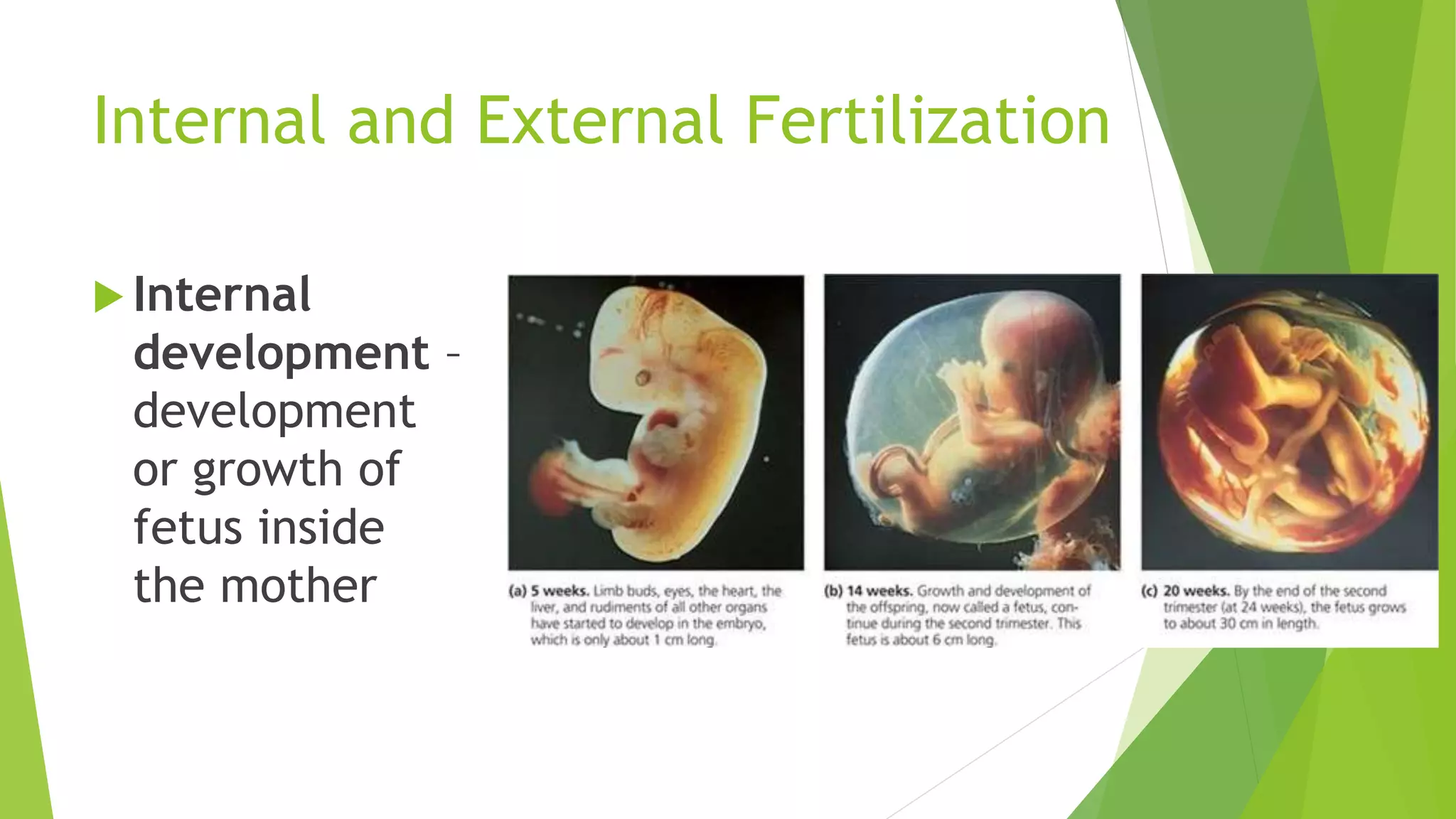
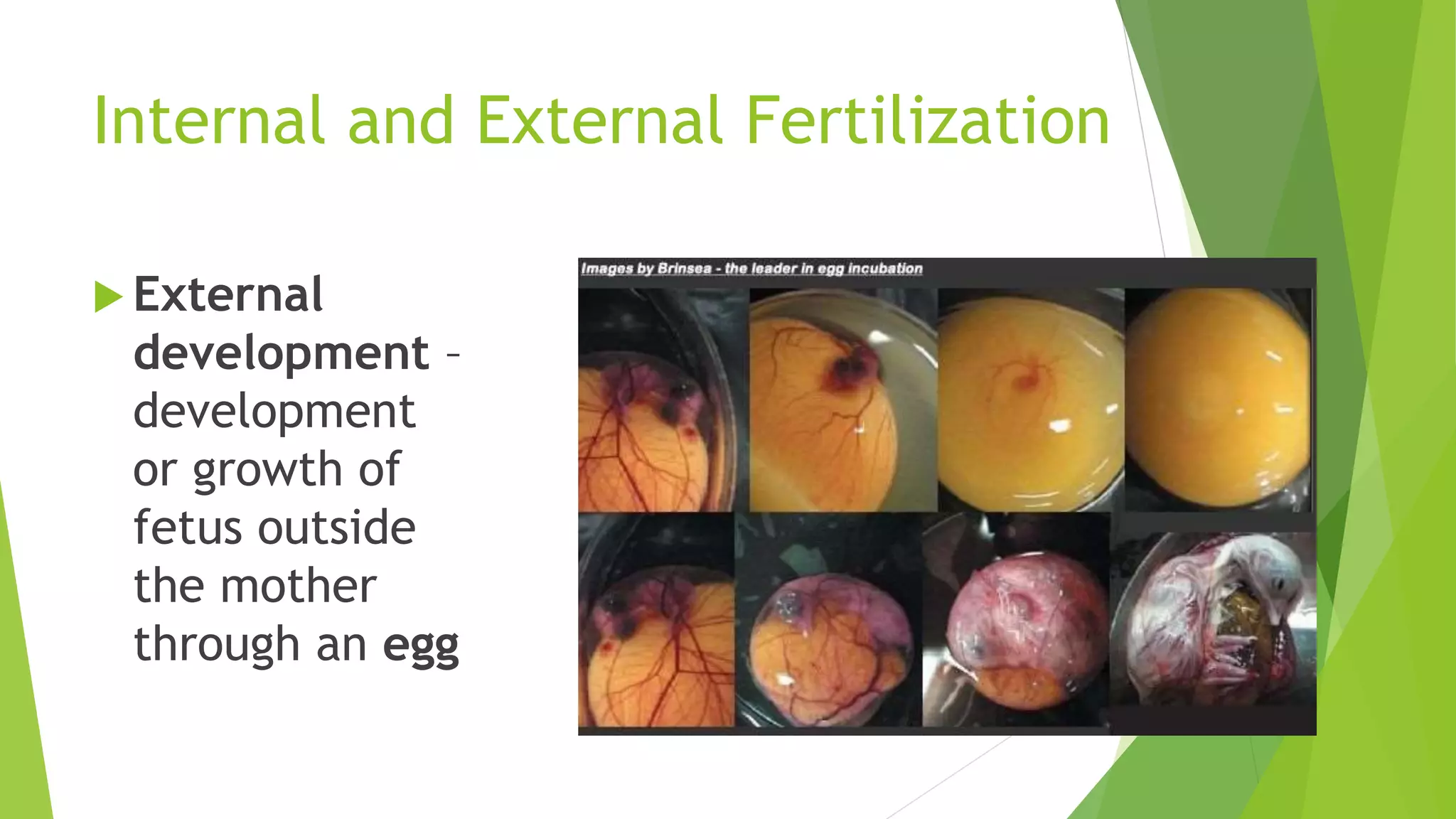
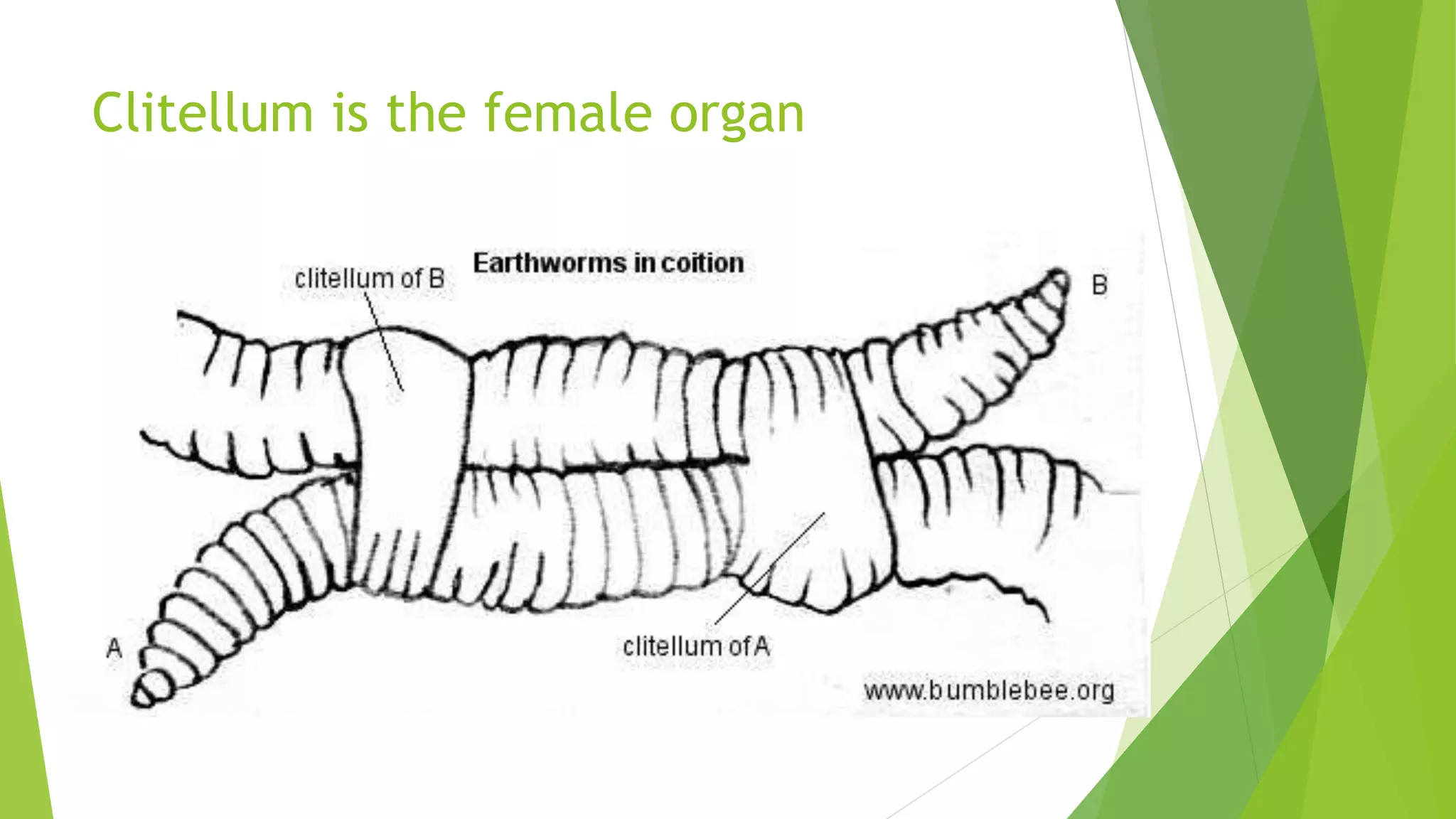
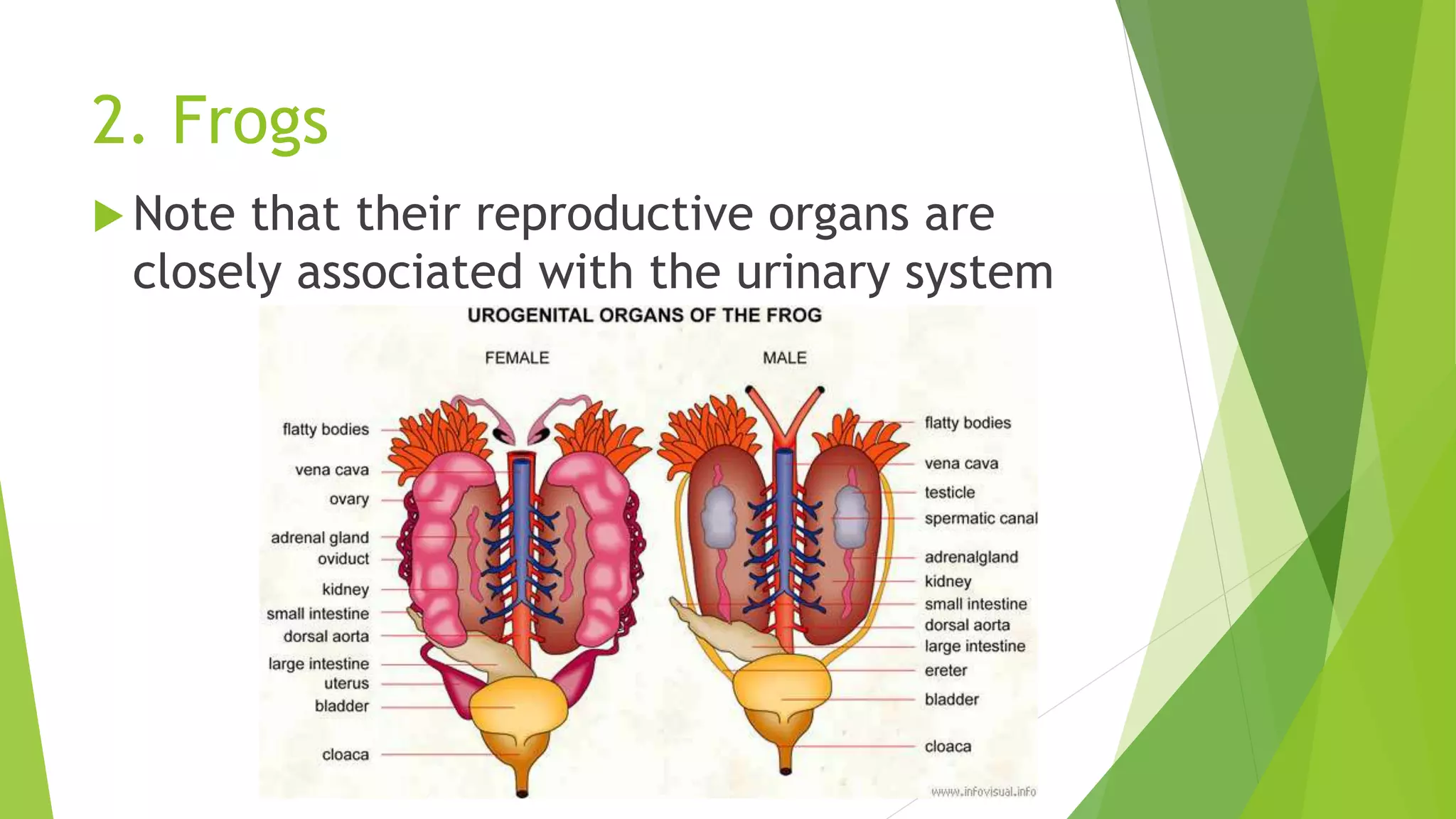
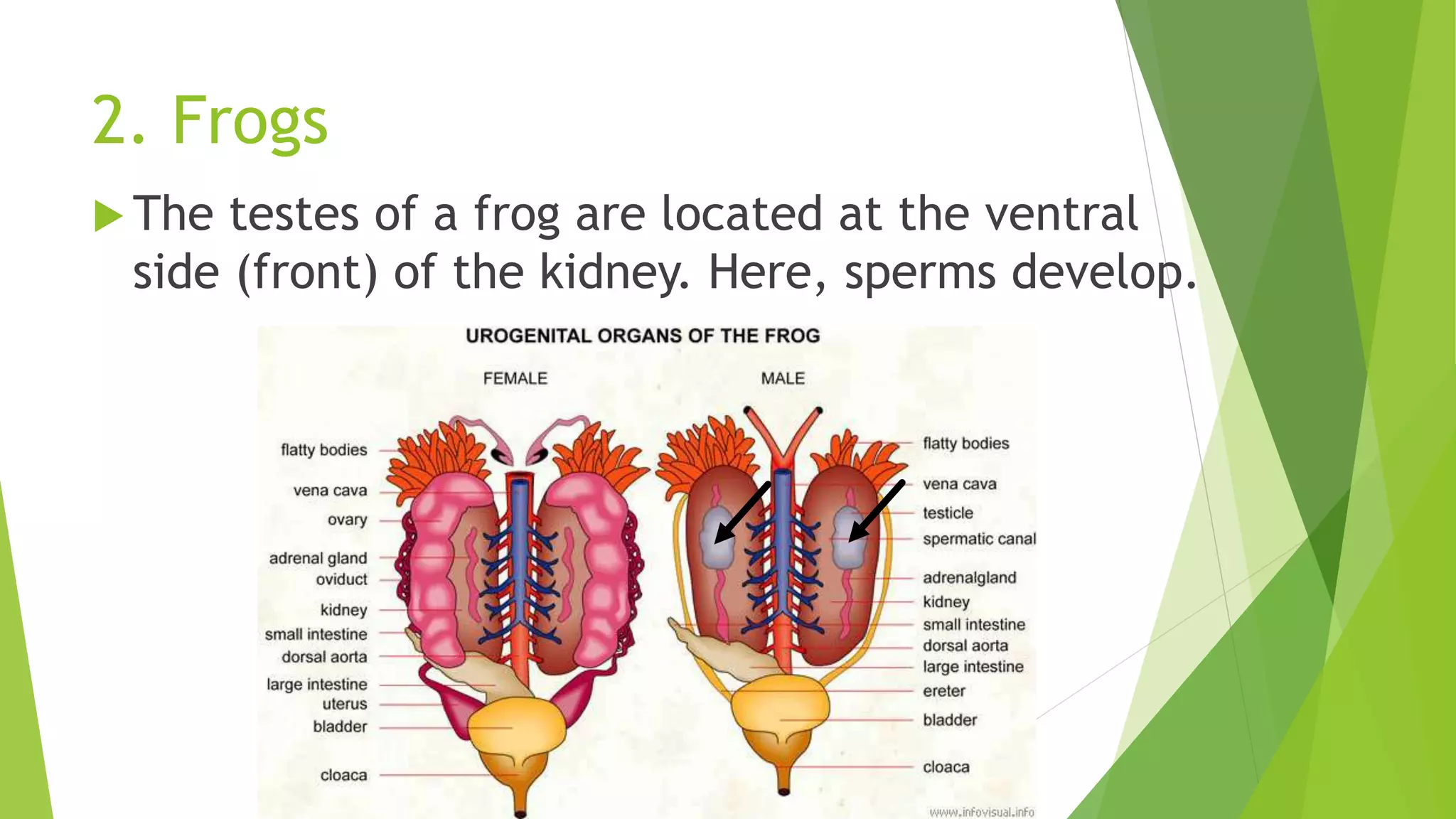
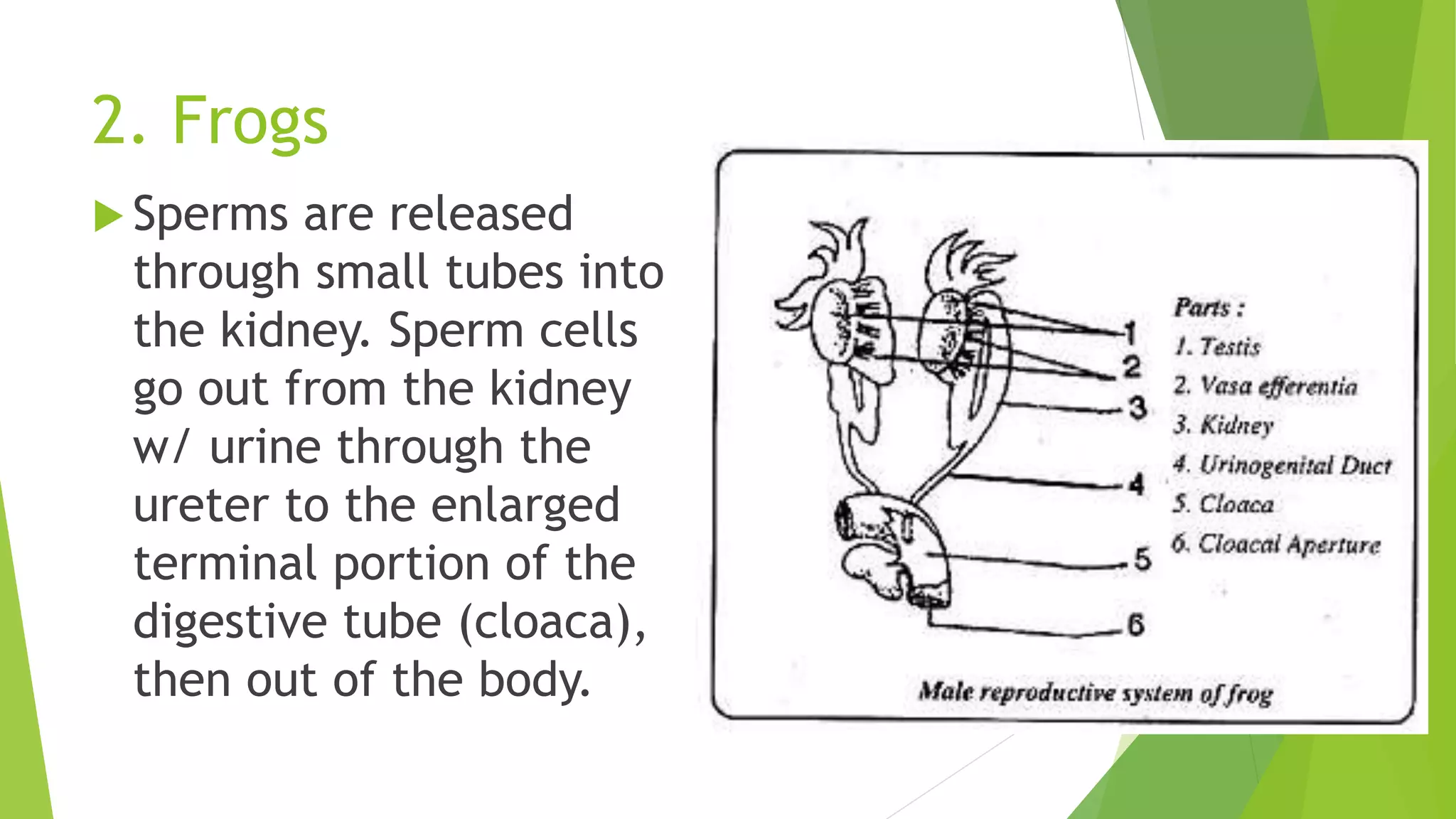
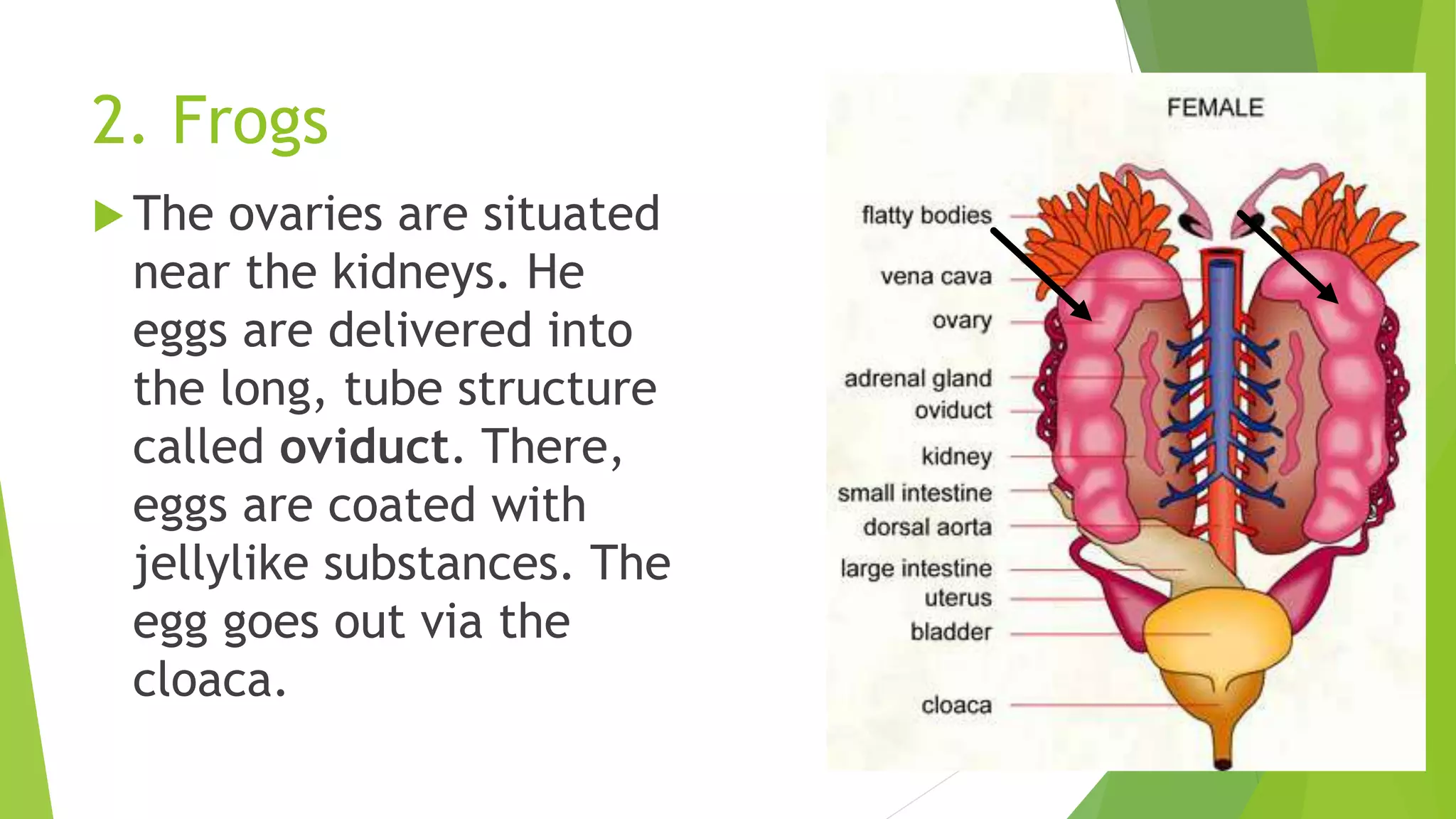
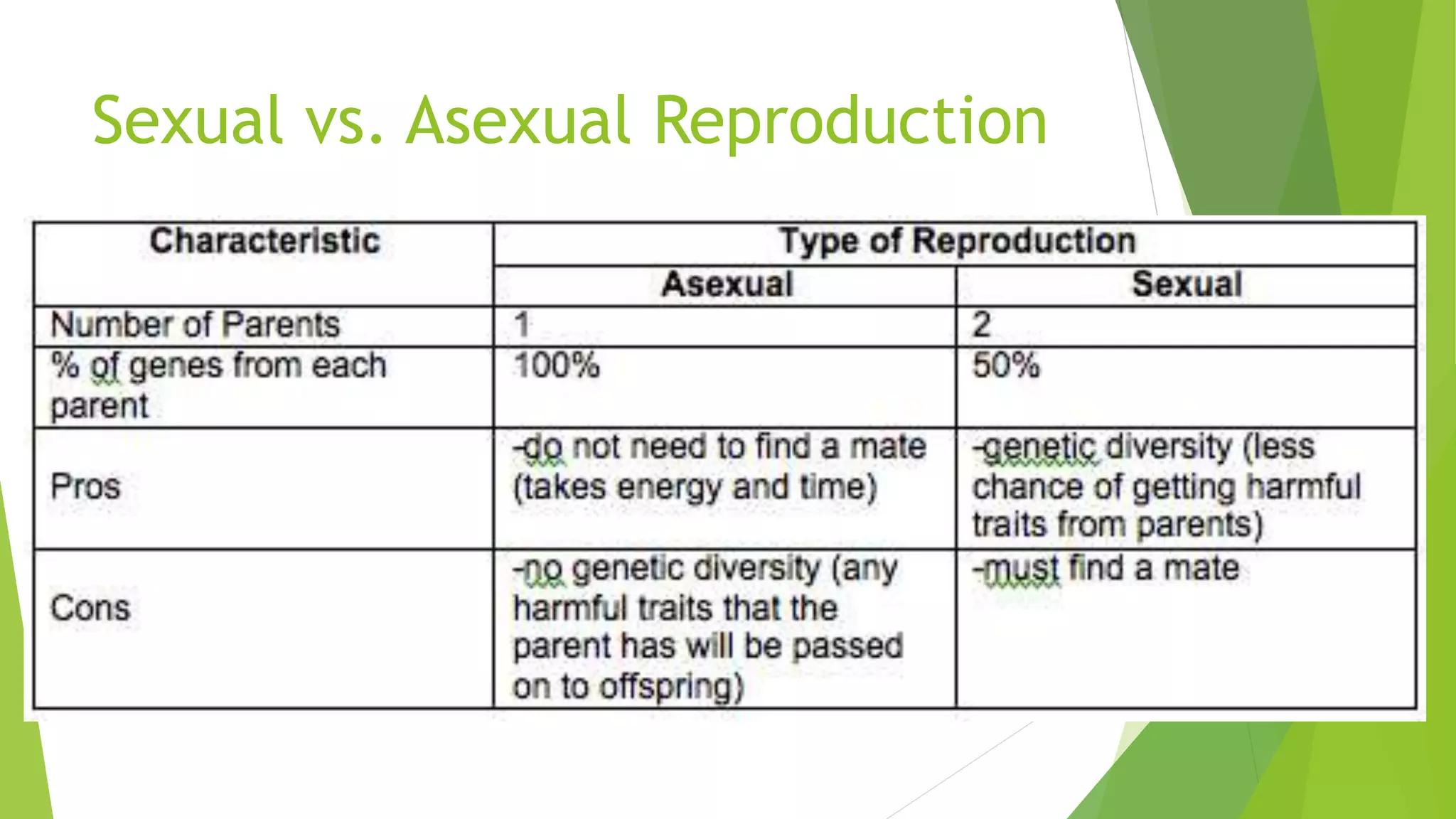
This document discusses sexual reproduction in animals, covering internal and external fertilization and development. It provides examples from different animal groups, including tapeworms, earthworms, frogs, and birds, detailing their reproductive processes. Additionally, it contrasts sexual reproduction with asexual reproduction and includes related activities and assignments.