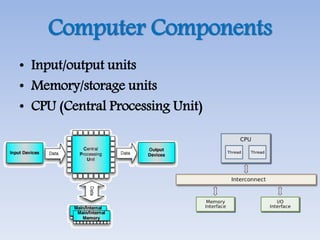
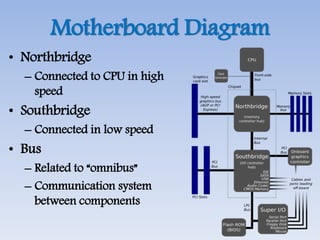
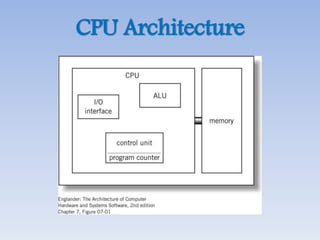
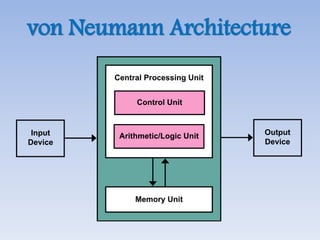
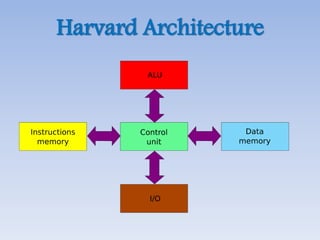
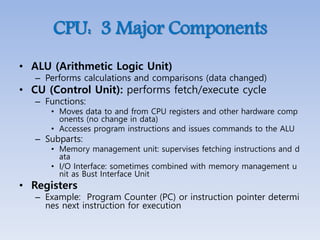
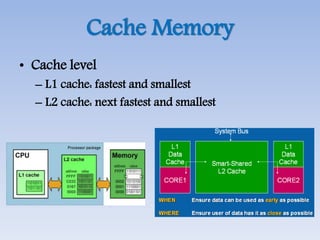
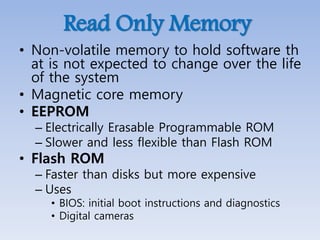
This document provides an overview of basic computer architecture and components. It discusses the history of computers and introduces Arduino. The main computer components are described as the input/output units, memory/storage units, and the CPU. The motherboard diagram shows the northbridge, southbridge, and bus. The von Neumann and Harvard CPU architectures are explained. The CPU has three major components: the ALU, CU, and registers. Memory types like RAM, ROM, cache memory and their functions are also summarized.