This document summarizes key concepts about how computers represent and process data. It discusses:
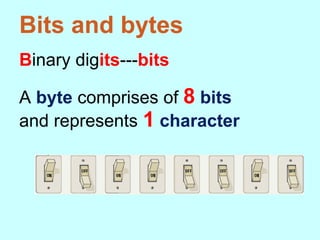
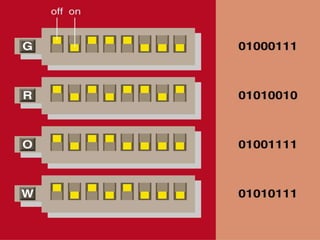
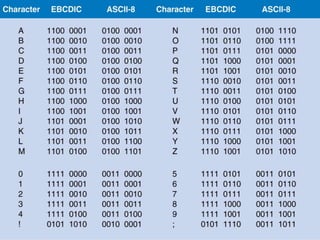
1. How computers represent data using bits, bytes, and text encoding standards like ASCII and Unicode.
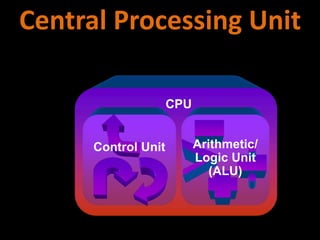
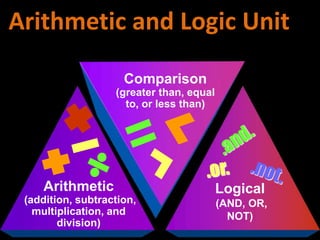
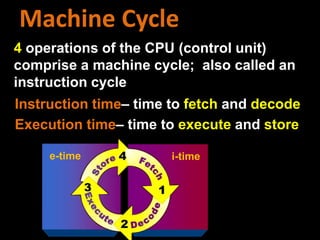
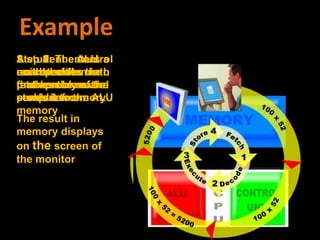
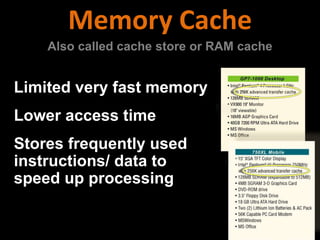
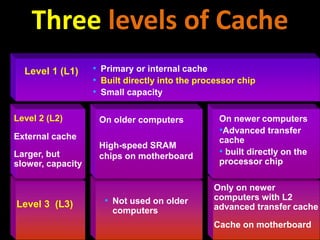
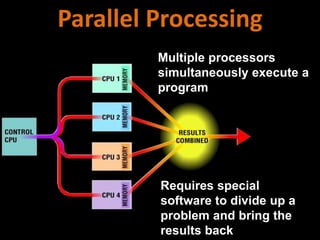
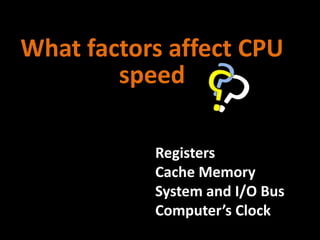
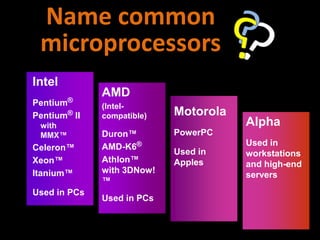
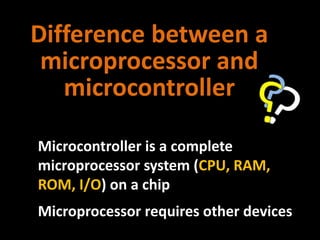
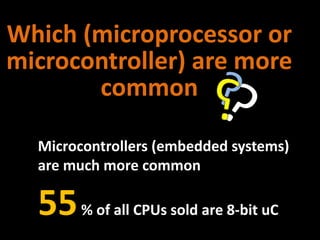
2. How computers process data using the CPU, which contains an ALU and control unit that fetch, decode, execute, and store instructions in a machine cycle. The CPU uses registers and cache memory.
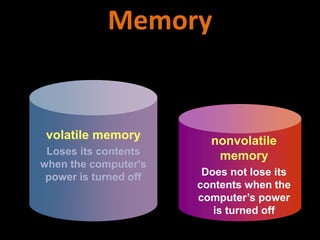
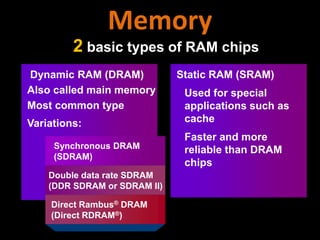
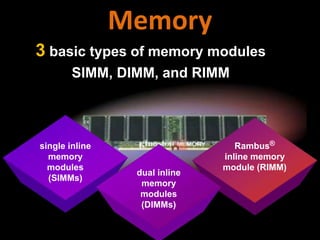
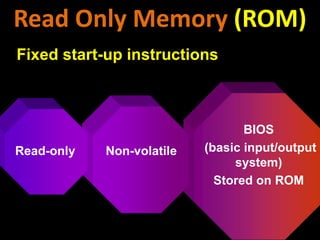
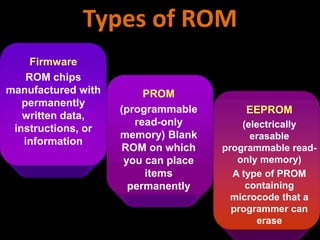
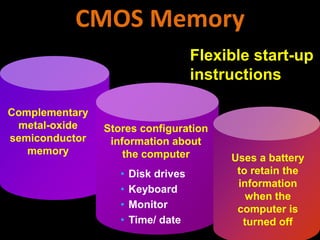
3. The different types of computer memory like RAM, ROM, flash memory, and CMOS memory and how they are used.