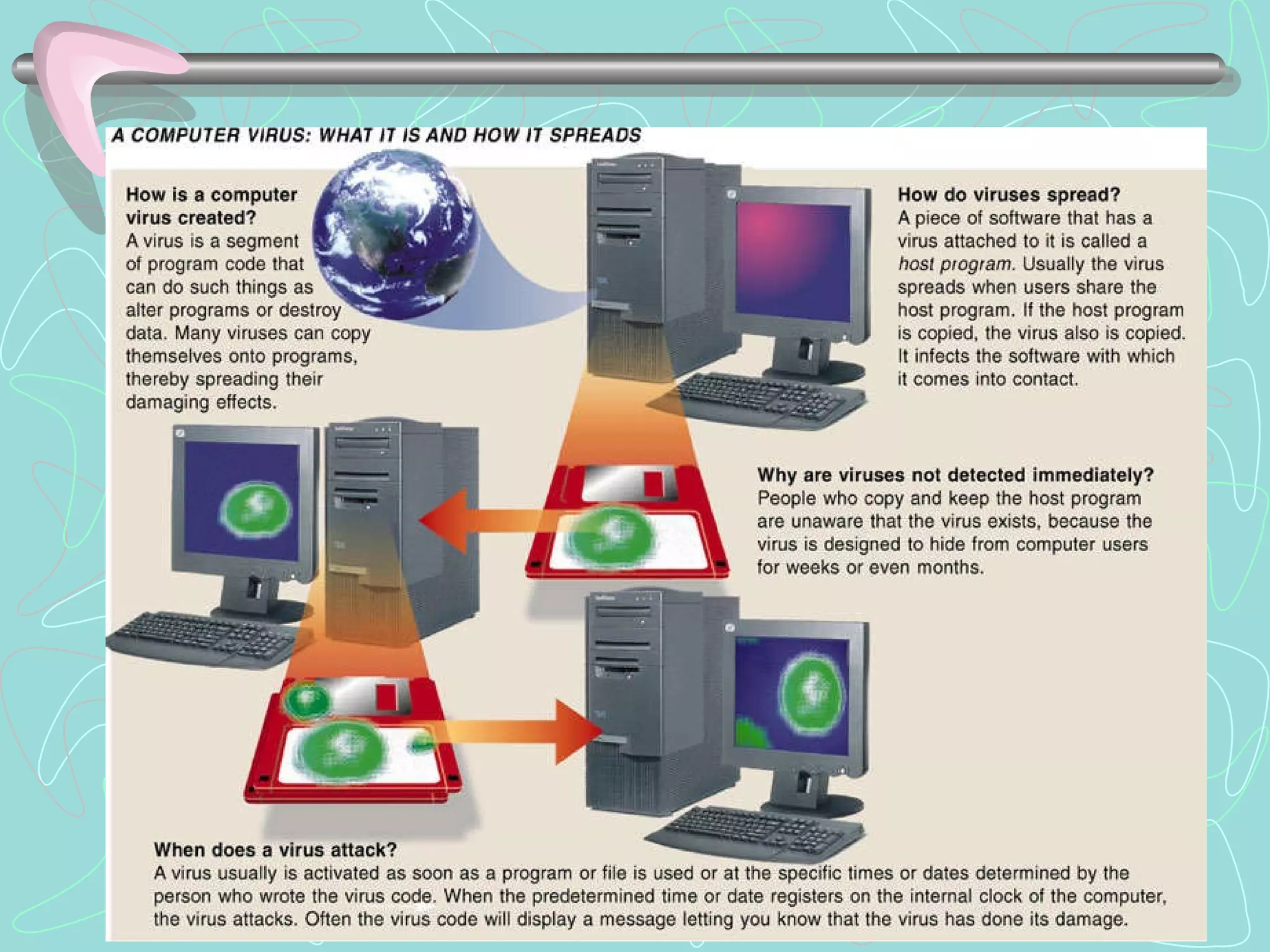
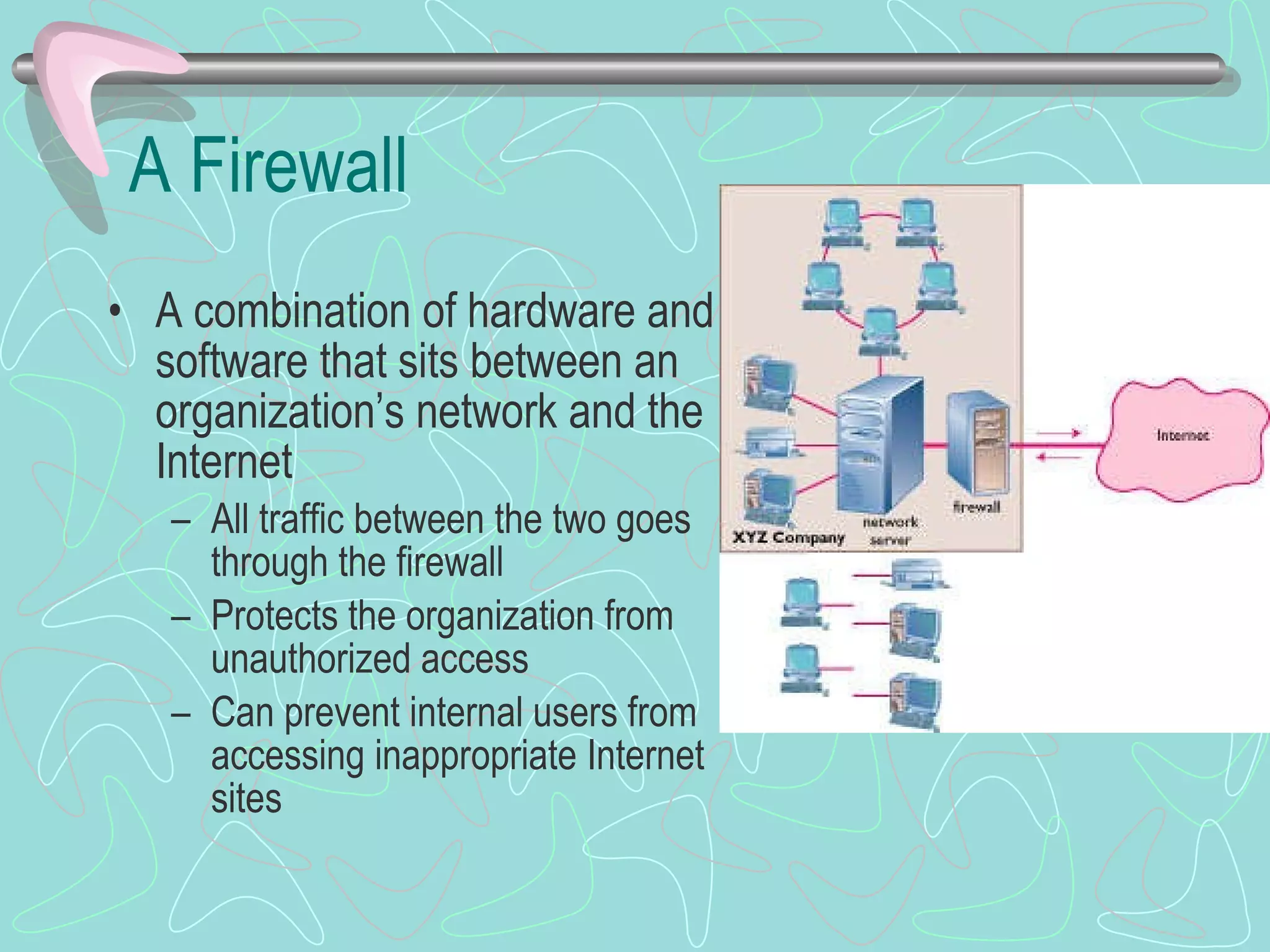
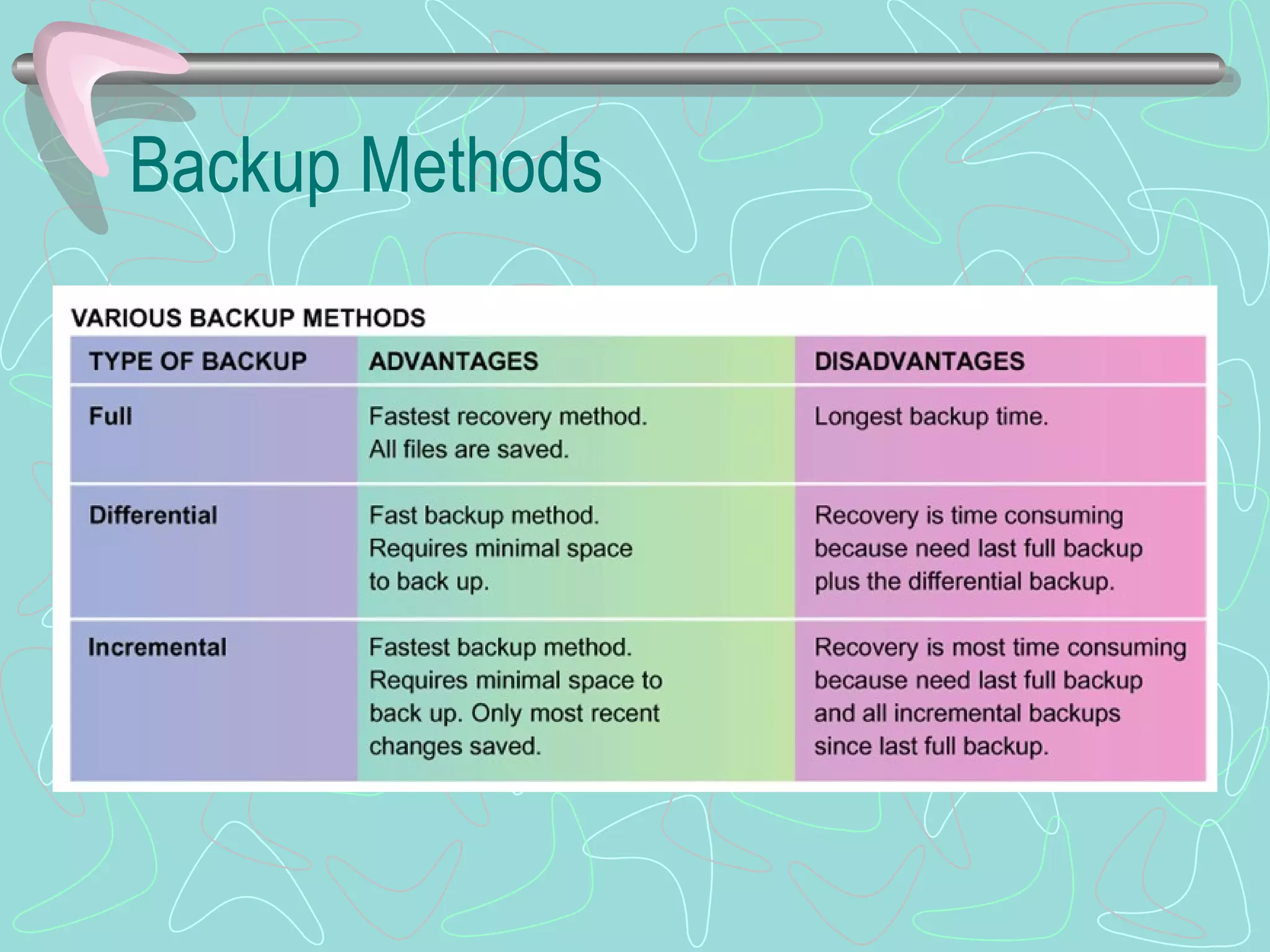
The document discusses various topics related to computer security and privacy. It covers types of computer crimes and challenges with detection and prosecution. Various methods used by computer criminals are described, along with tools for securing systems, data, and networks. Best practices for backups, disaster recovery, and privacy protection are provided. Computer forensics processes are summarized for investigating computer crimes.