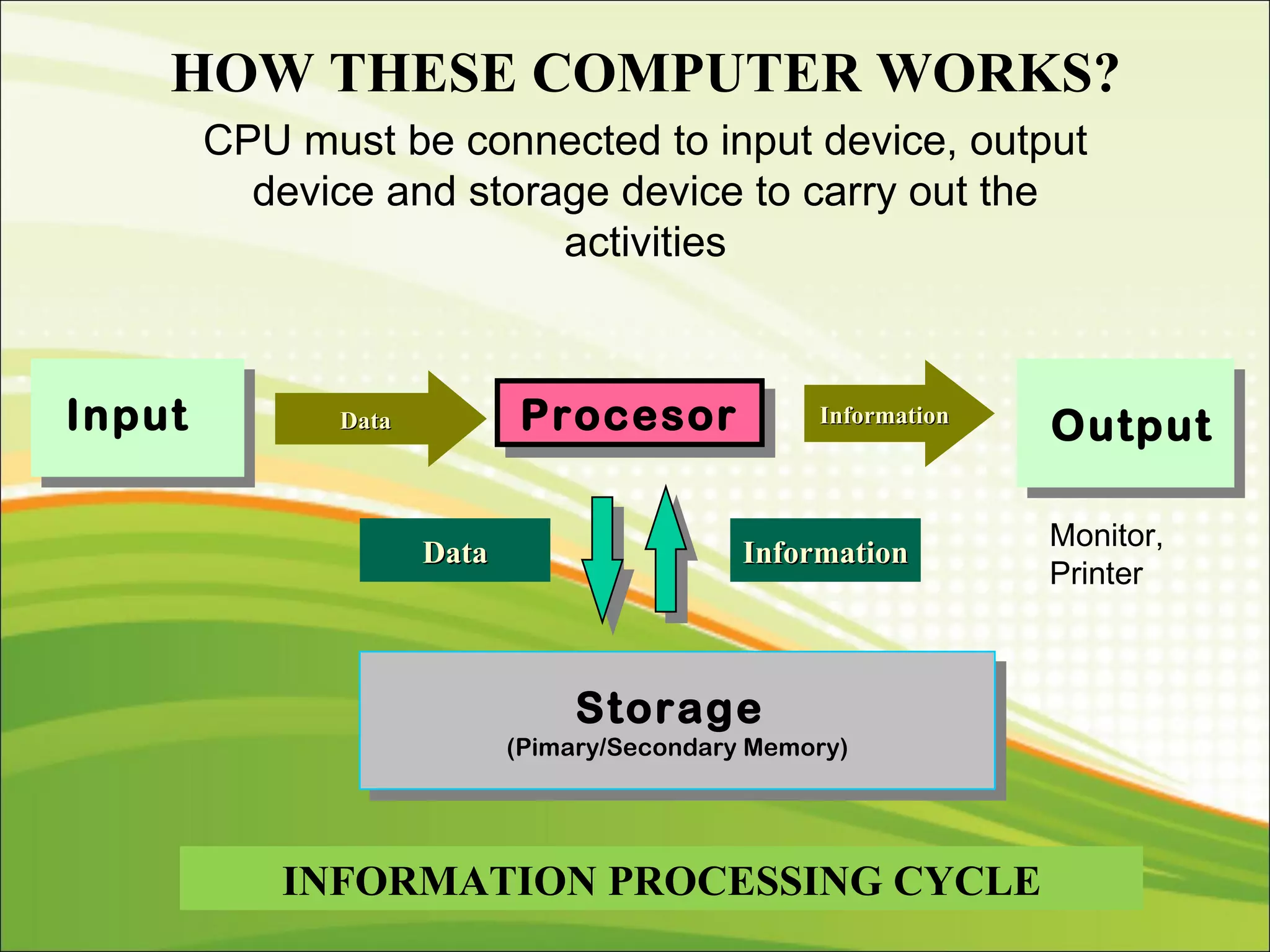
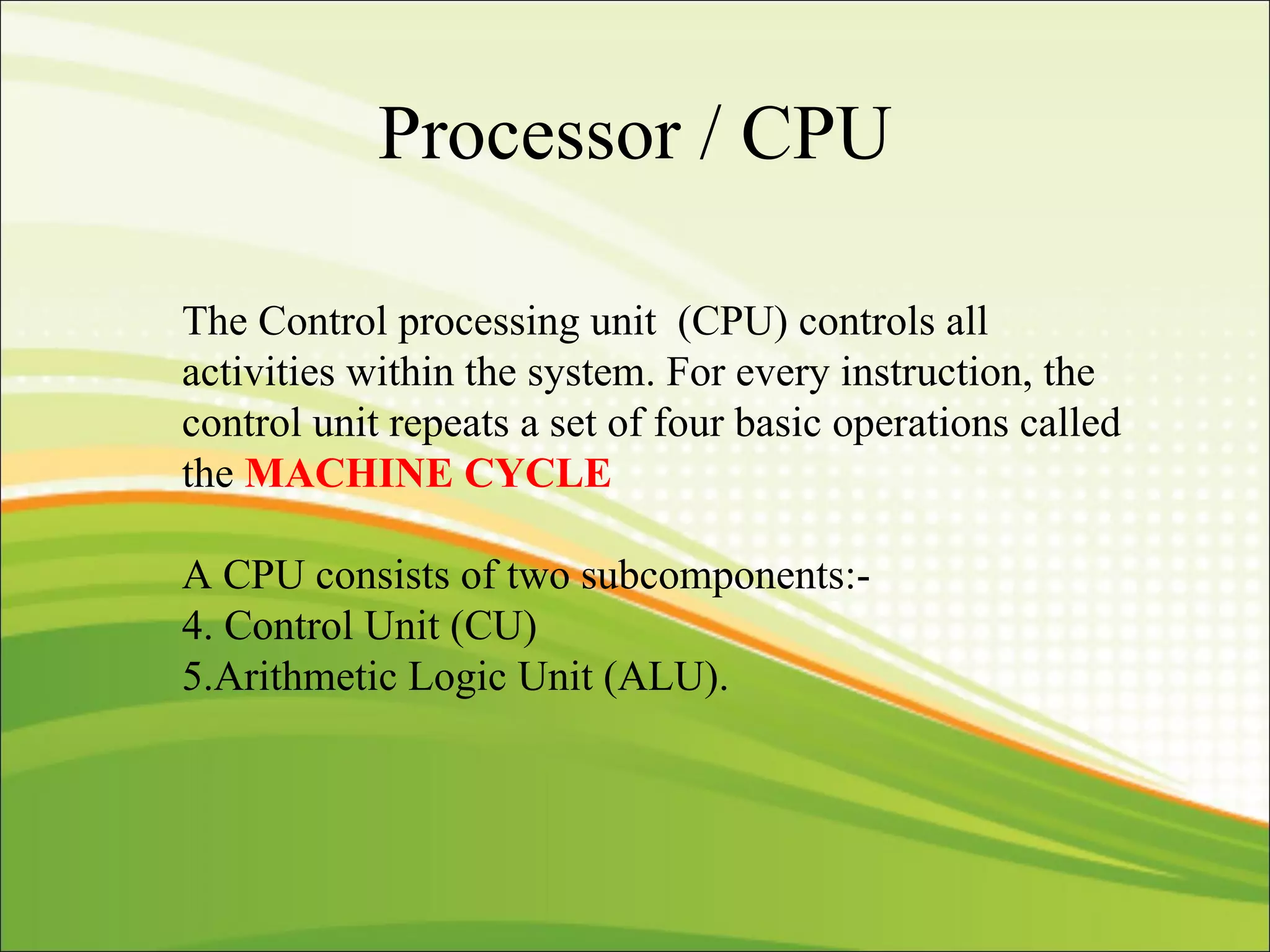
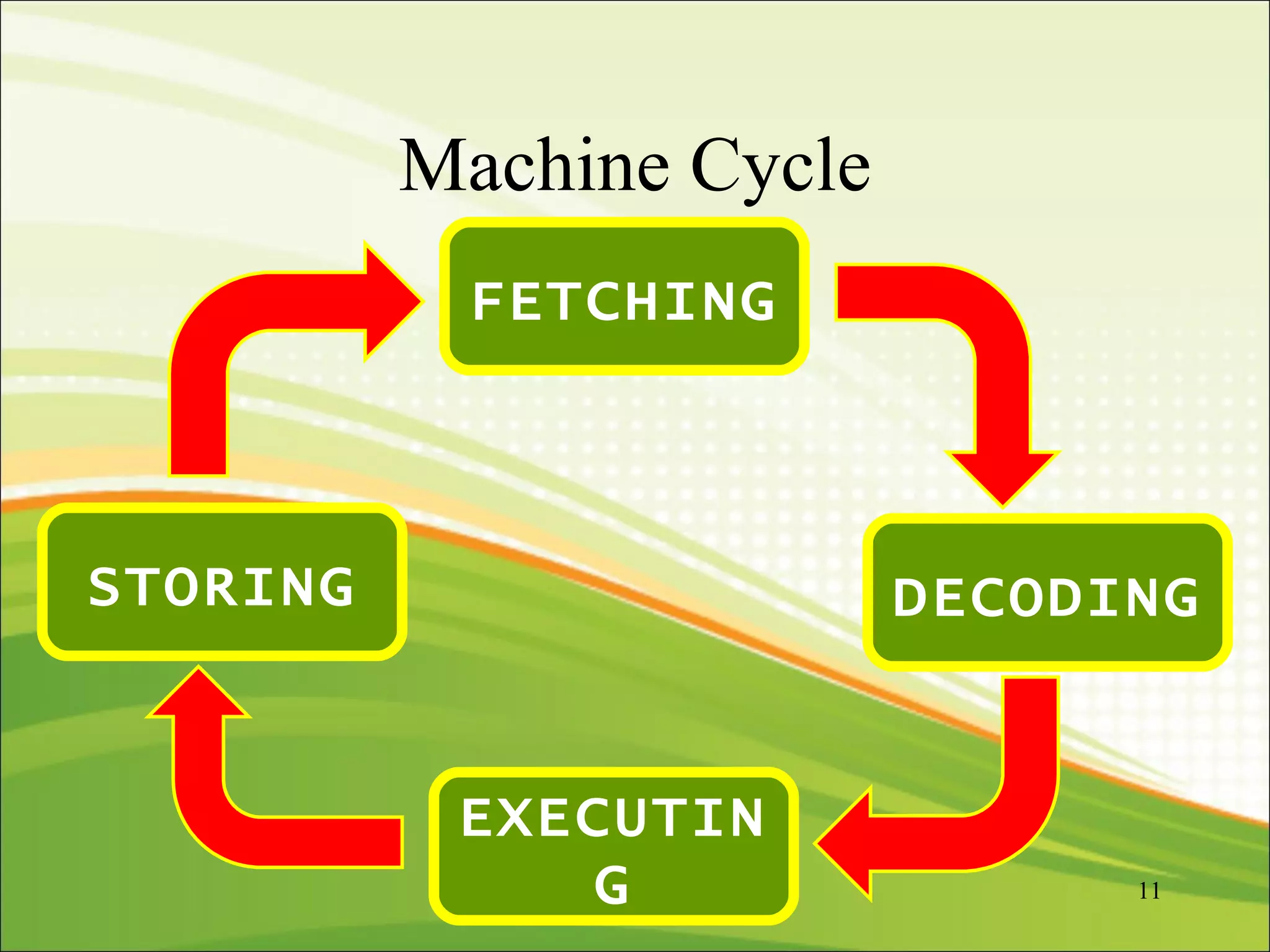
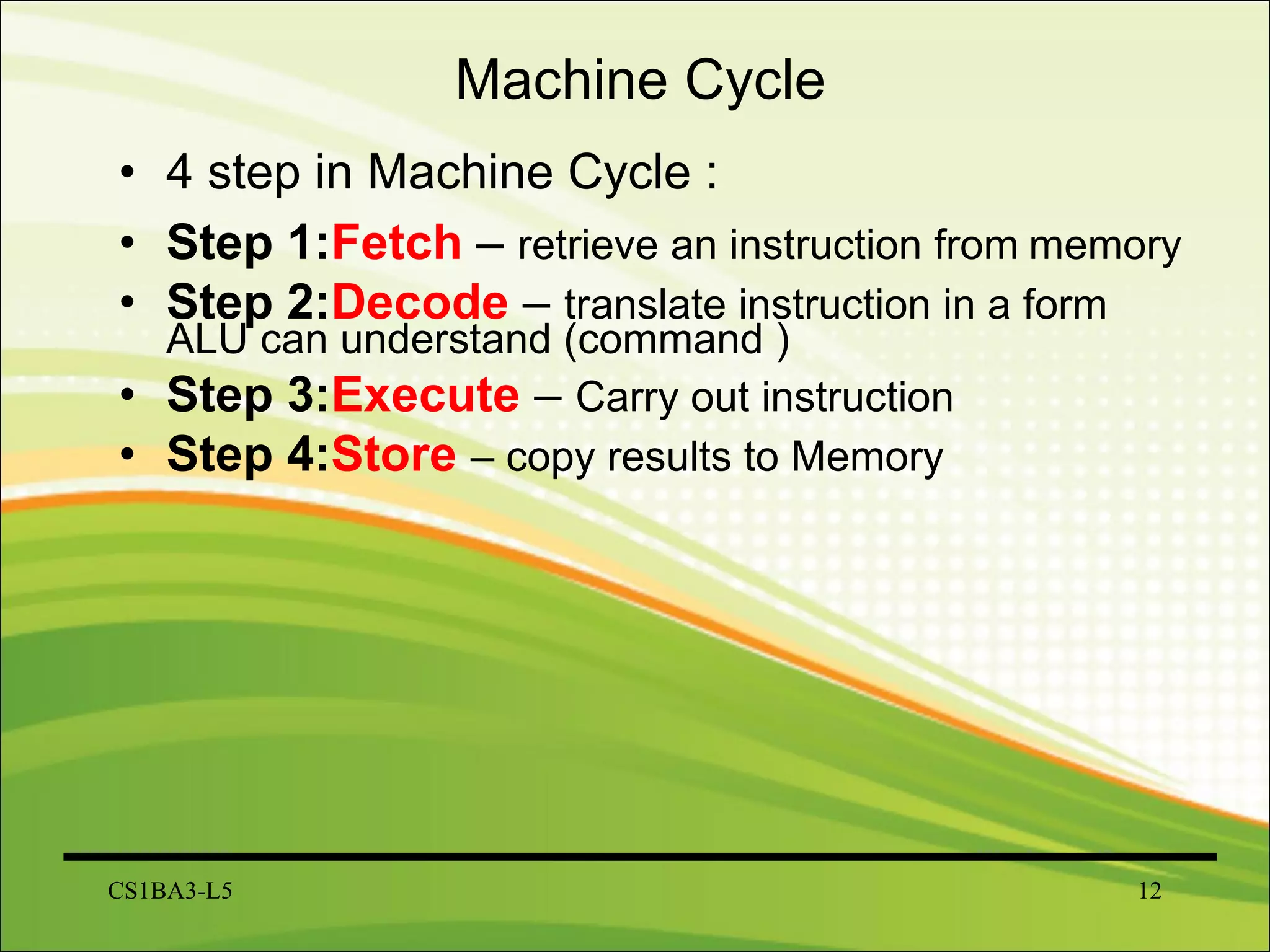
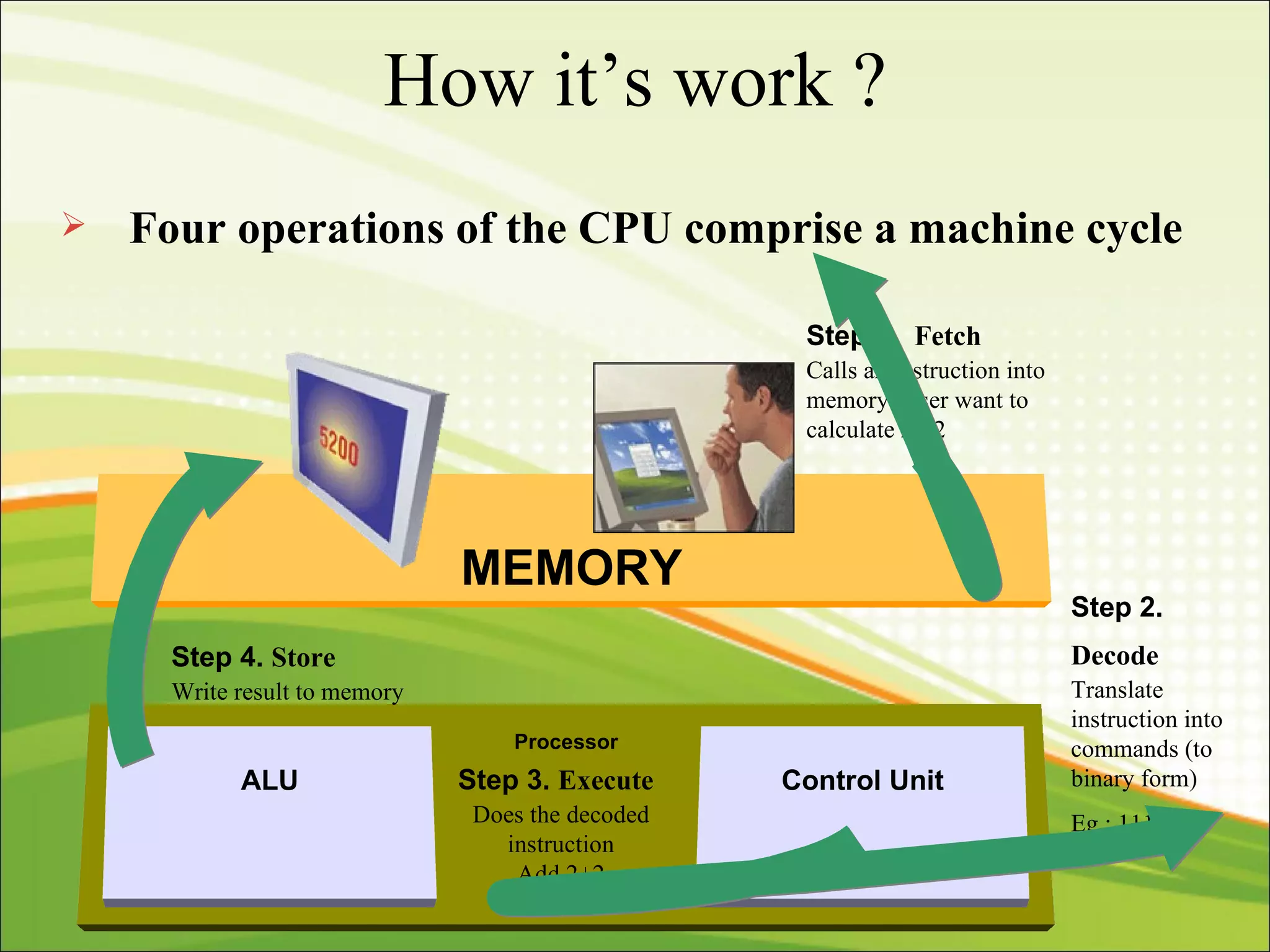
The CPU interprets instructions and performs logical and arithmetic operations to control the computer. It follows a machine cycle of fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, executing the operations, and storing results. The CPU consists of a control unit that manages resources and a machine cycle, and an ALU that performs arithmetic and logical functions according to the control unit's instructions.