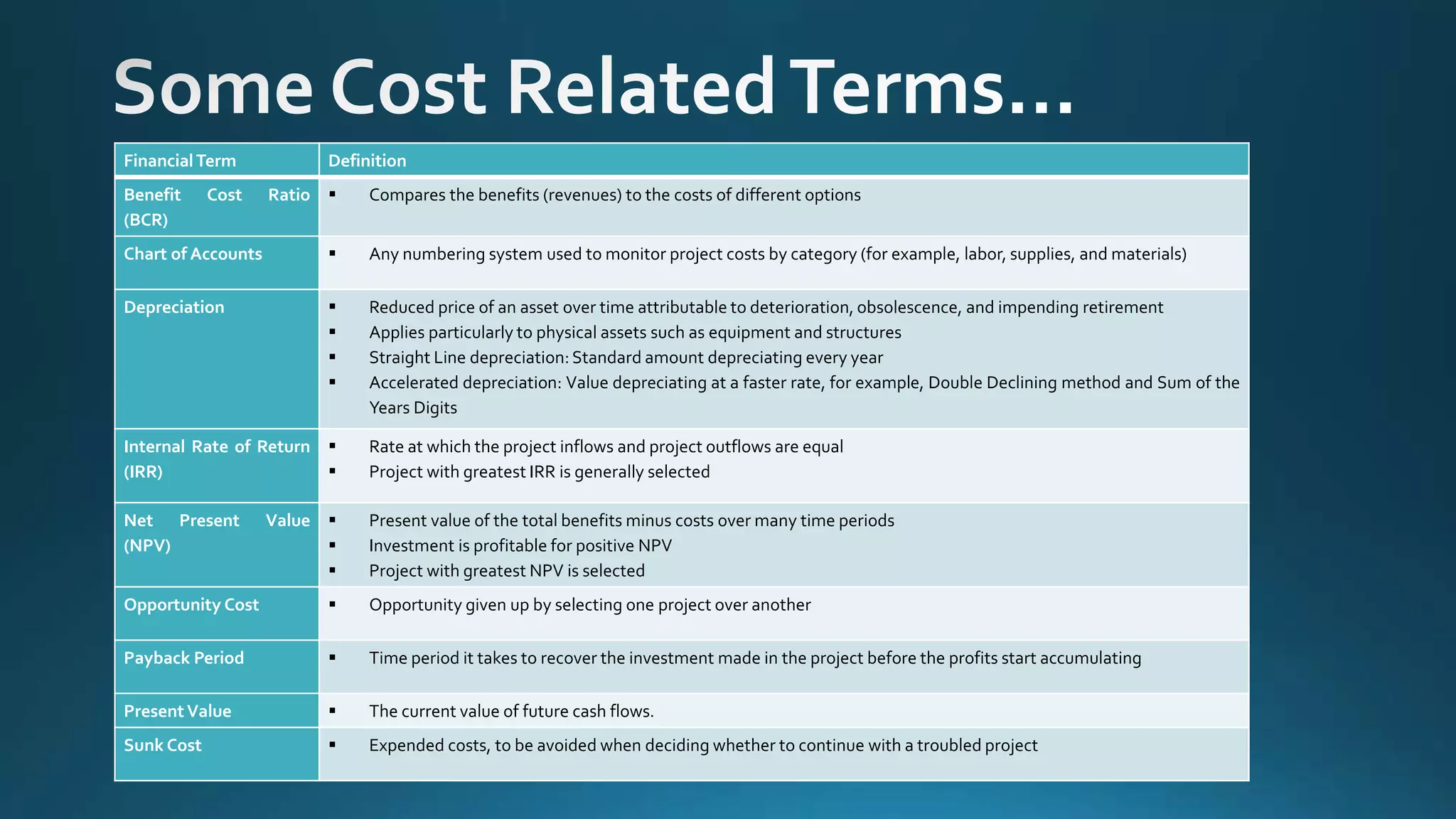
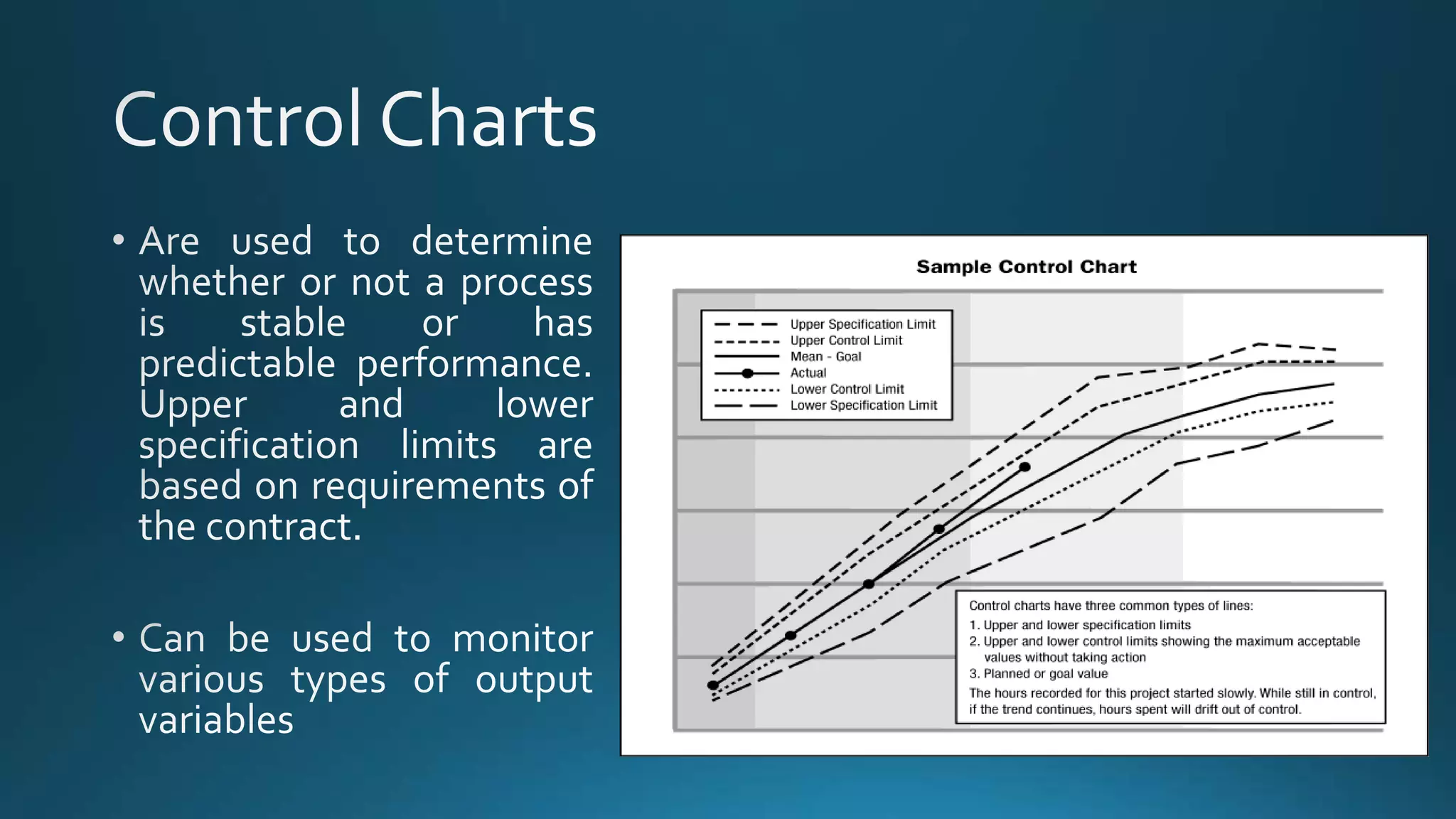
The document outlines key financial performance metrics used in project management, including cost variance (CV), schedule variance (SV), cost performance index (CPI), and schedule performance index (SPI), along with their formulas and interpretations. It also explains concepts related to project budgeting and financial evaluation such as estimate at completion (EAC), net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), and opportunity cost. By analyzing these metrics, project managers can assess budget performance and project progress critical for decision-making.







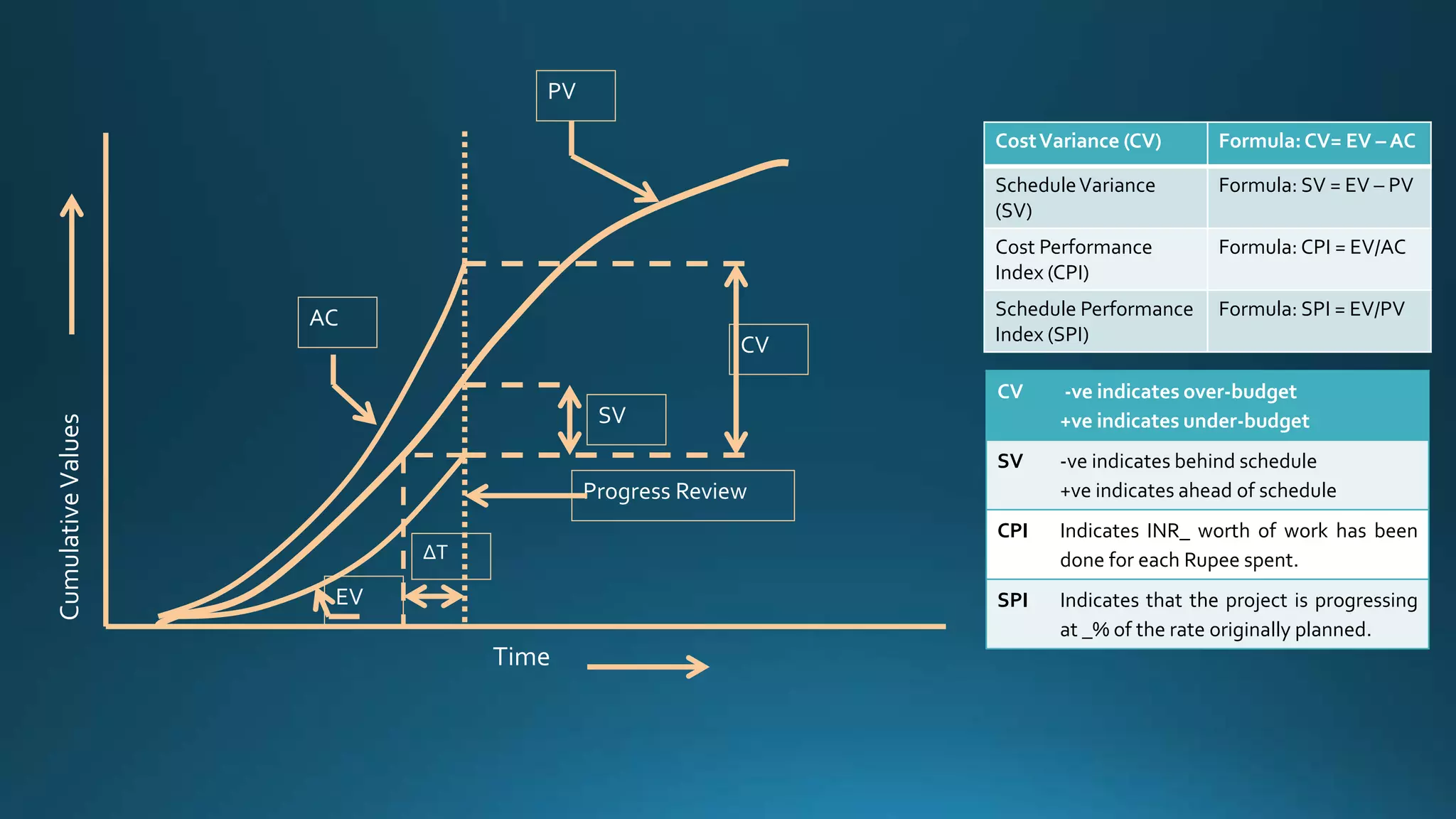
![Item Formula Remark
Cost Variance (CV) EV – AC Negative value indicates over budget and positive
value indicates under budget
ScheduleVariance (SV) EV – PV Negative value indicates behind schedule and positive
value indicates ahead of schedule
Cost Performance Index (CPI) EV / AC Lesser than one indicates over budget and greater
than one indicates under budget
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) EV / PV Lesser than one indicates behind schedule and greater
than one indicates ahead of schedule
Estimate at Completion (EAC) BAC / CPI Considering that the rate of spending remains the
same
AC + ETC Considering that the current estimate is fundamentally
flawed
AC + (BAC – EV) Considering atypical variances
AC + [(BAC – EV) /CPI] Considering typical variances
Estimate to Complete (ETC) EAC – AC Considering that the current estimate is fundamentally
flawed
BAC – EV Considering atypical variances
(BAC – EV) / CPI Considering typical variances
Variance at Completion (VAC) BAC – EAC Considering the status of the budget expected at the
end of the project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-iv-150401071907-conversion-gate01/75/Project-Monitoring-and-Controlling-Processes-10-2048.jpg)