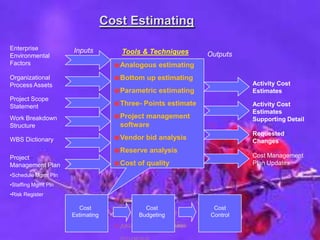
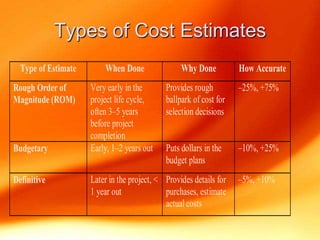
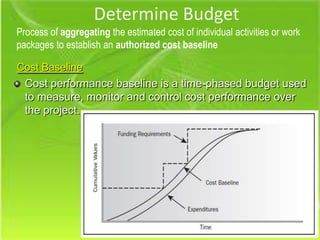
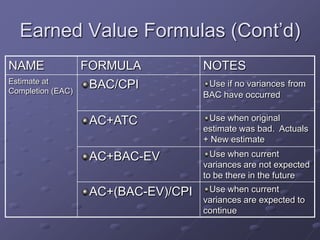
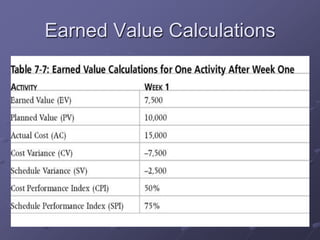
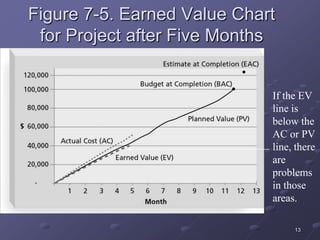
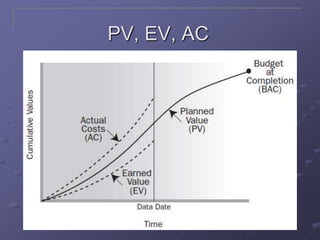
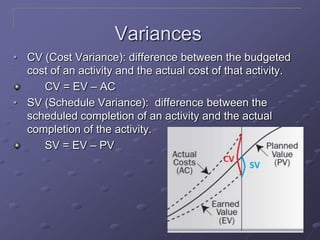
The document discusses three key processes for managing project costs: cost estimating, cost budgeting, and cost control. It provides details on cost estimation methods like analogous estimating and three-point estimating. Cost budgeting involves setting a cost baseline budget. Cost control tools like earned value management measure planned vs. actual costs and schedules to identify variances enabling corrective actions. Earned value charts and calculations like CPI and SPI are used to forecast final costs and identify if projects will finish over or under budget.