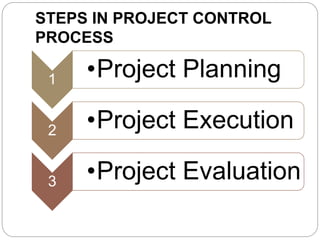
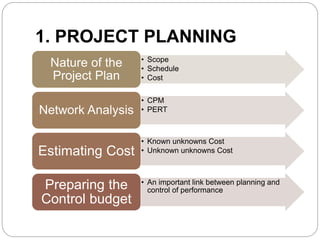
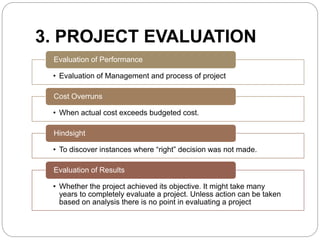
This document discusses project control and management. It defines a project as a temporary endeavor with a defined start and end, undertaken to meet unique goals. Project management is the process of planning, organizing, motivating and controlling resources to achieve specific goals. Project control refers to management actions to achieve desired results or corrective measures prompted by monitoring. The key steps in project control are project planning, project execution, and project evaluation. Project planning involves scope, schedule, cost, and risk analysis. Project execution involves comparing actual performance to estimates. Project evaluation assesses management performance, cost overruns, lessons learned, and whether objectives were achieved.