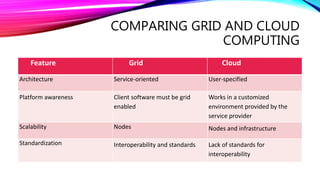
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned with minimal management effort. It has characteristics of on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. Cloud computing provides advantages like cost reduction, universal access, flexibility, and potential environmental benefits. Factors driving adoption include consumerization of IT, economic pressures, globalization, workforce trends, and the rise of data and analytics. Concerns include technology maturity, lack of standards, and security concerns.