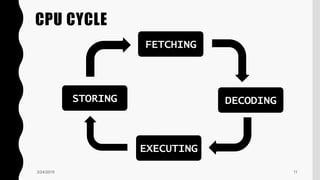
The document discusses the central processing unit (CPU). It describes the CPU as the multipurpose, programmable component of a computer that interprets instructions and performs logical and arithmetic operations. The CPU is composed of an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that performs calculations, a control unit (CU) that directs signals between memory and the ALU, and register arrays that temporarily store processed data. Factors like clock rate, memory size, and instruction set complexity can impact a CPU's processing speed. The CPU executes a cycle of fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, executing operations, and storing results.