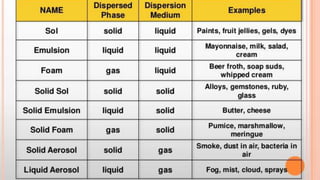
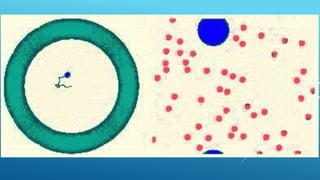
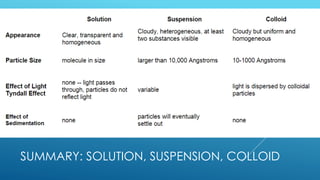
The document discusses the differences between suspensions, colloids, and solutions, highlighting their characteristics and behaviors. It includes properties of colloids such as the Tyndall effect, Brownian movement, and adsorption. Assignments related to the importance of colloids in daily life are also provided.