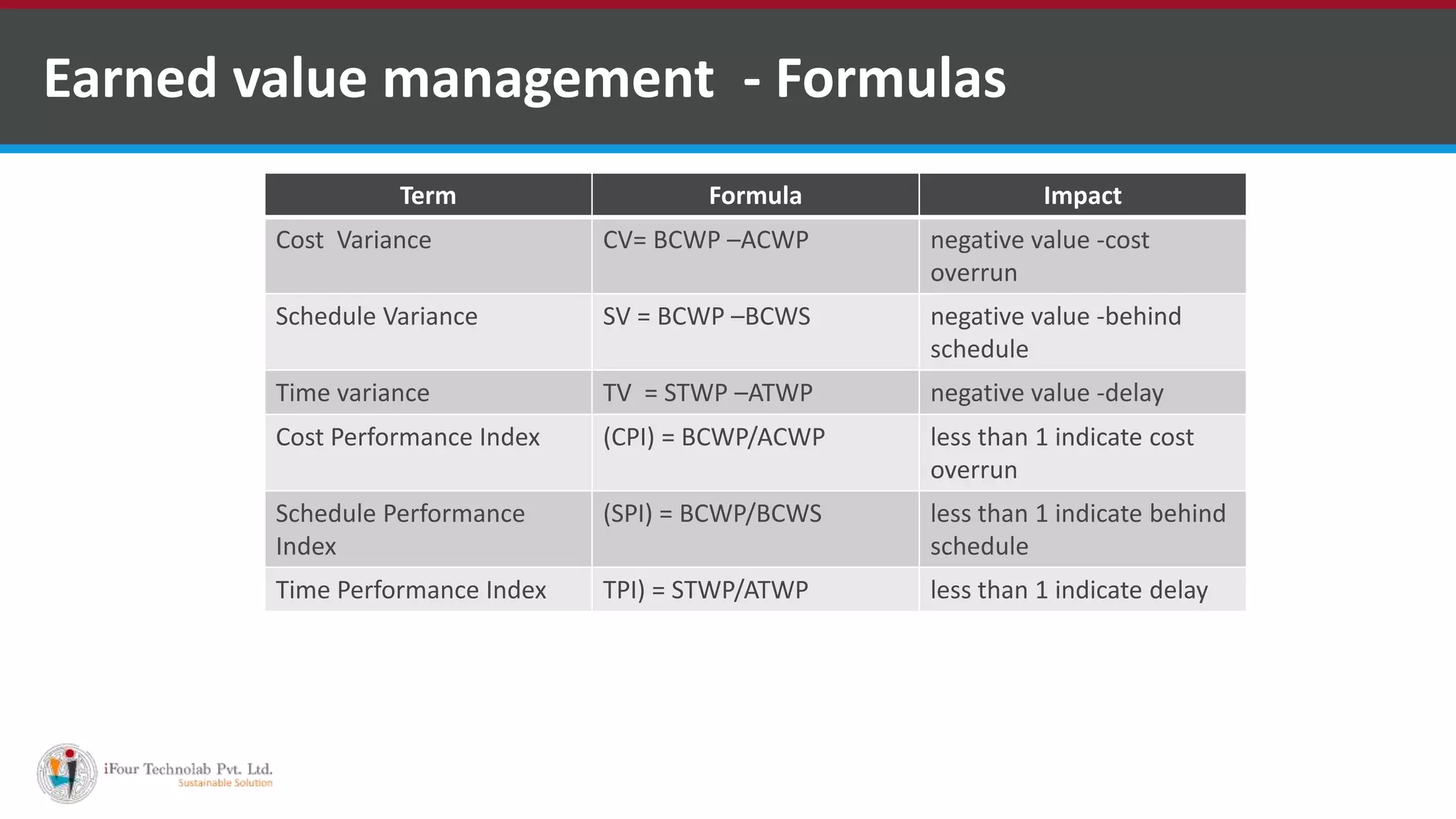
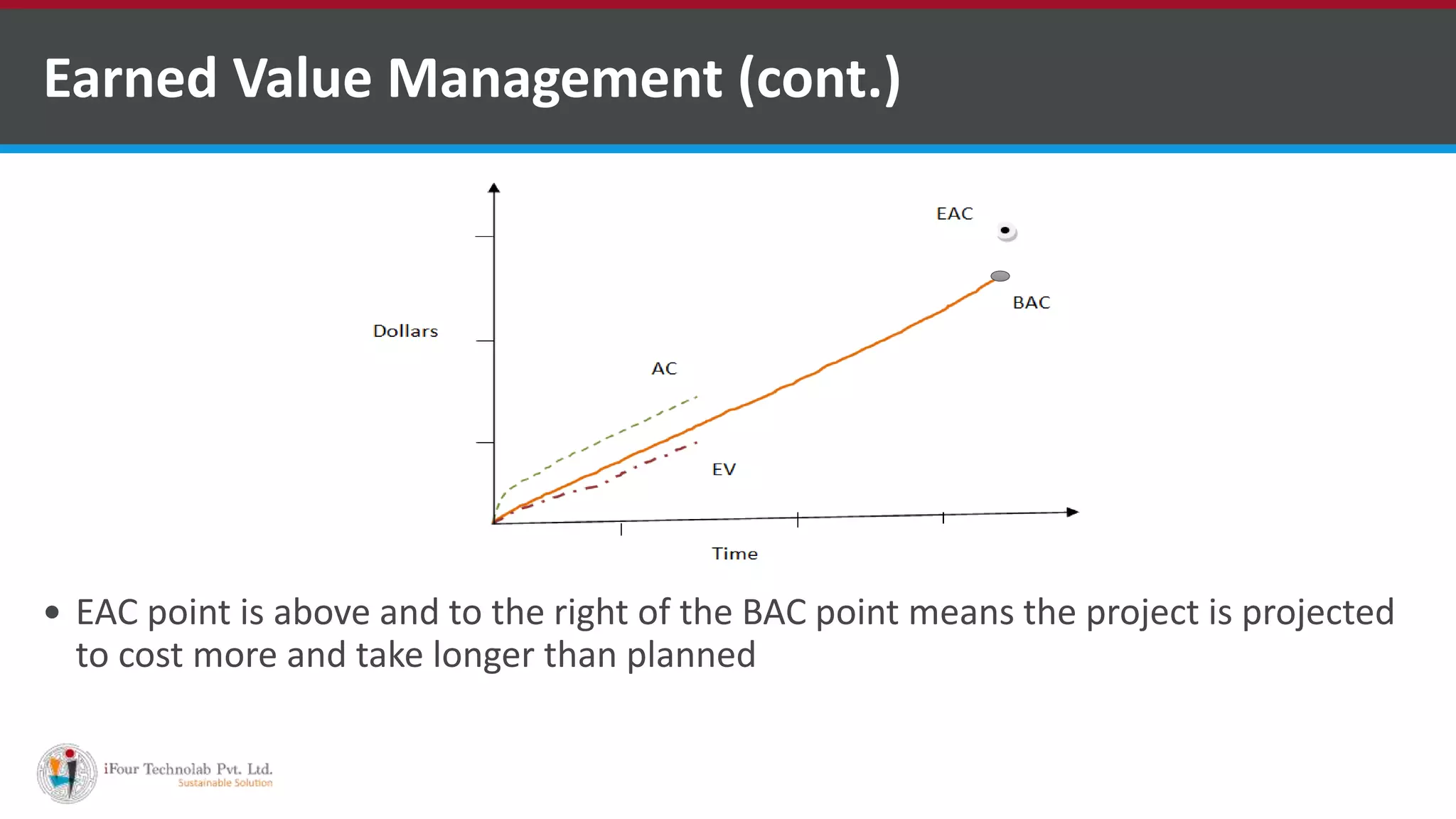
The document outlines a comprehensive framework for project monitoring and control, detailing objectives such as measuring progress, managing deviations, and achieving specific goals through systematic practices. Key techniques include earned value management and stakeholder involvement, ensuring effective communication and corrective action management. The document emphasizes institutionalizing both defined and optimizing processes to ensure continuous improvement and adherence to project standards.