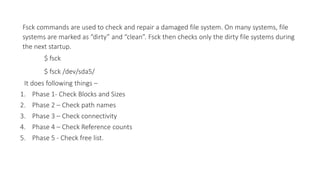
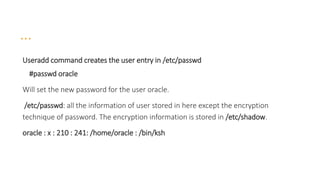
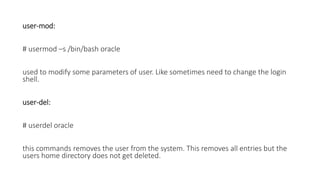
The document discusses various topics related to Unix system administration including device files, block and character devices, major and minor numbers, the Unix file system structure, partitions, file systems, inodes, mounting and unmounting file systems, disk space usage commands, compression tools, printing files, file system checking, user management commands, the role of init in startup and shutdown, run levels, and backup tools. Some key points include:
1. Device files allow all physical devices like tapes, printers, disks to be accessed as normal files.
2. Block and character devices are distinguished based on whether access is via blocks (block devices) or directly (character devices).
3. Major and minor numbers help the