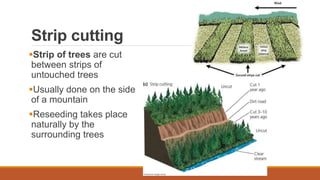
The document focuses on methods for conserving soil and forests, emphasizing techniques such as cover cropping, strip cropping, terracing, contour farming, and the use of windbreaks and dams for soil conservation. It discusses sustainable forest practices like sustained-yield tree farming and reforestation programs, which aim to maintain forest resources while preventing soil erosion. Additionally, the document provides assignment instructions and sources for further study.