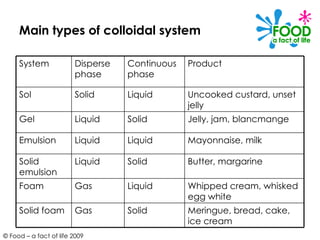
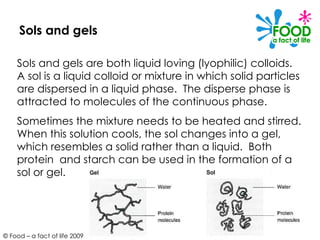
Colloidal systems give structure, texture and mouthfeel to many foods. They include gels, sols, foams and emulsions. Gels and sols both involve solid particles dispersed in liquid, with gels forming solid-like networks and sols remaining liquid. Emulsions disperse either oil or water droplets throughout another liquid using emulsifiers. Foams incorporate gas bubbles within a liquid or solid through mechanical agitation, as seen with whipped egg whites. These colloidal systems play important functional roles in foods like ice cream, mayonnaise and bread.