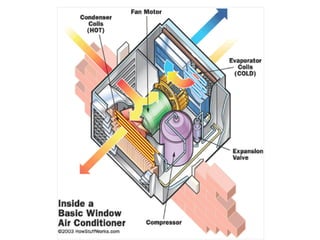
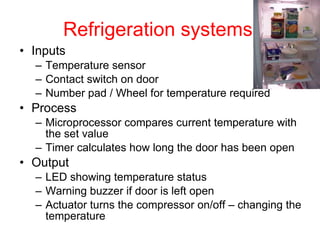
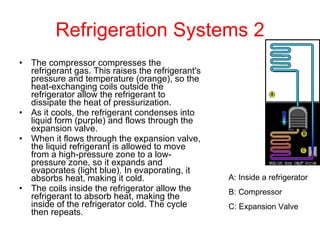
A control system uses sensors to monitor conditions, a microprocessor to process input data and compare it to preset values, and outputs to regulate the condition. Common examples are central heating, air conditioning, and refrigeration systems which use temperature sensors, microprocessors to turn heating/cooling on or off to maintain the set temperature, and fans or compressors as outputs. Control systems operate continuously and automatically but have disadvantages like cost, reliance on computer functioning, and inability to react flexibly like humans.