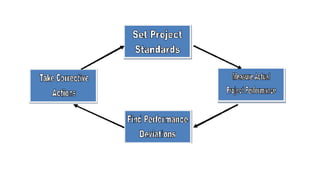
The document outlines the importance of project control as a management function, emphasizing the necessity of monitoring progress, performance, scheduling, and cost throughout a project's lifecycle. It describes four key components: progress control, performance control, schedule control, and cost control, detailing various methods and parameters for each. Effective project control aims for the complete and efficient completion of projects, ensuring alignment with organizational objectives.