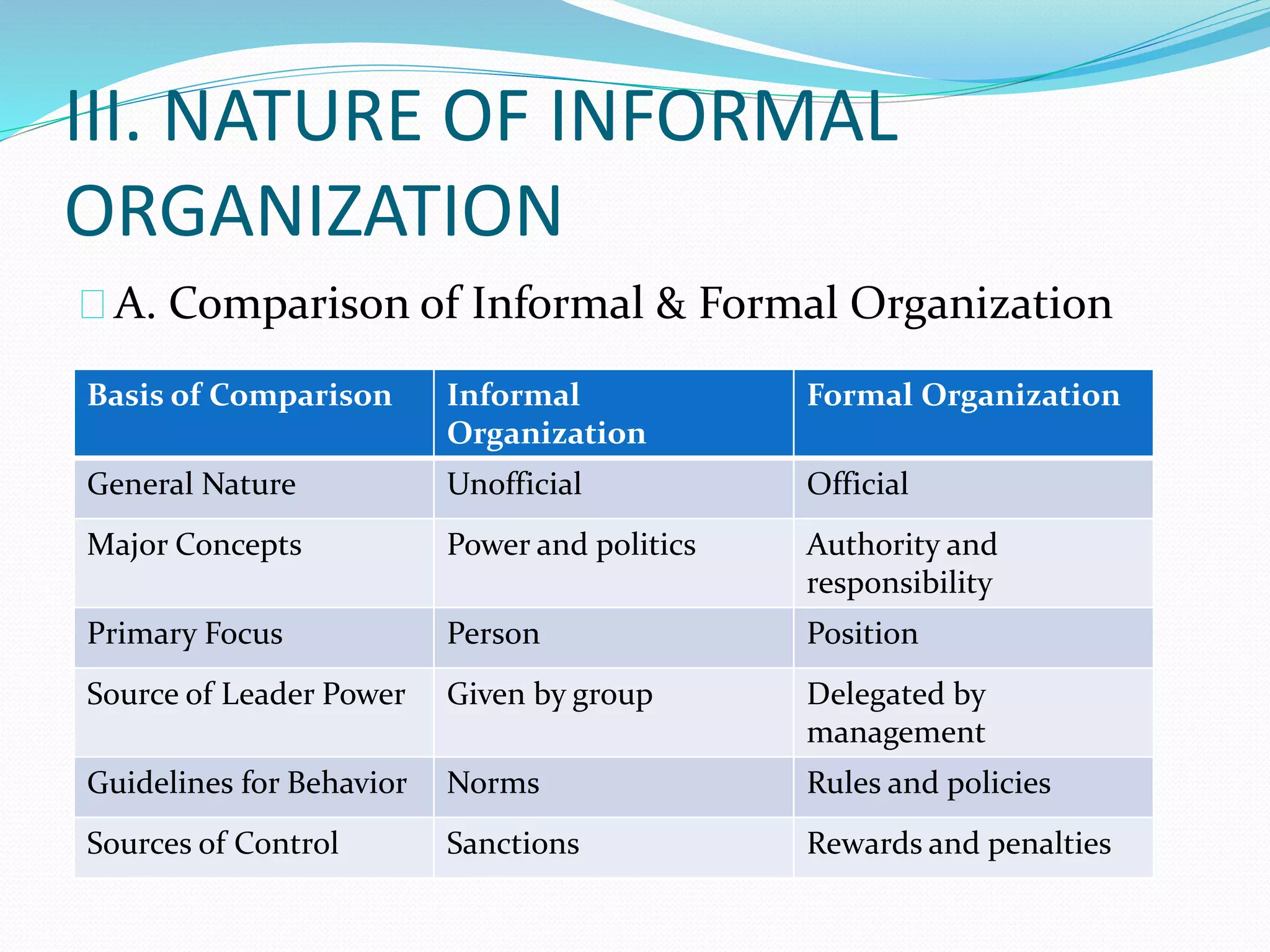
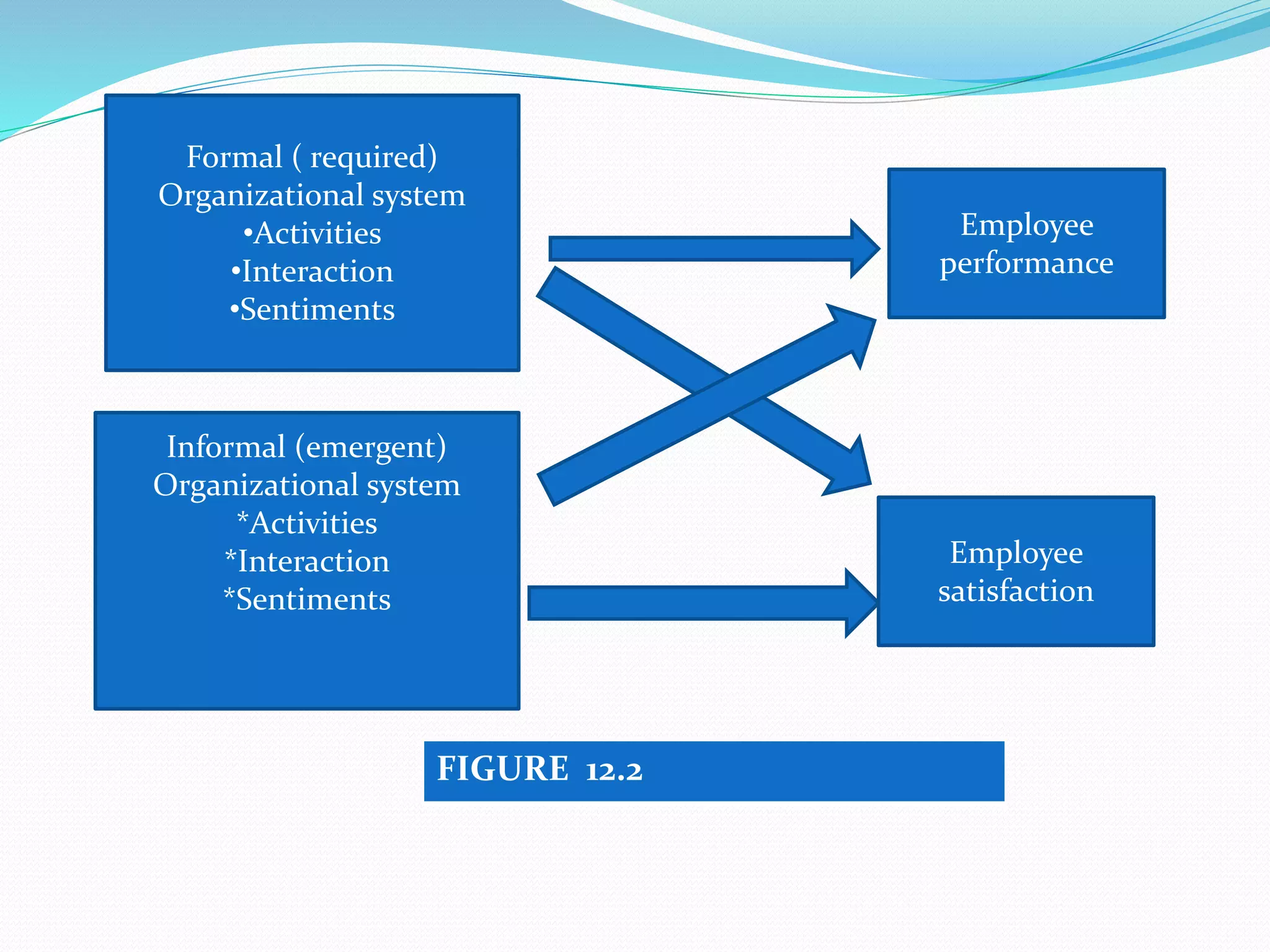
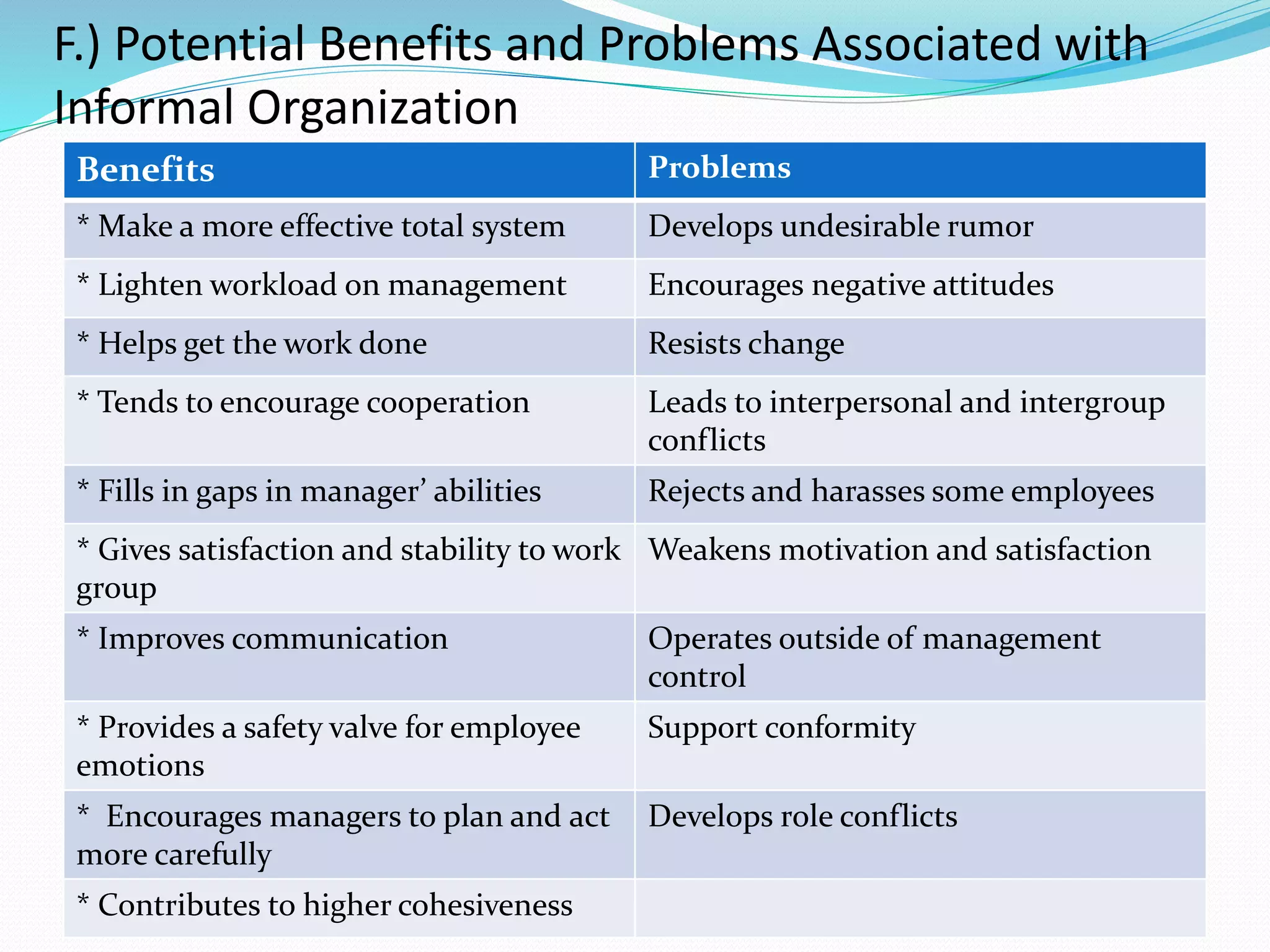
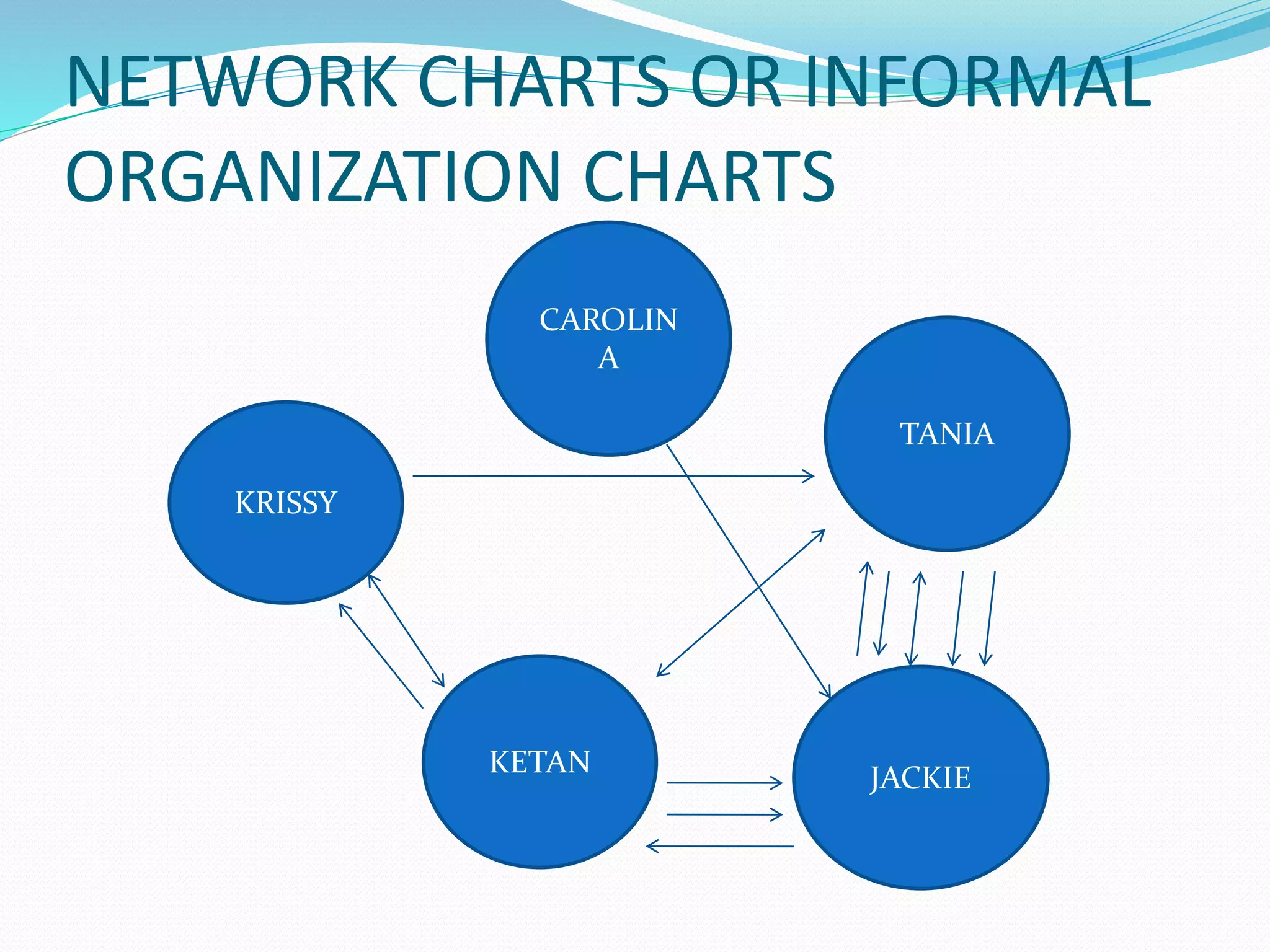
This document discusses group dynamics and informal groups within organizations. It begins by defining key concepts like group dynamic and informal groups. It then discusses the nature and effects of informal groups, including how they emerge spontaneously but can either help or hinder the formal organization. The document outlines the roles of informal leaders and how they differ from formal leaders. It also discusses techniques for managing informal groups, like identifying informal leaders and considering their influence when making decisions.