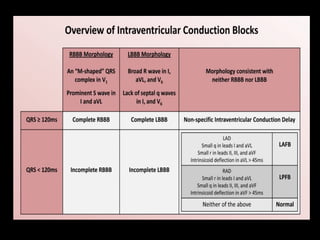
The document discusses intraventricular conduction blocks, including right bundle branch block (RBBB), left bundle branch block (LBBB), incomplete blocks, and fascicular blocks, detailing their criteria, causes, clinical significance, and diagnostic criteria for myocardial infarction. It emphasizes the impact of these blocks on myocardial infarction prognosis and the implications of various electrocardiogram (ECG) patterns. Additionally, it covers conditions such as Brugada syndrome and explains the significance of bifascicular and trifascicular blocks.