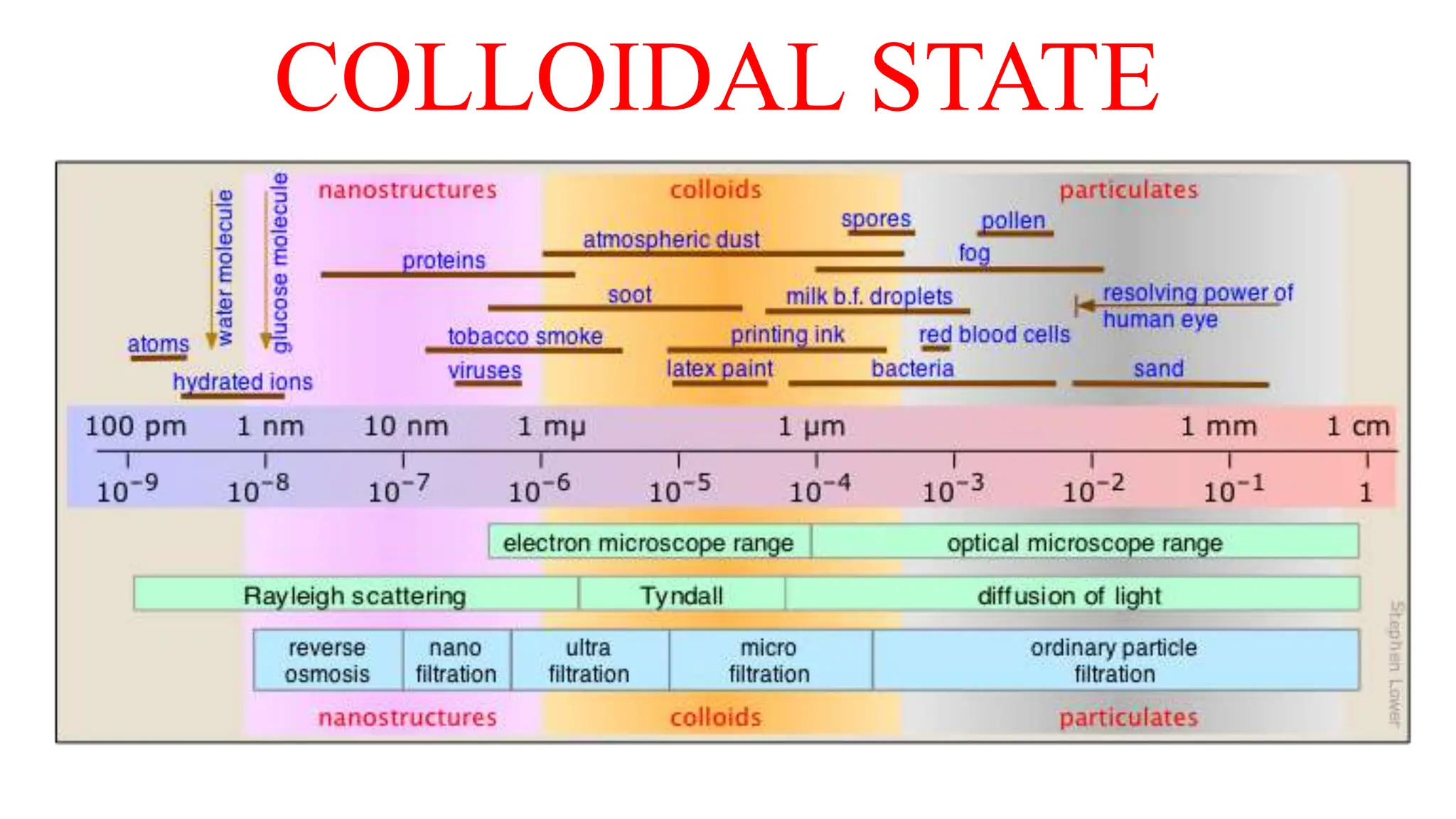
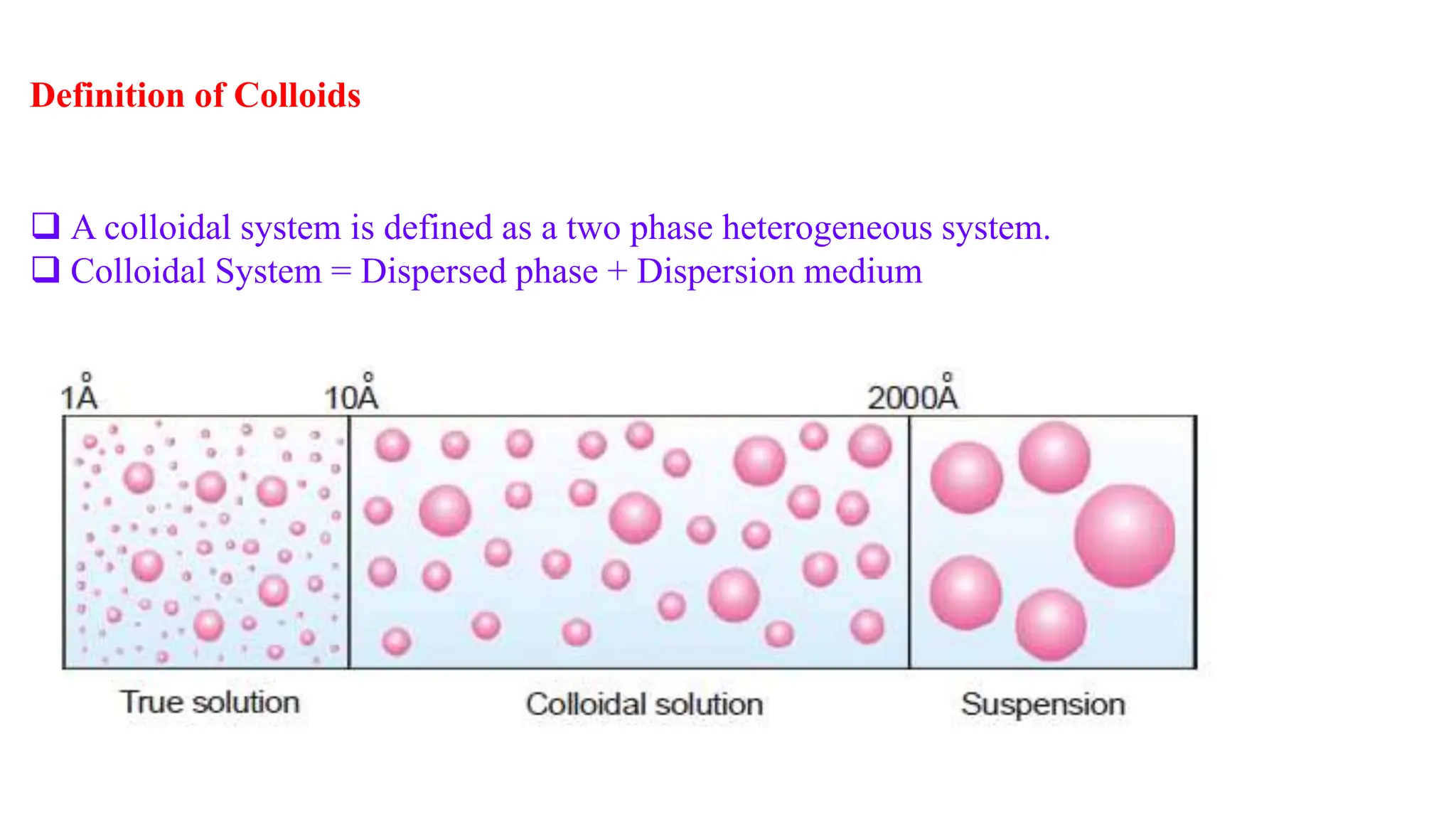
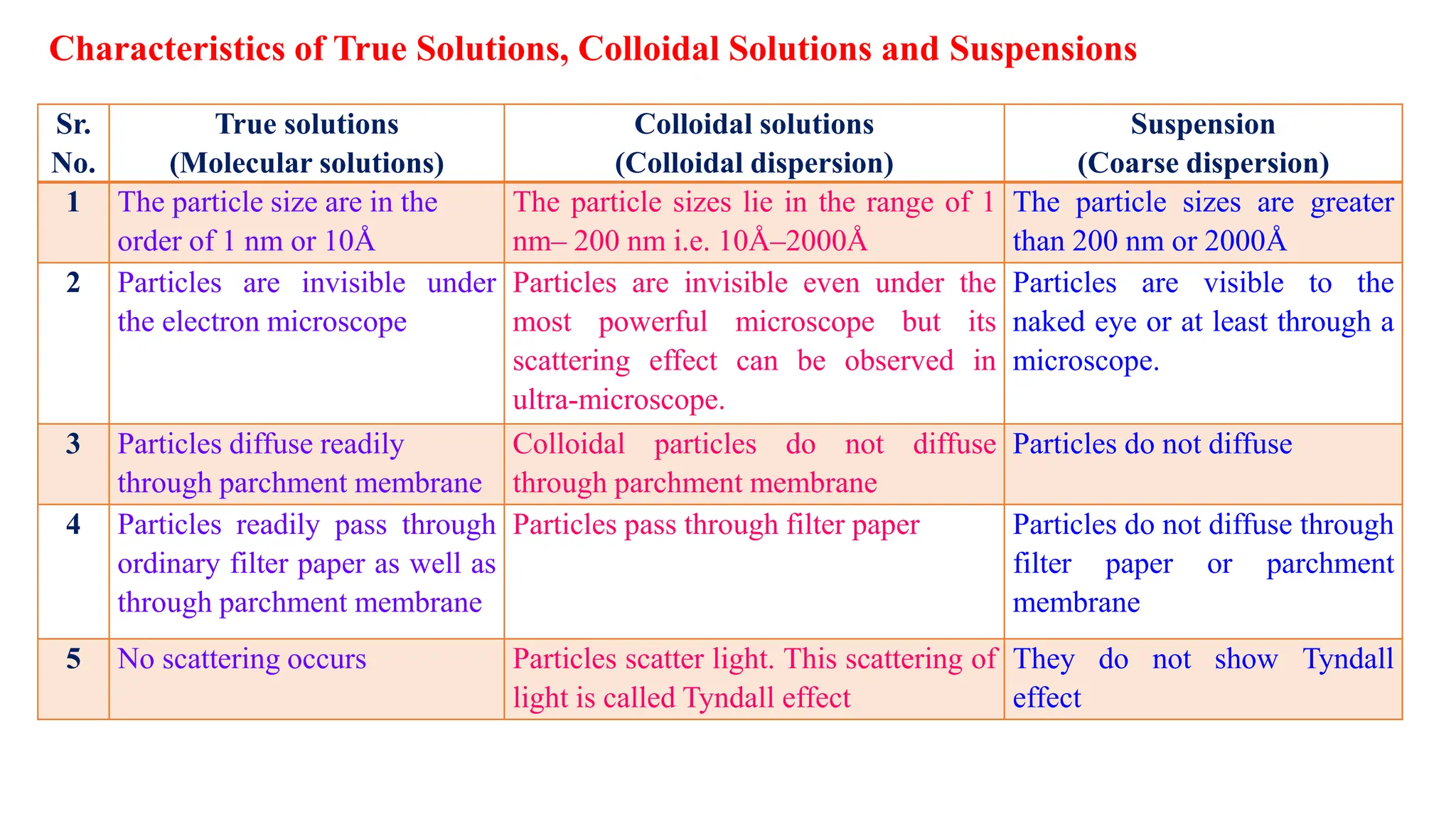
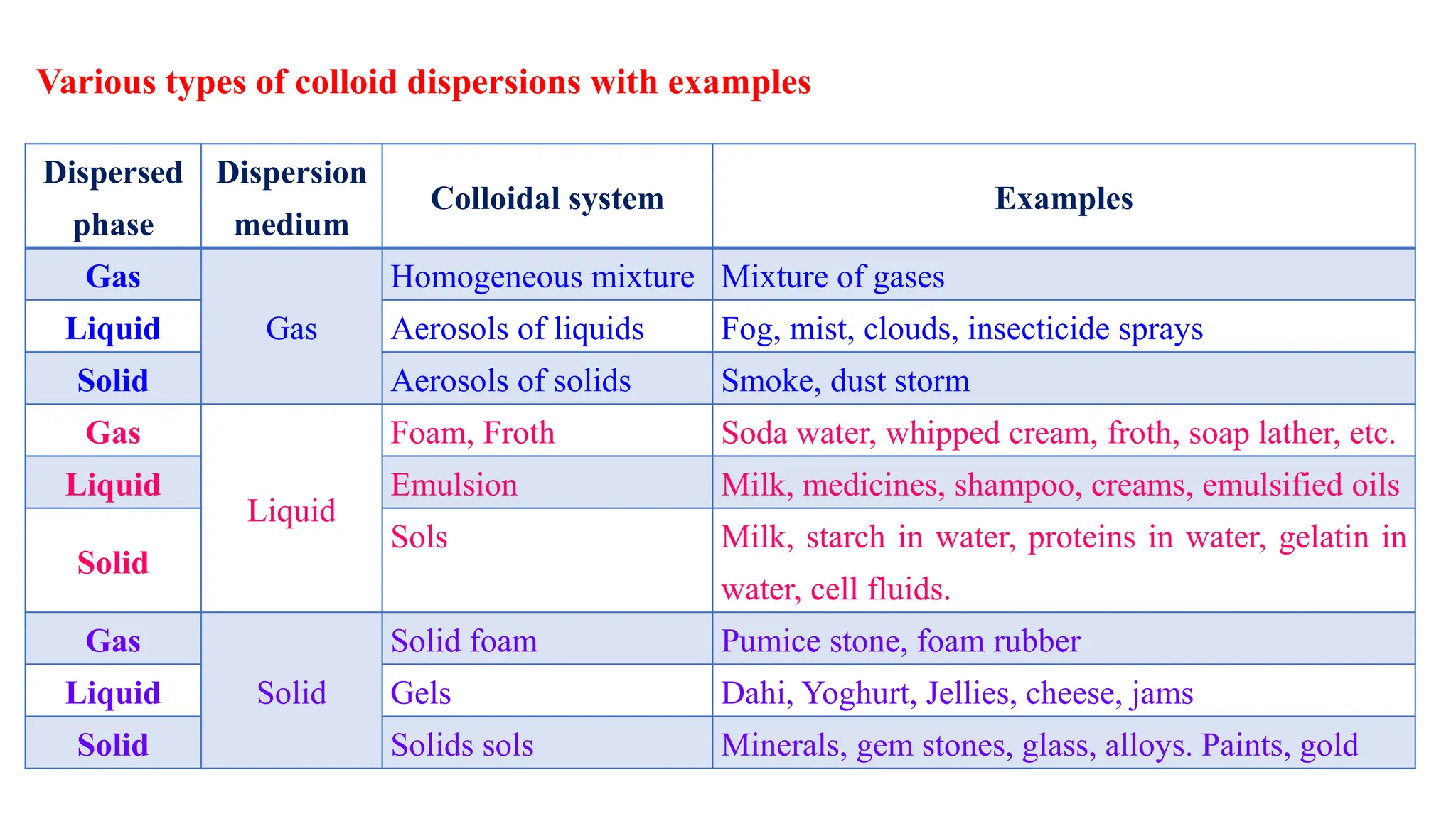
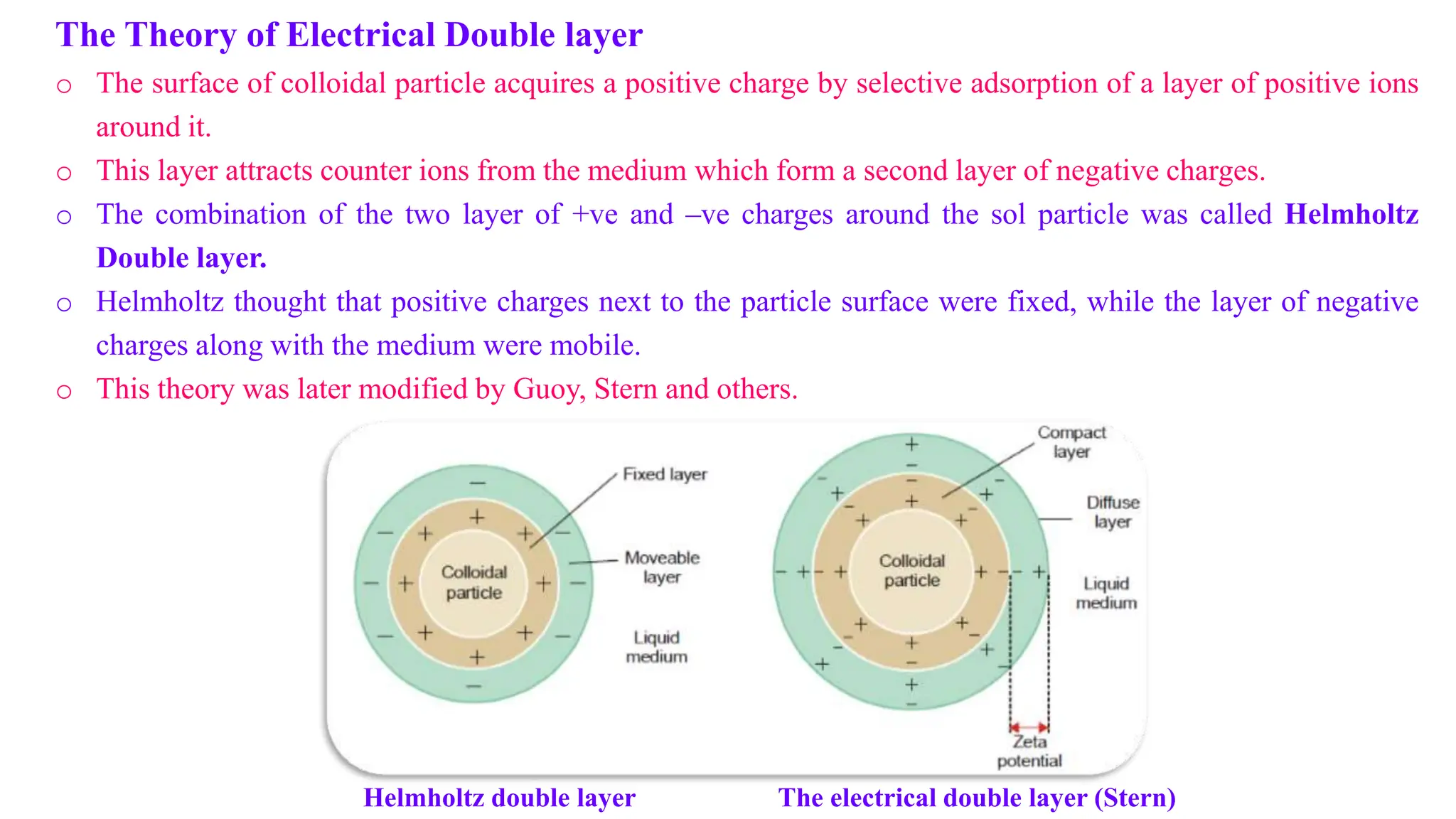
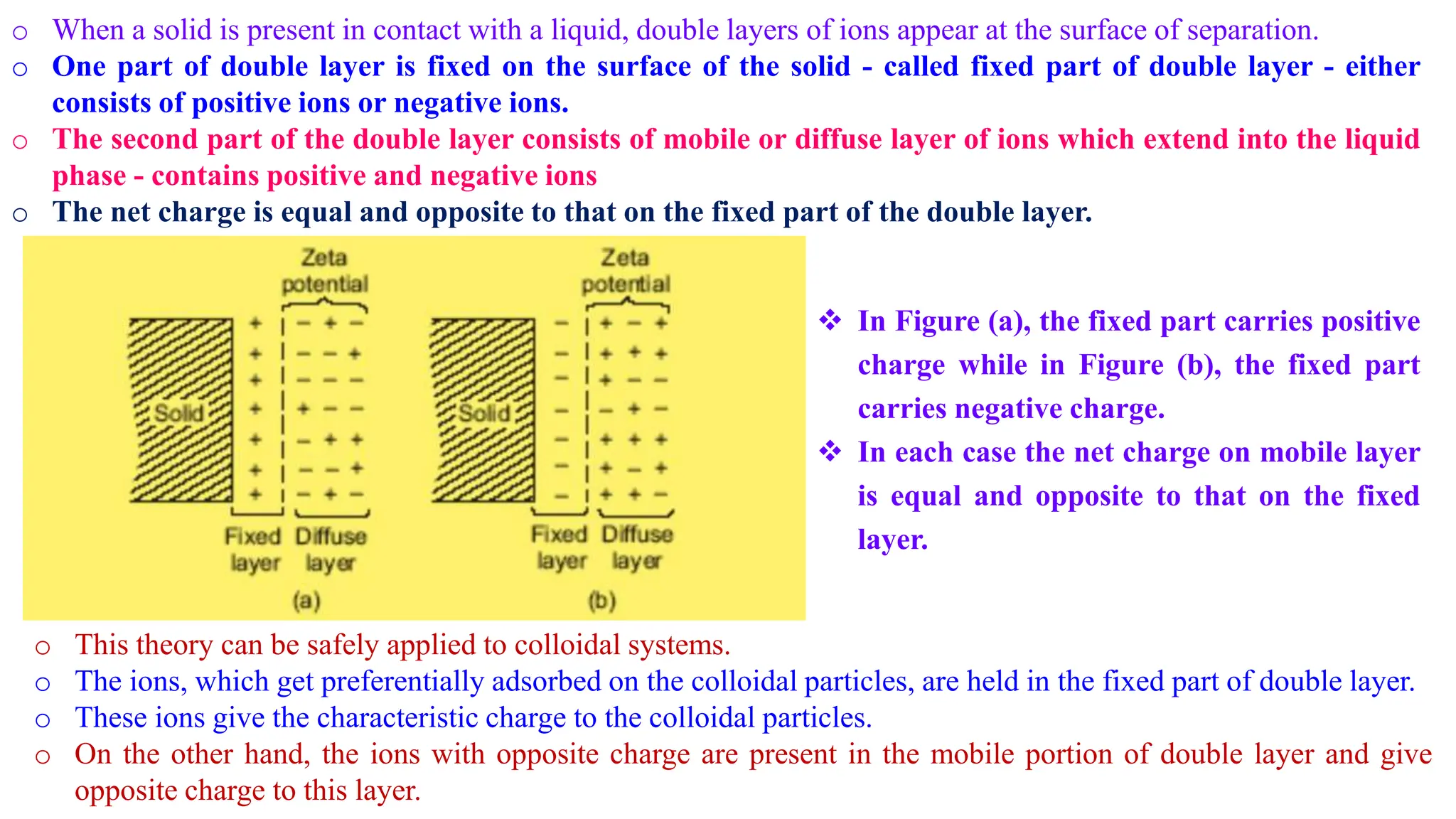
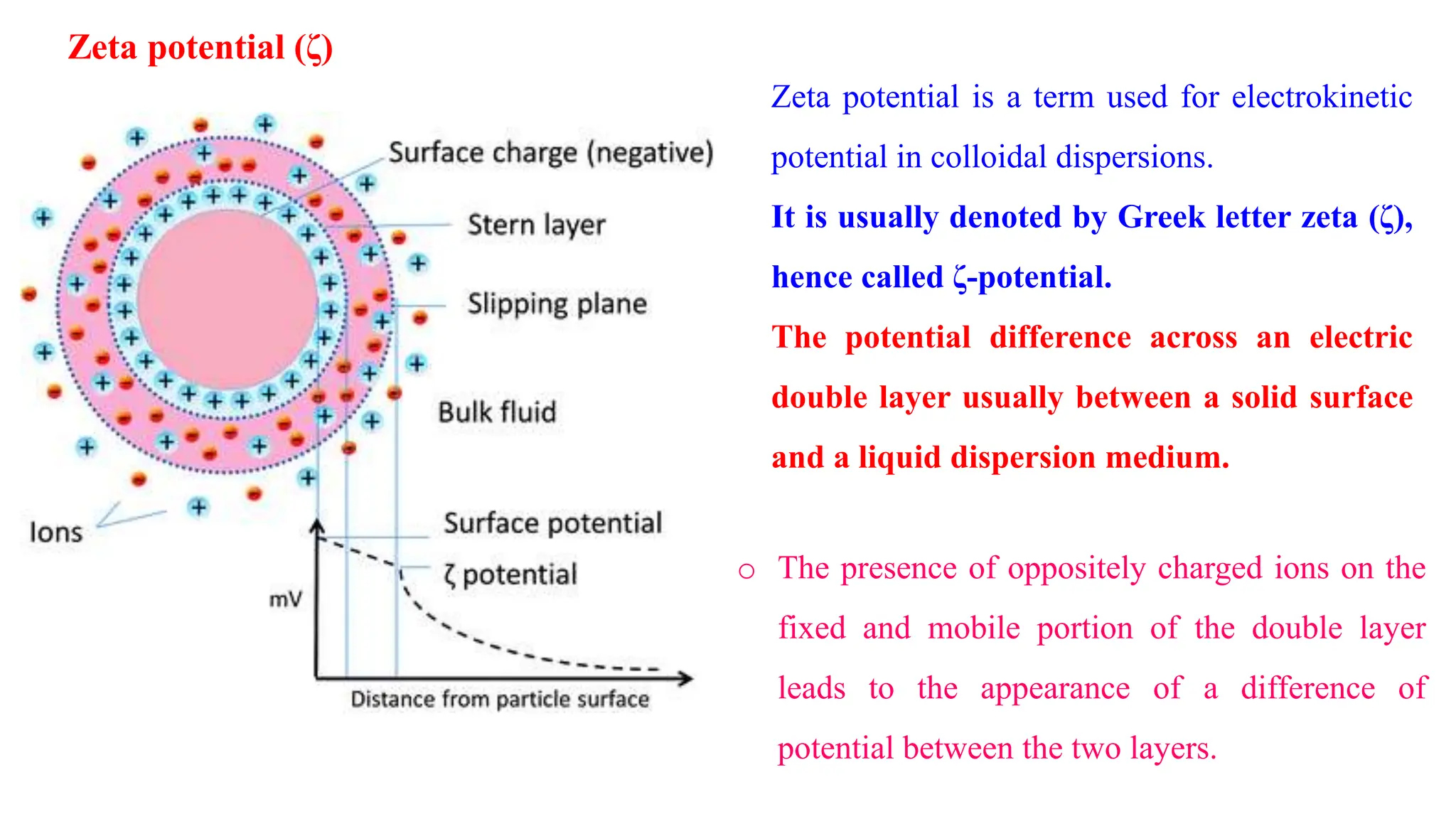
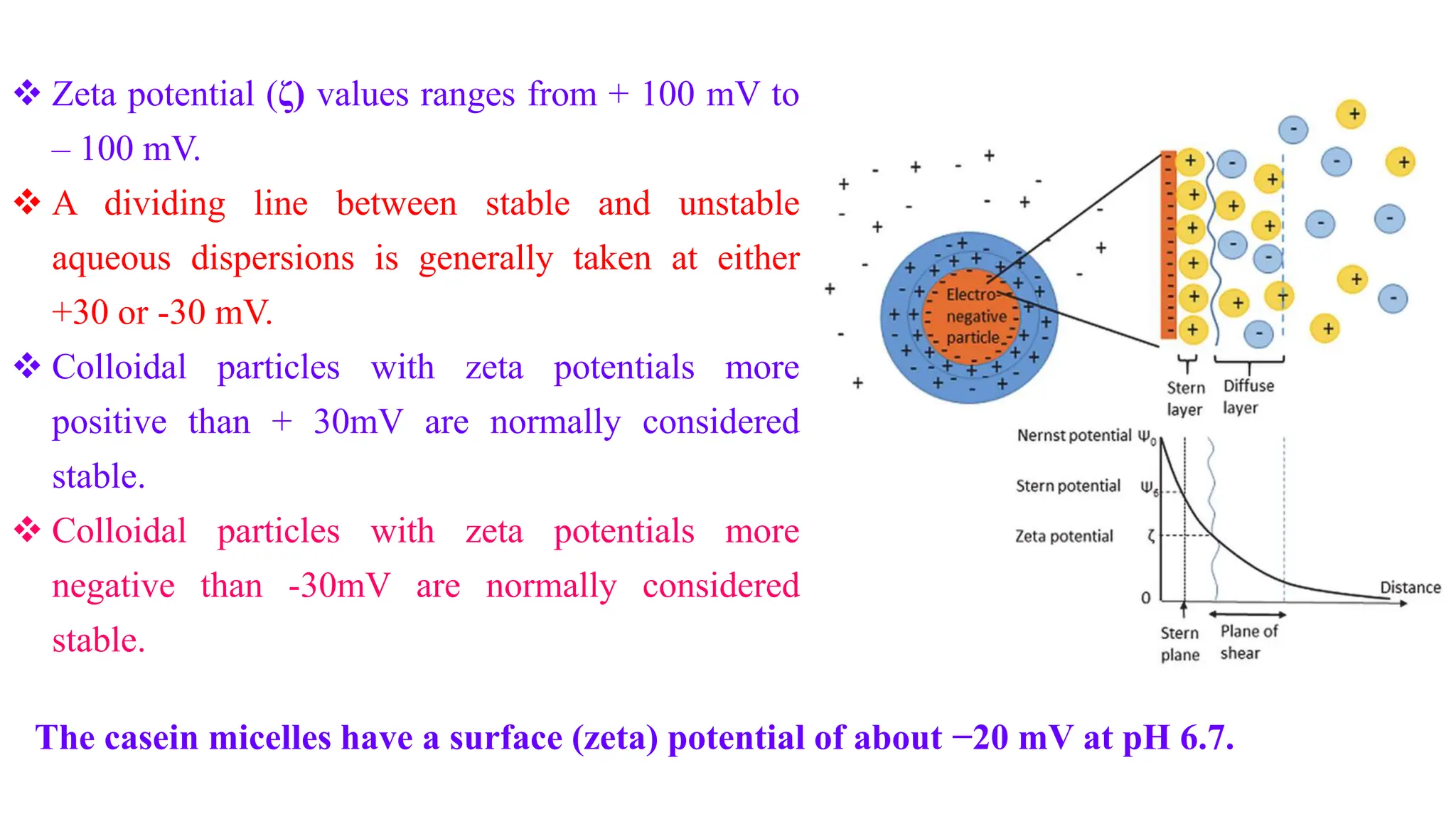
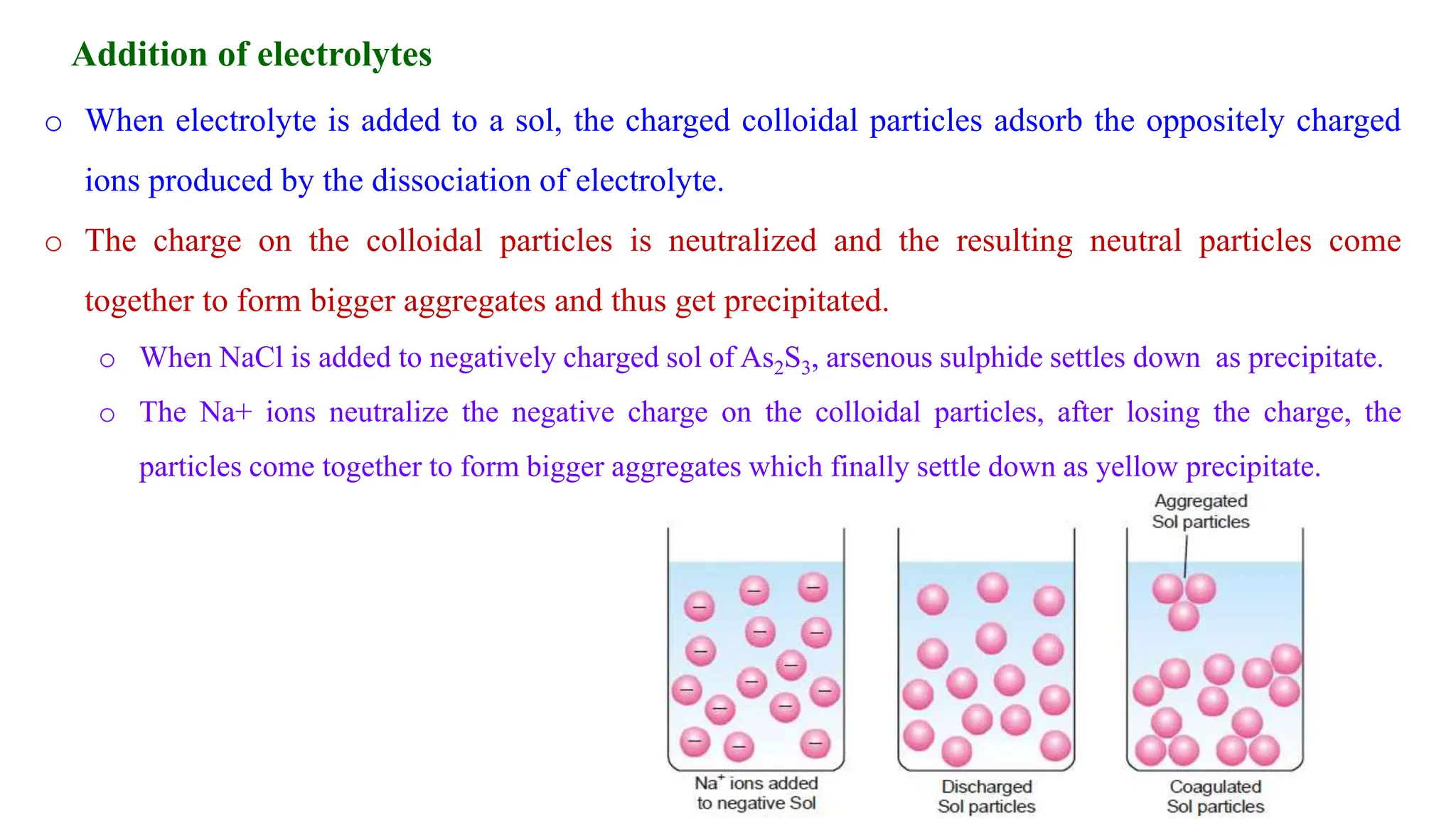
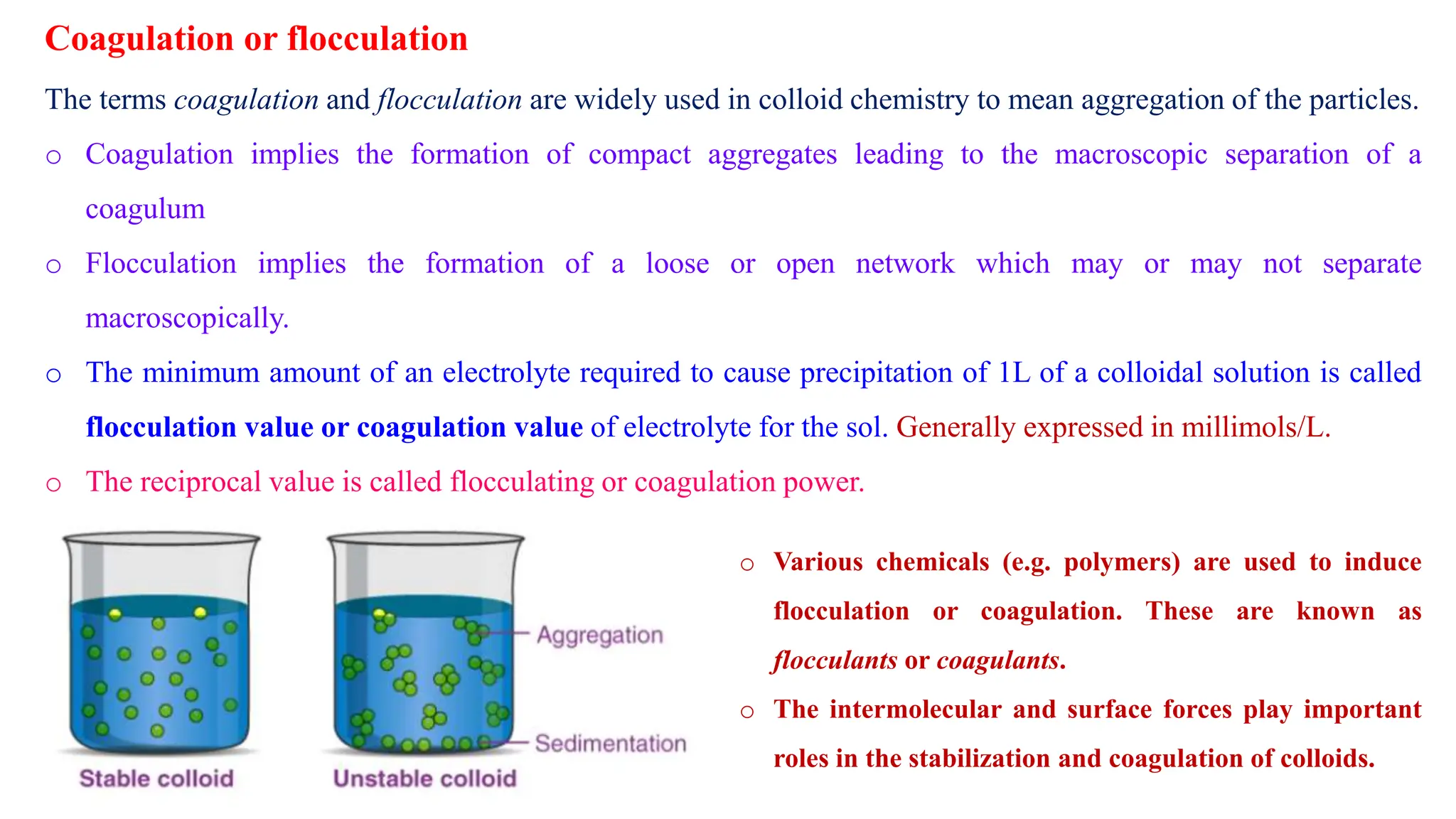
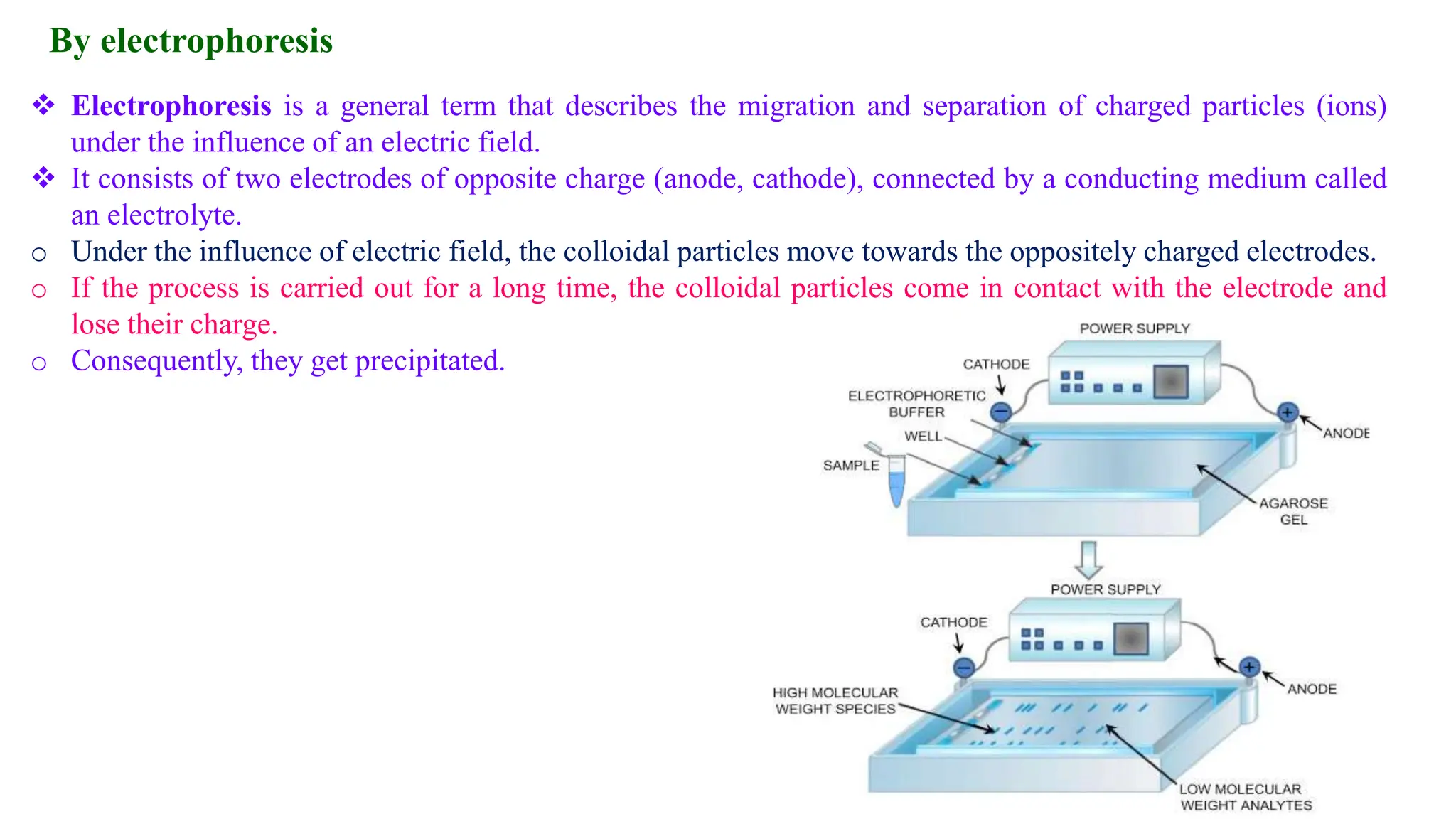
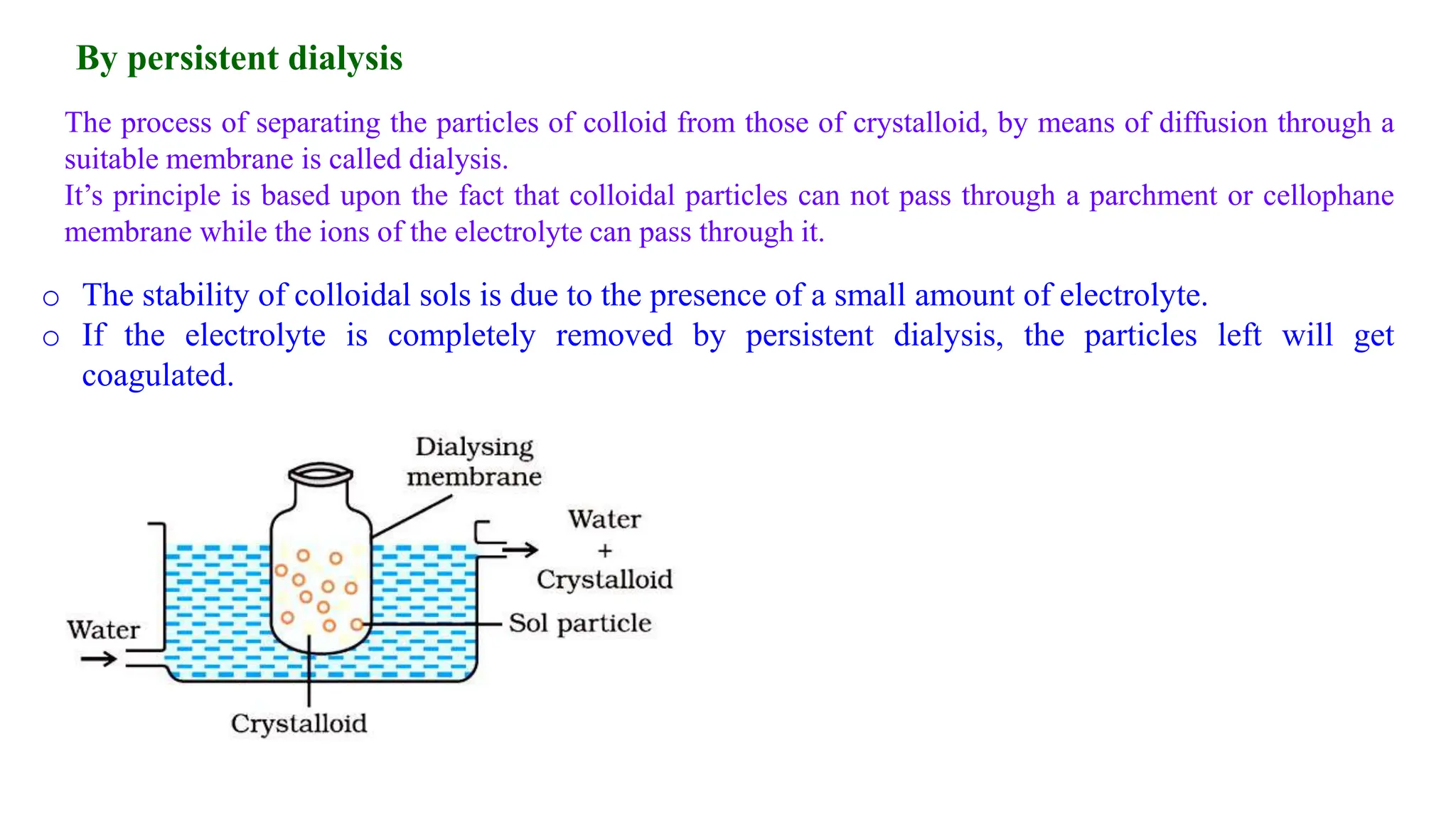
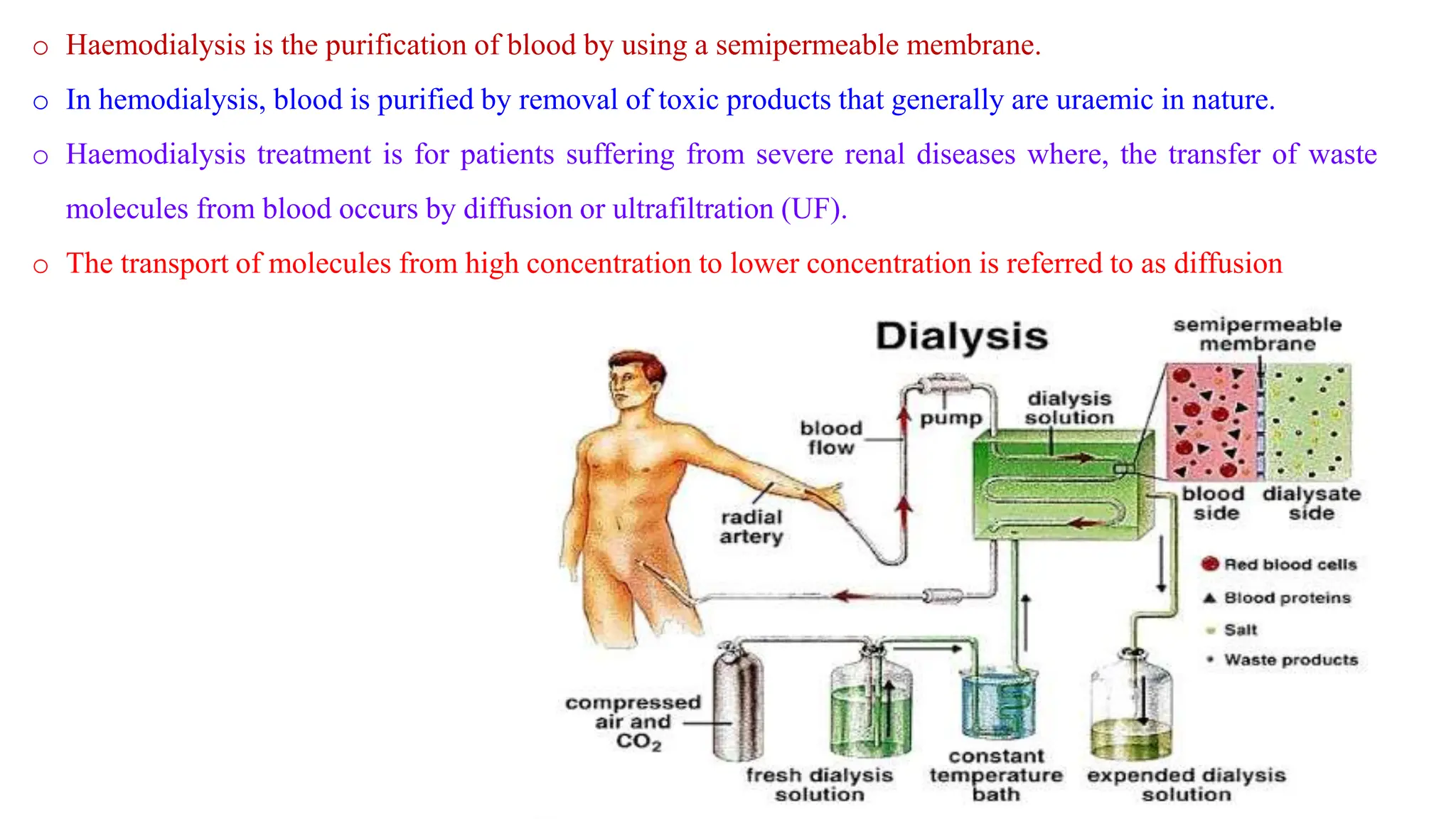
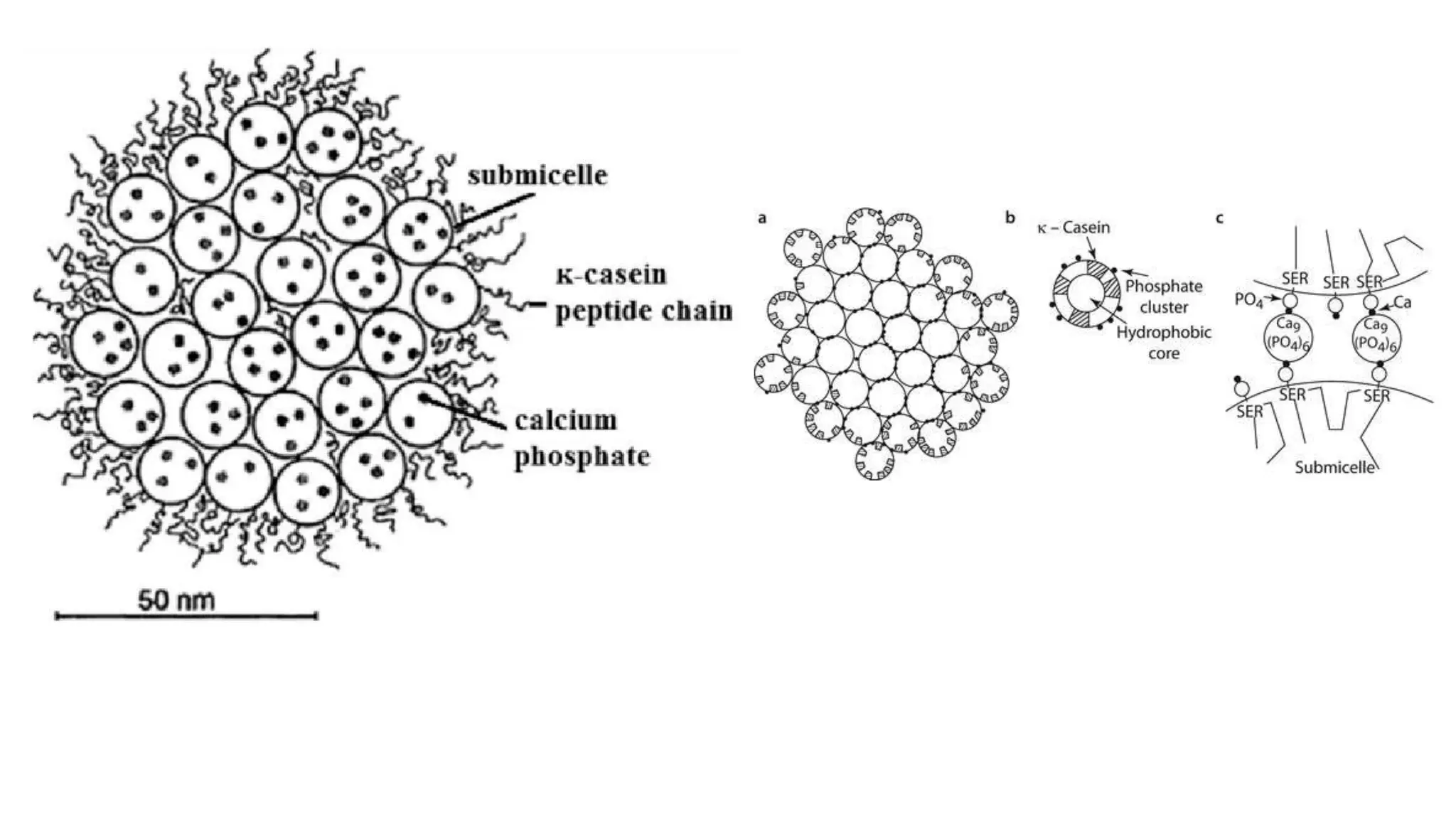
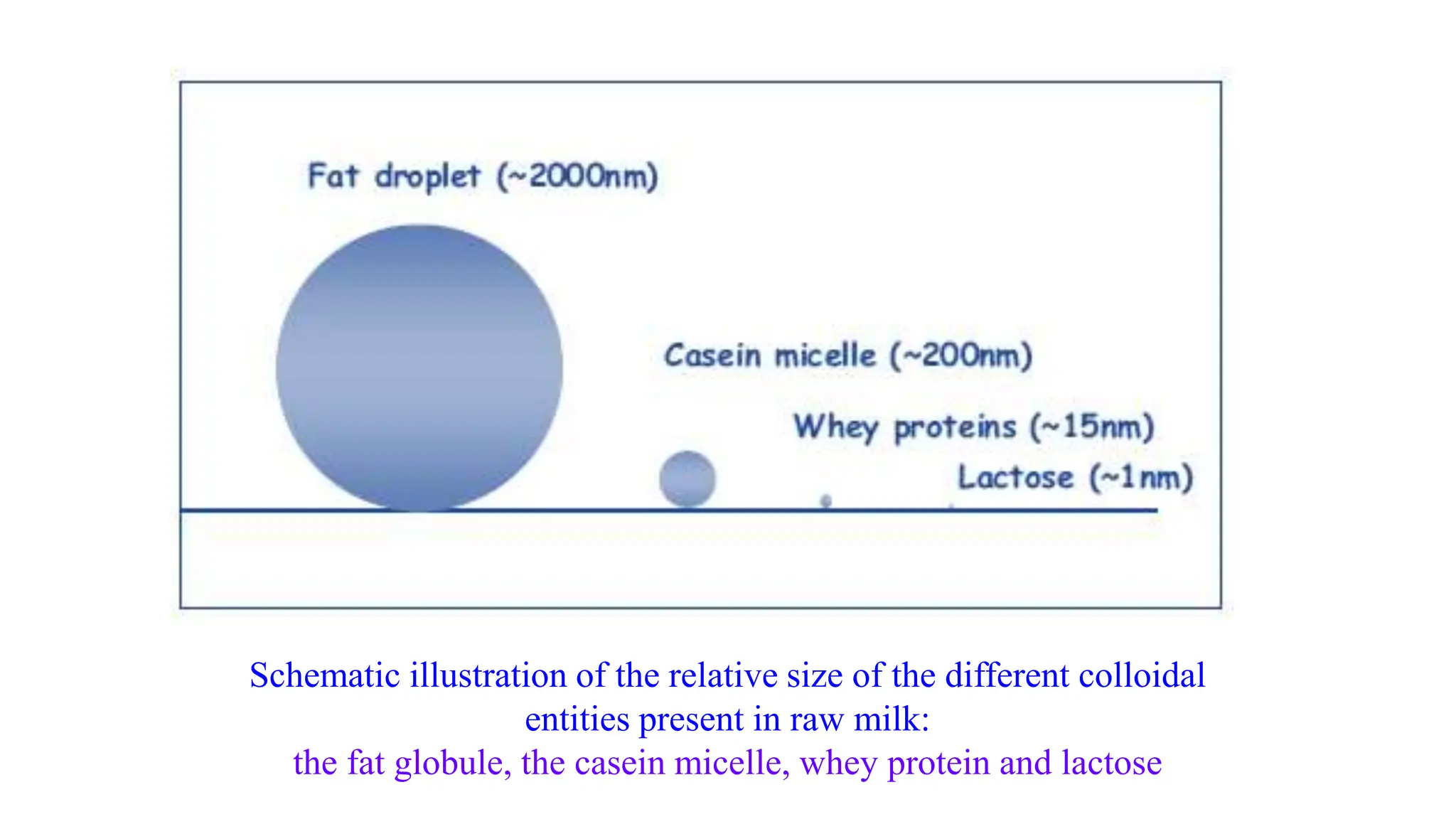
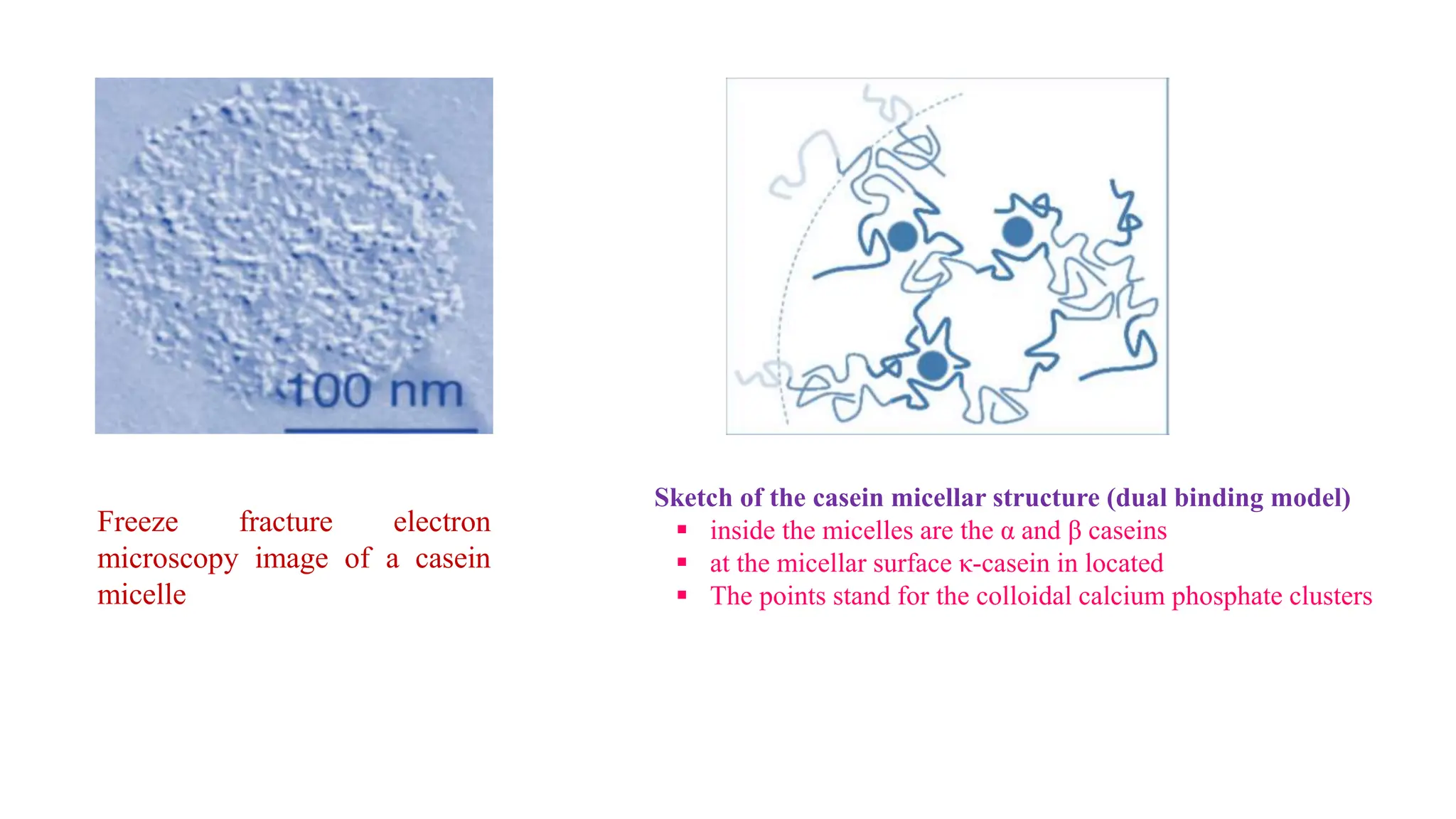
This document discusses colloidal systems and their properties. It begins by defining colloids as mixtures where one substance is divided into minute particles dispersed throughout a second substance. The particles in a colloid are larger than atoms or molecules in solutions, but smaller than particles in suspensions.
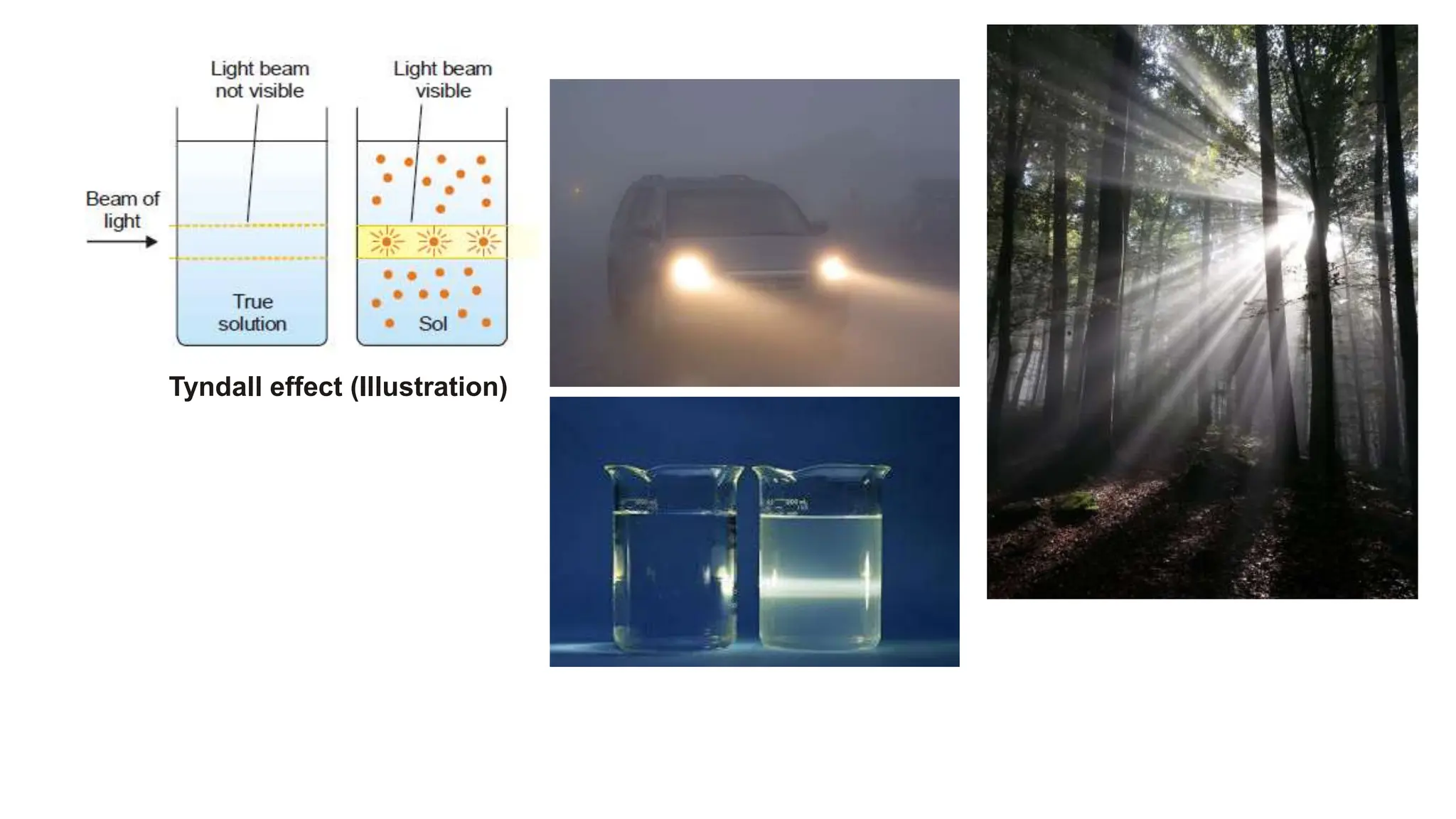
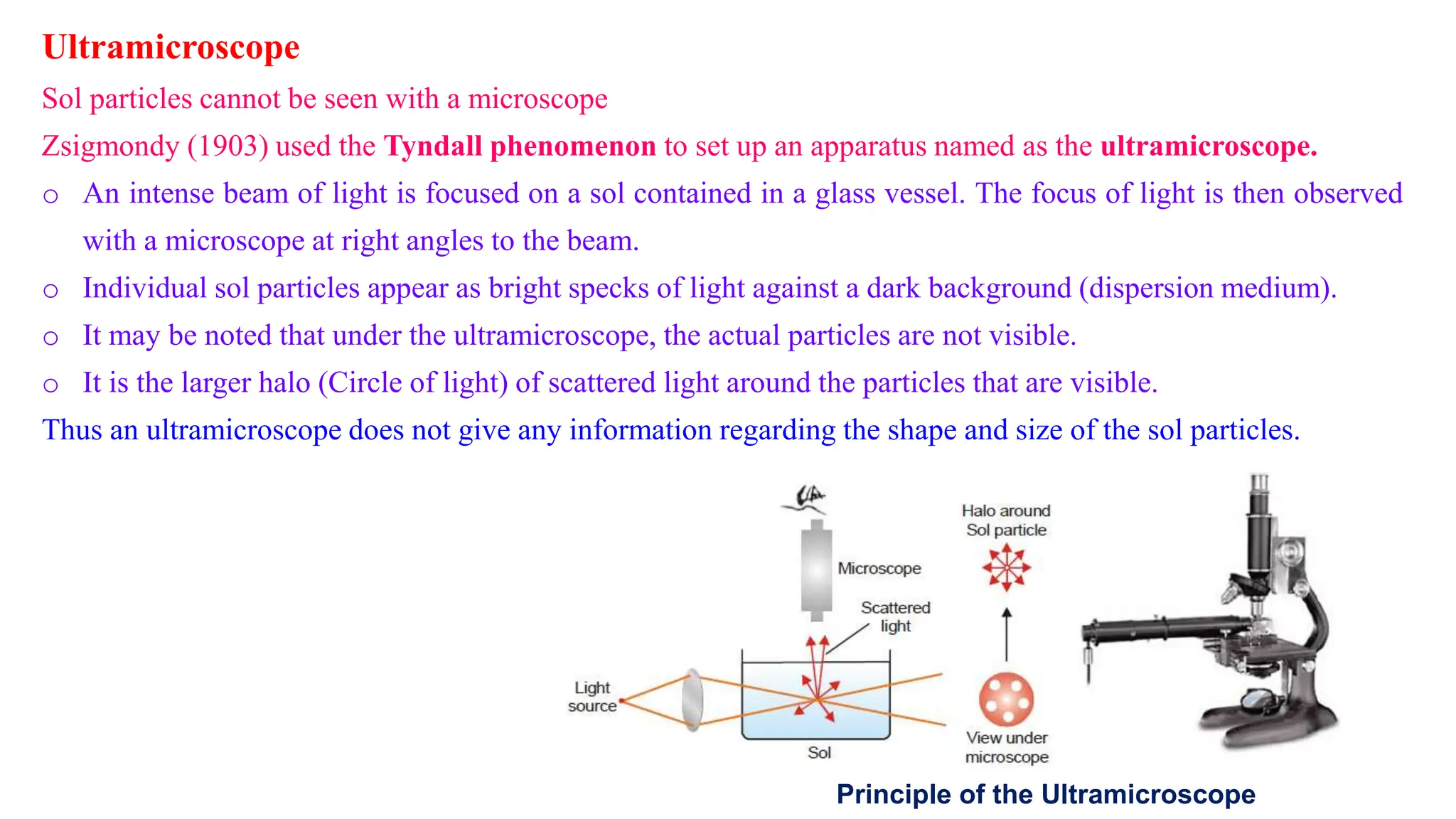
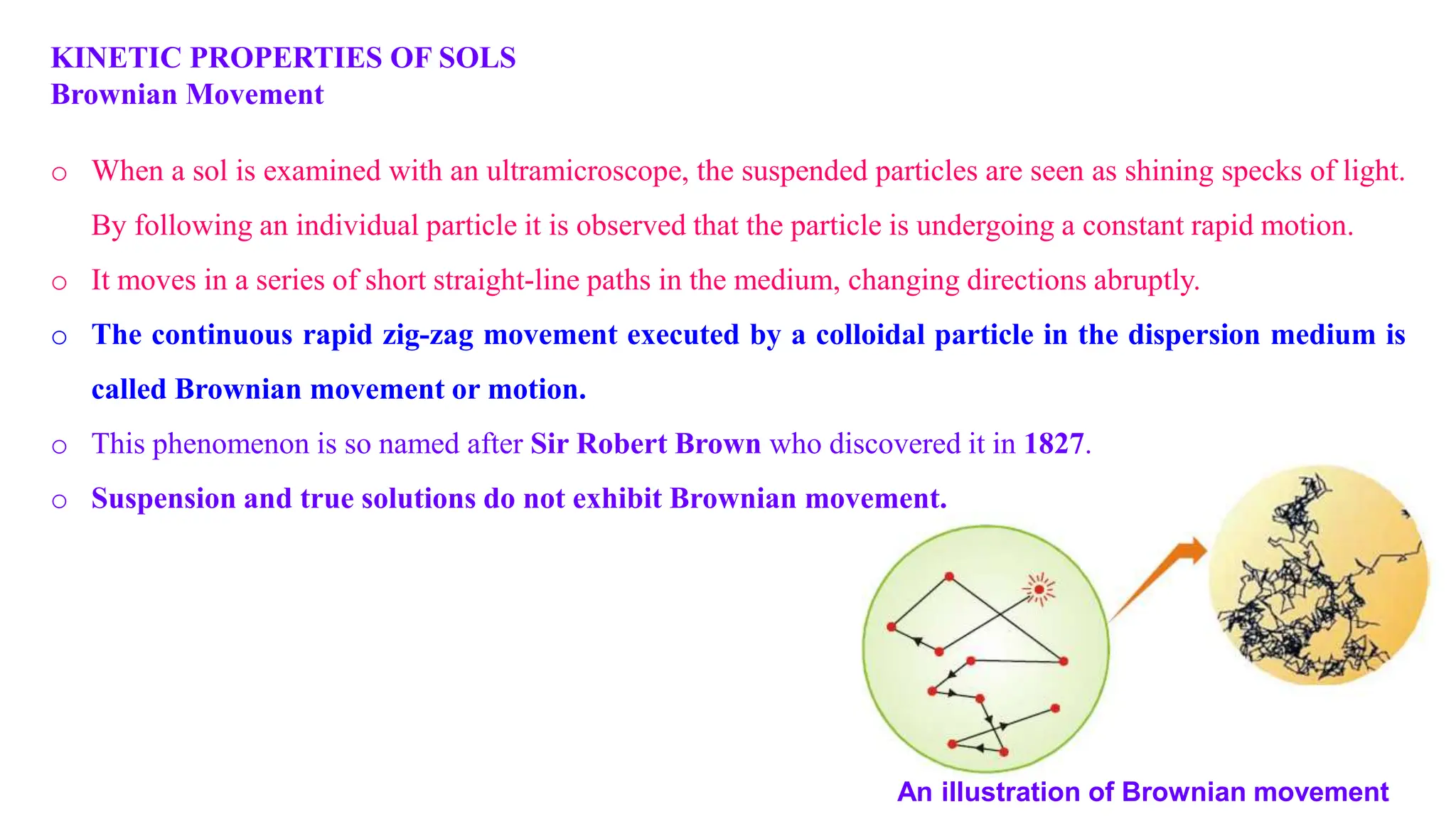
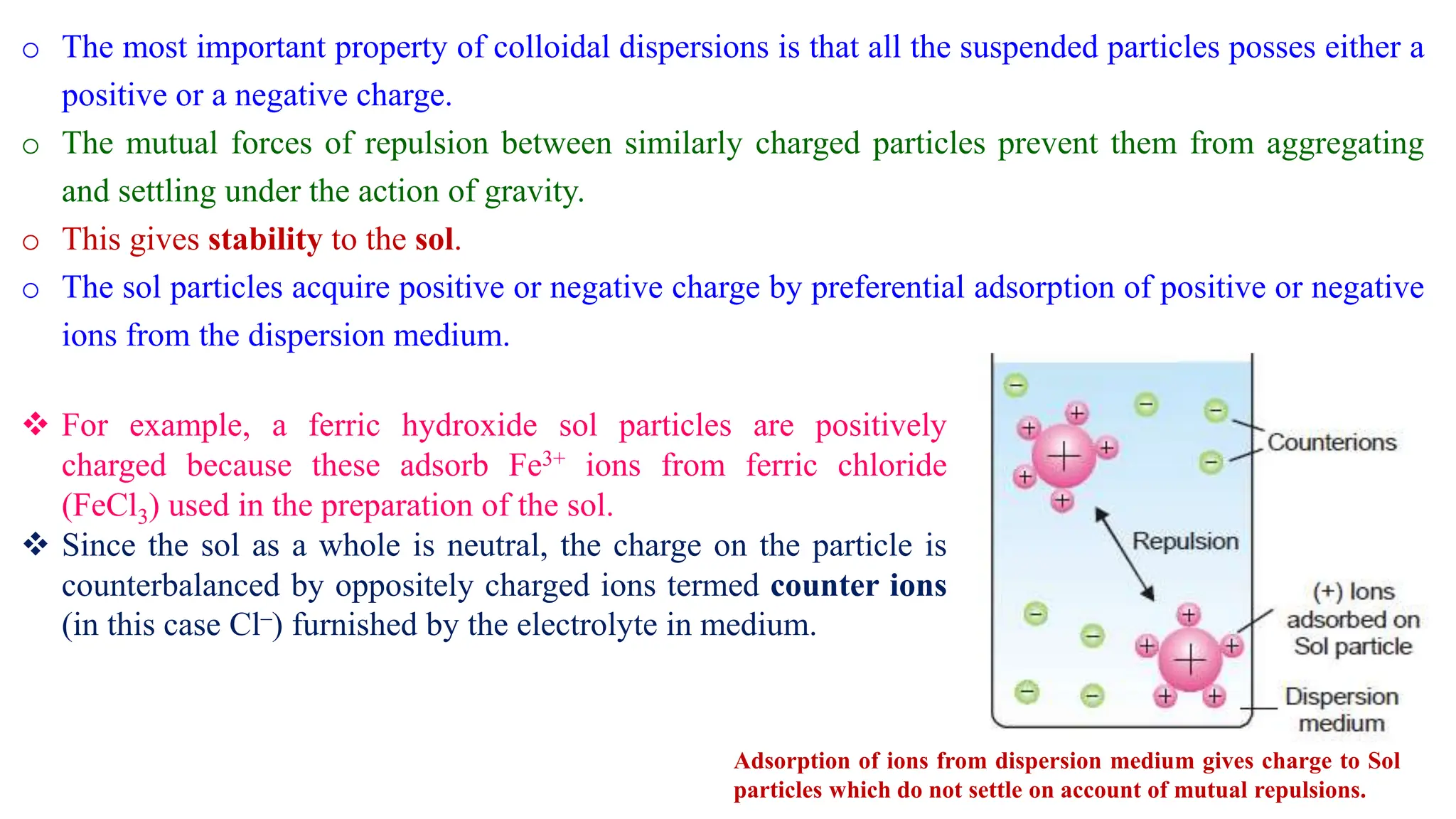
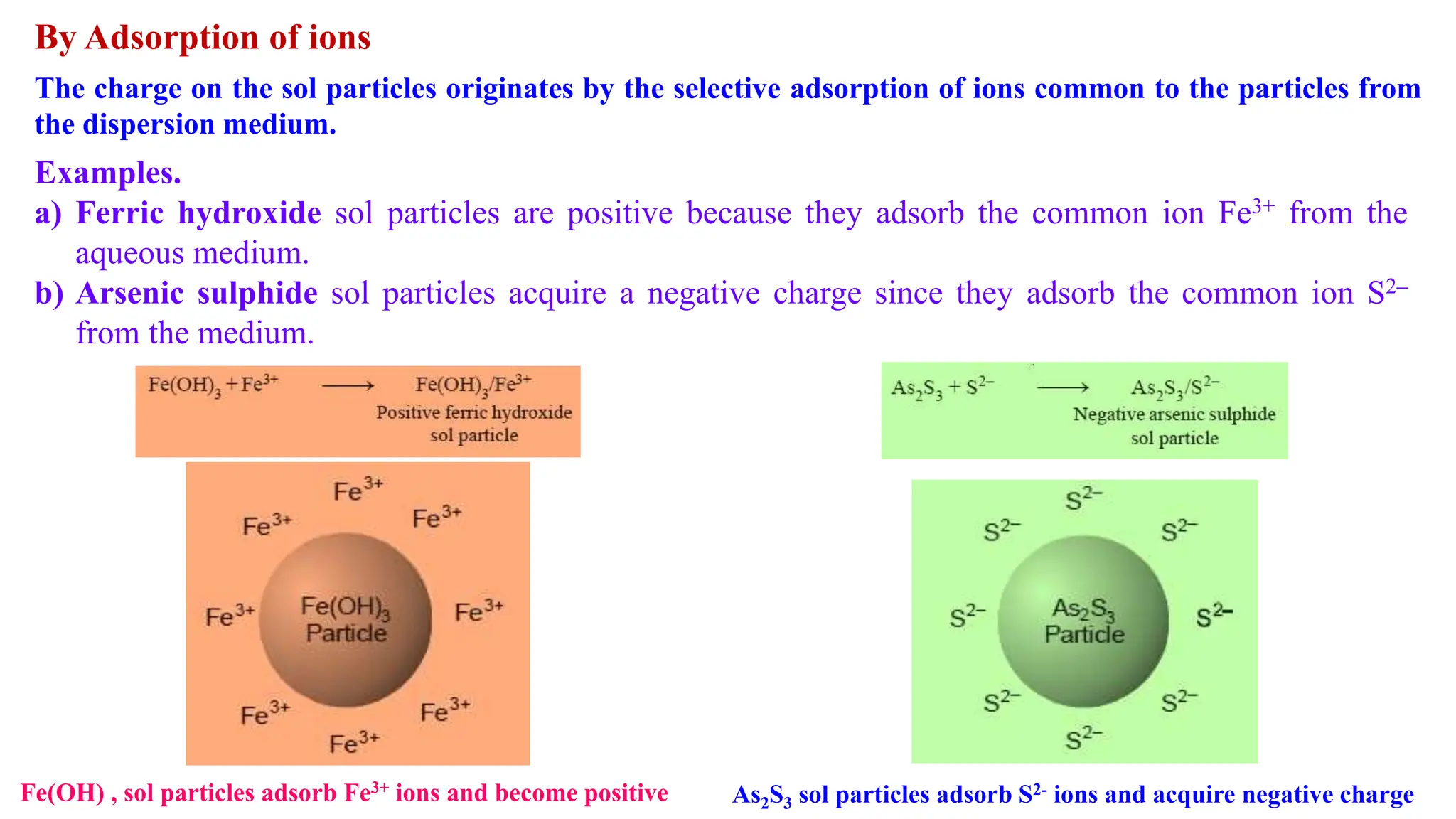
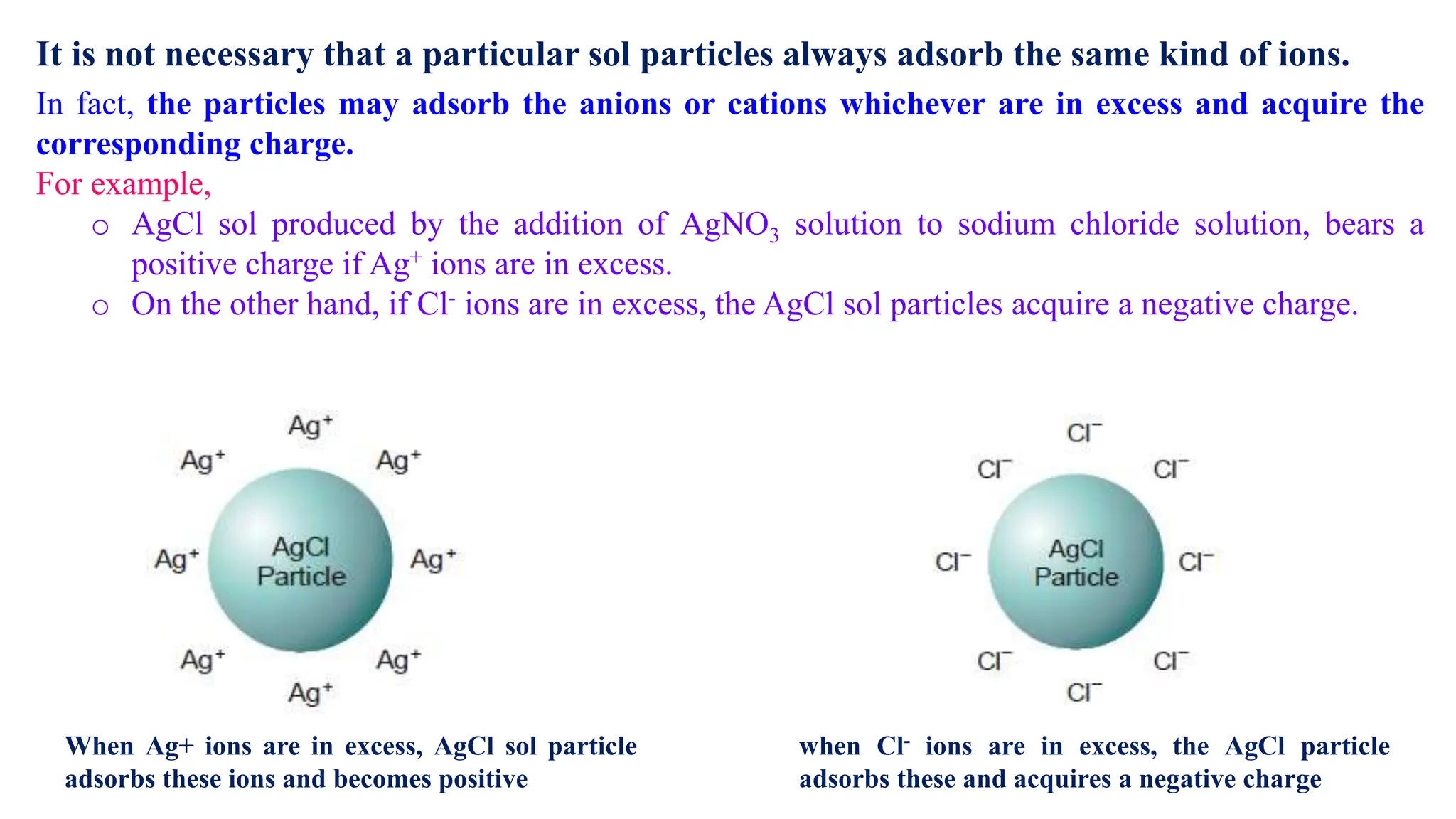
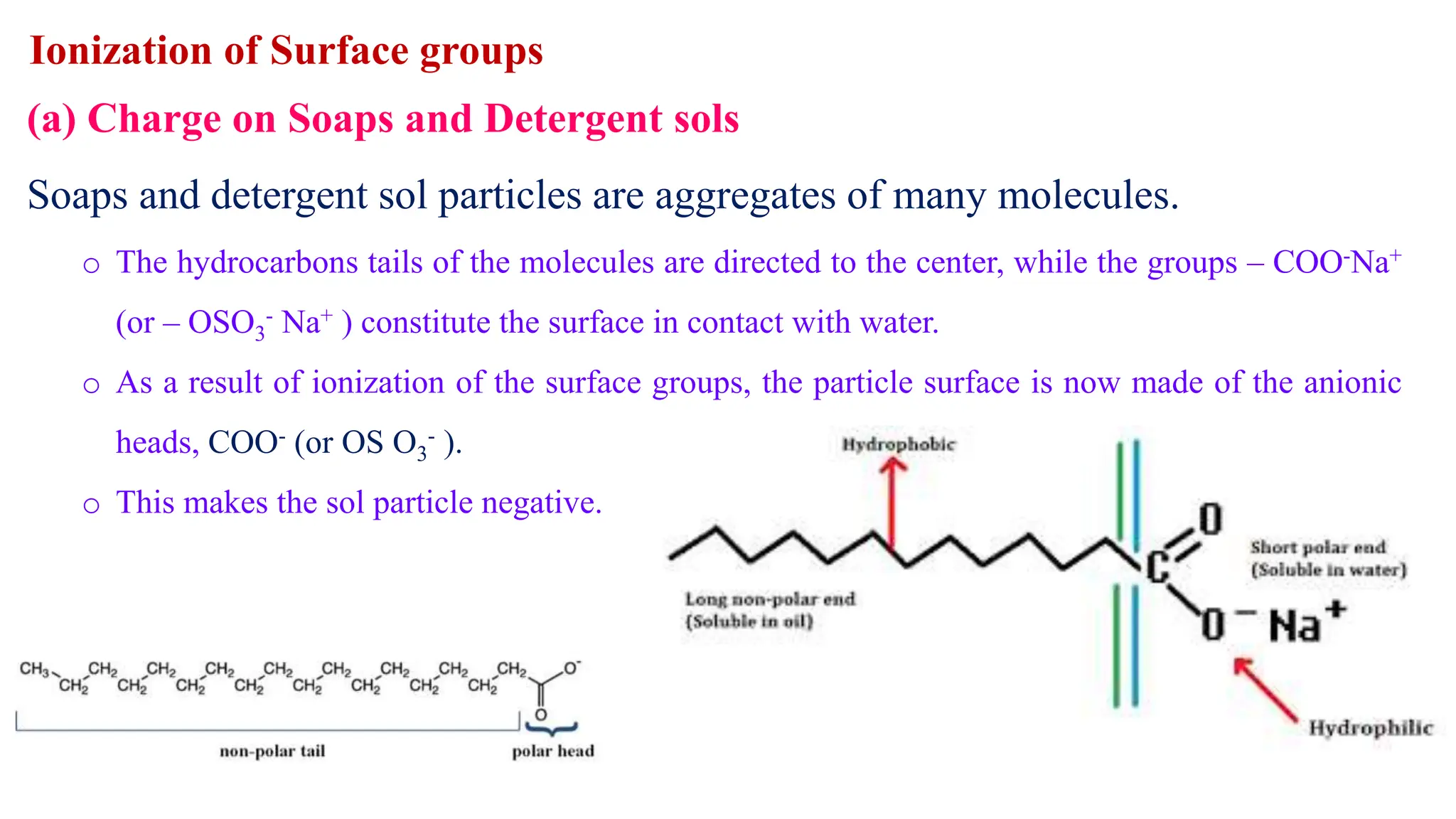
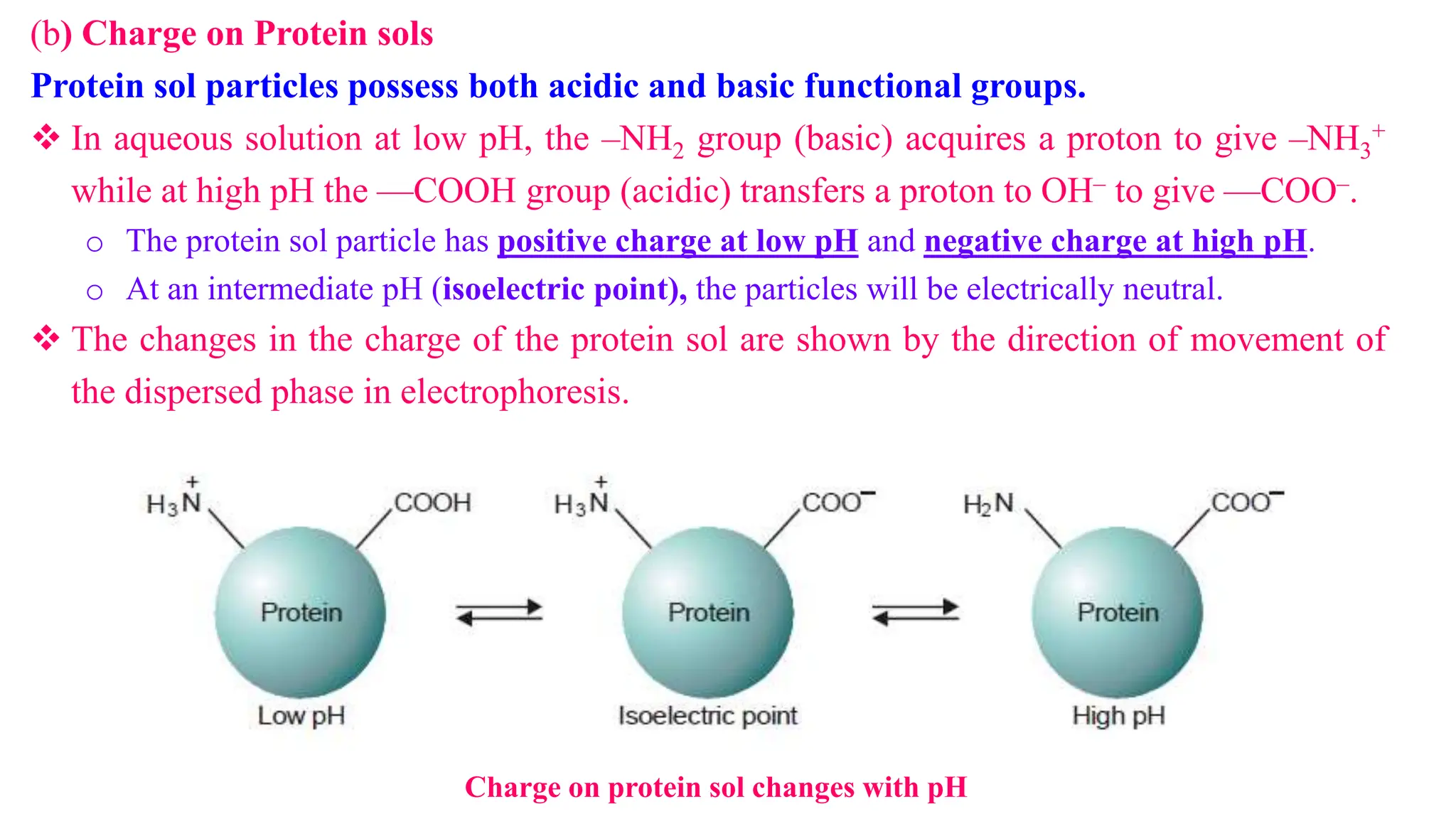
It then discusses some key properties of colloids, including that colloidal particles do not diffuse through membranes, they scatter light and exhibit the Tyndall effect, and they undergo constant random motion called Brownian movement. Colloidal particles also acquire and maintain a net electric charge via preferential adsorption of ions from the dispersion medium. This charge prevents the particles from aggregating due to electrical repulsions between them.
In