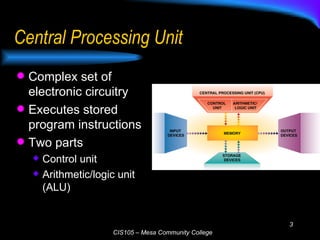
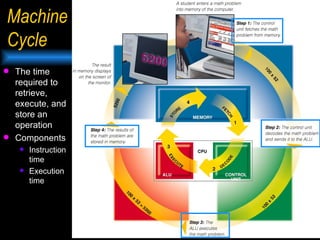
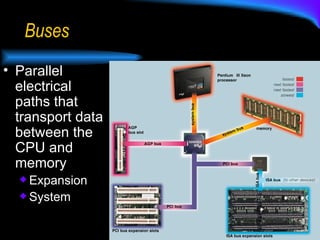
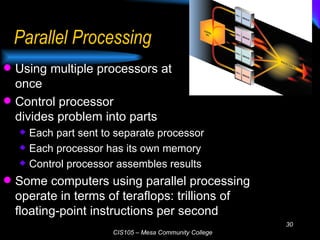
The document discusses the central processing unit (CPU) and its components. The CPU contains an arithmetic logic unit and a control unit which work together to execute stored program instructions. It retrieves instructions and data from memory, decodes and executes the instructions by performing arithmetic and logical operations, and stores the results back in memory. Modern CPUs use techniques like reduced instruction sets, pipelining, and parallel processing to increase their speed and processing power.