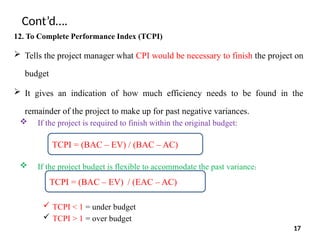
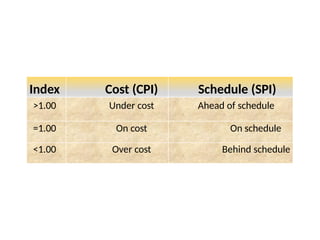
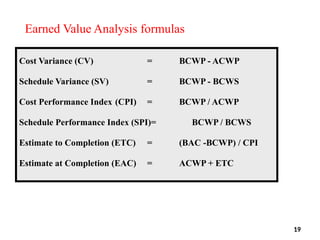
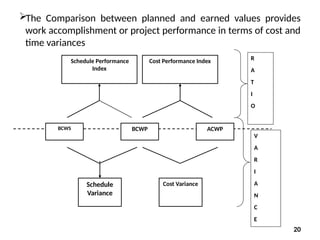
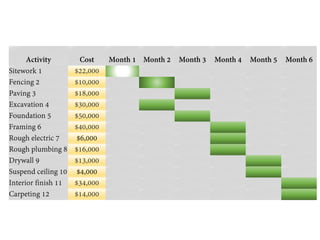
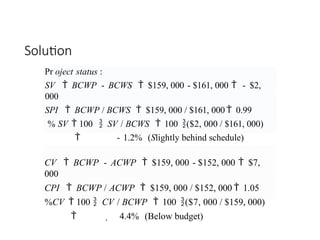
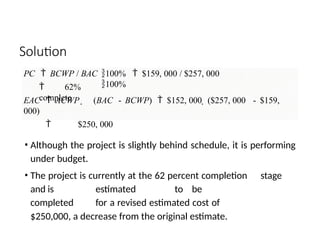
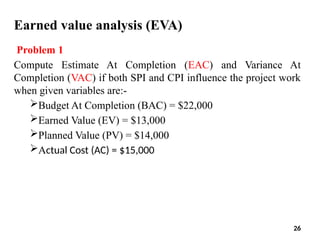
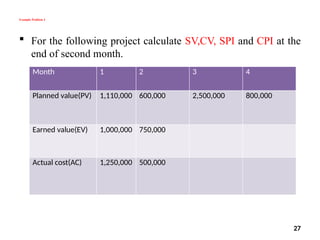
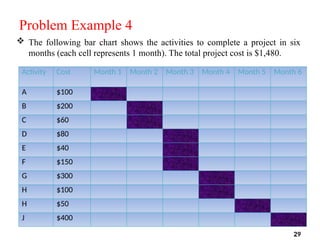
The document discusses Earned Value Analysis (EVA) in construction project management, outlining its role in measuring project health through scope, time, and cost metrics. It explains key concepts such as Planned Value, Earned Value, Actual Cost, and various performance indices (e.g., Cost Performance Index and Schedule Performance Index) that help project managers assess project performance and make informed decisions. Additionally, it provides formulas and examples to illustrate the calculation of these metrics and their implications on project status and budgeting.








![Cont’d…
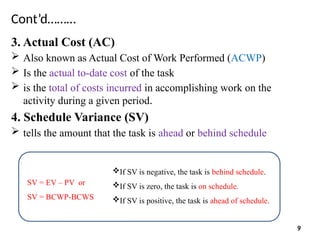
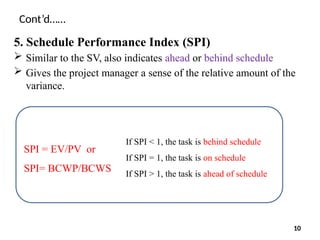
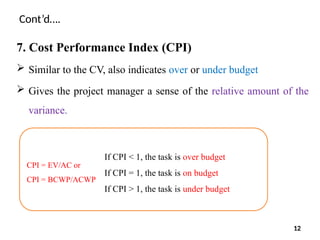
9. Estimate at Completion (EAC)
This value tells the project manager what the overall project
budget will be if everything else went according to plan
It is the extrapolation of the current project status to the end of
the project
EAC = BAC/CPI
EAC = AC + [(BAC – EV)/(SPI x CPI)]
EAC = AC + ETC 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3evapptvalueeng-250115111113-774e8def/85/Earned-Value-Analysis-in-construction-projects-14-320.jpg)