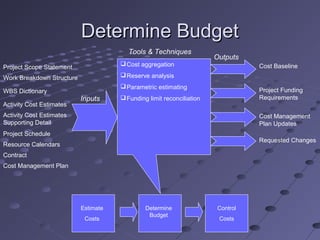
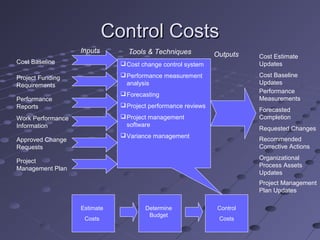
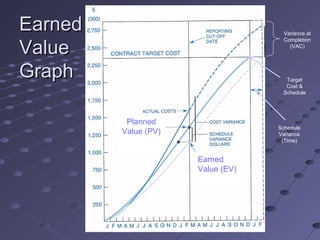
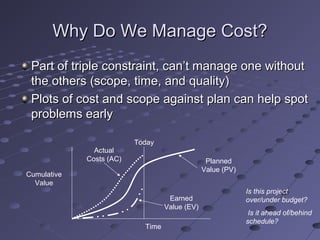
This document provides an overview of project cost management. It discusses estimating costs, determining budgets, and controlling costs. Key aspects include estimating methods like analogous, bottom-up, and parametric; determining a cost baseline; using earned value formulas like CPI, SPI, ETC, and EAC to track performance; and controlling costs through variance analysis and forecasting. The goal is planning, estimating, budgeting, and controlling costs to complete projects within approved budgets.




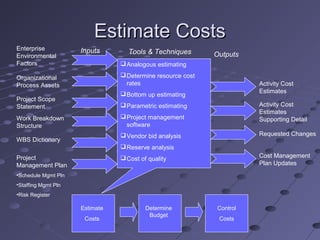
![Estimating MethodsEstimating Methods
Analogous (Top Down) estimatingAnalogous (Top Down) estimating – Managers– Managers
use expert judgment or similar project costsuse expert judgment or similar project costs
[quick, less accurate][quick, less accurate]
Bottom-Up estimatingBottom-Up estimating – People doing work– People doing work
estimate based on WBS, rolled up into projectestimate based on WBS, rolled up into project
estimate [slow, most accurate]estimate [slow, most accurate]
Parametric estimatingParametric estimating – Use mathematical model– Use mathematical model
(i.e. cost per sq ft). [accuracy varies](i.e. cost per sq ft). [accuracy varies] Two types:Two types:
Regression analysis – based on analysis of multipleRegression analysis – based on analysis of multiple
data pointsdata points
Learning Curve – The first unit costs more than theLearning Curve – The first unit costs more than the
100100thth
, forecasts efficiency gains, forecasts efficiency gains](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectcostmanagement-171205012032/85/Project-cost-management-7-320.jpg)
![Estimating MethodsEstimating Methods
Vendor Bid AnalysisVendor Bid Analysis – Estimating using bids +– Estimating using bids +
allowances for gaps in bid scope [slow, accuracyallowances for gaps in bid scope [slow, accuracy
depends on gaps]depends on gaps]
Reserve AnalysisReserve Analysis – Adding contingency to each– Adding contingency to each
activity cost estimates as zero duration item [slow,activity cost estimates as zero duration item [slow,
overstates cost]overstates cost]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectcostmanagement-171205012032/85/Project-cost-management-8-320.jpg)