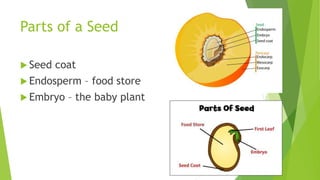
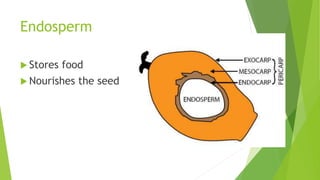
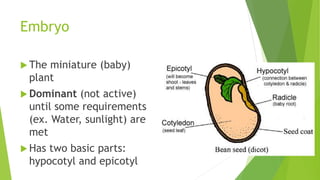
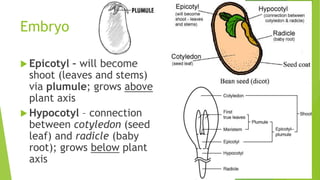
The document outlines a lesson on seeds, detailing their structure, including the seed coat, endosperm, and embryo, as well as the seed germination process. It highlights the importance of water, oxygen, and temperature in facilitating seed germination, where the embryonic plant grows and eventually becomes a seedling. The lesson also includes an assignment and a reference to additional sources.