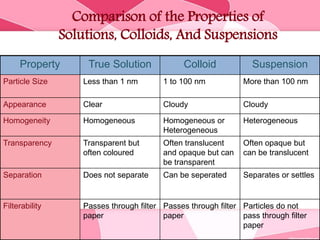
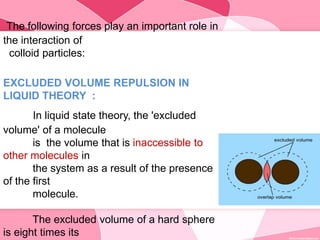
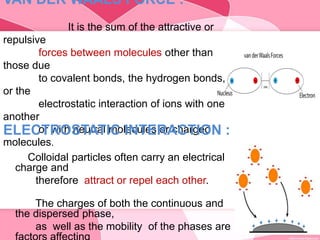
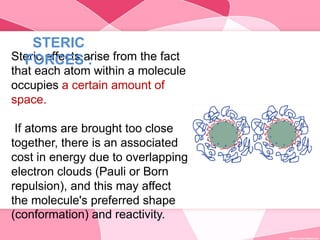
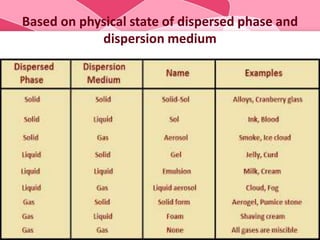
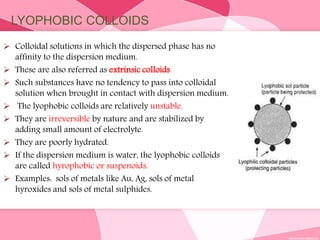
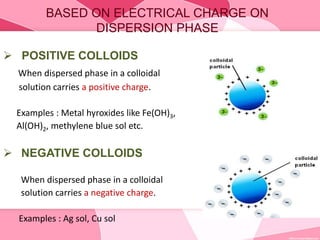
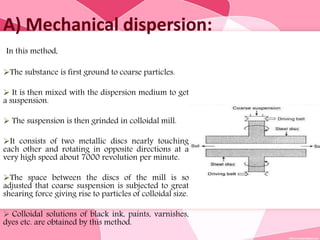
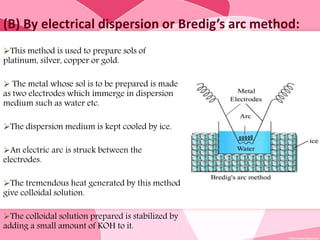
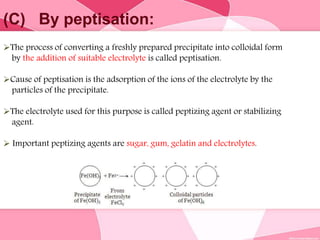
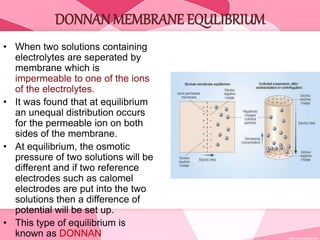
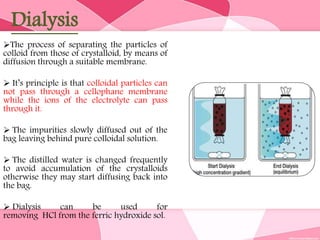
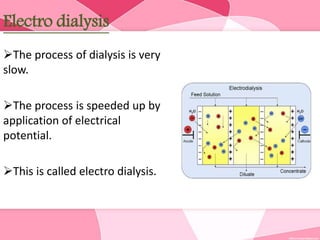
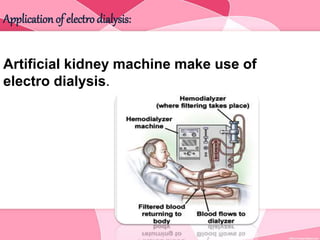
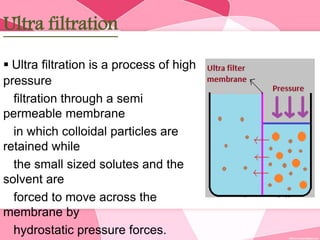
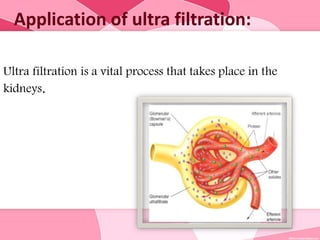
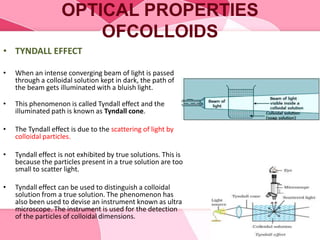
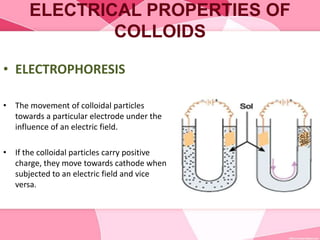
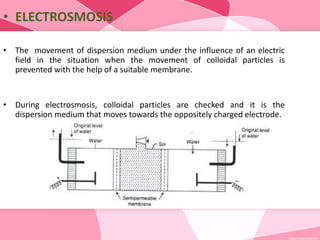
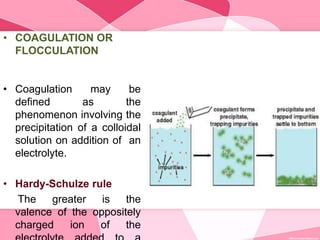
Colloids are substances microscopically dispersed throughout another substance. The dispersed particles range in size from 1-100 nm. Colloids exhibit properties between true solutions and suspensions due to their intermediate particle size. They are able to pass through filters but not semipermeable membranes. Common examples include milk, fog, mayonnaise and paints. Colloids can be classified based on factors like the physical state of the phases, the interaction between the phases, the size and nature of dispersed particles, and the electrical charge on particles. They are purified using techniques like dialysis, electrodialysis, and ultrafiltration which separate colloidal particles from dissolved substances.