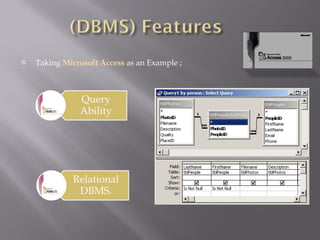
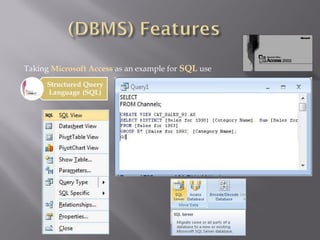
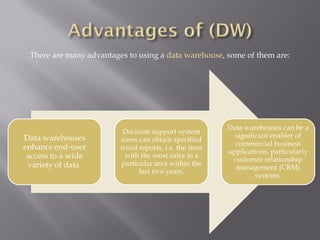
Topics in Data Management include data analysis, database management systems, data modeling, database administration, data warehousing, data mining, data quality assurance, data security, and data architecture. Data analysis involves looking at and summarizing data to extract useful information and develop conclusions. Database management systems are used to manage databases and are used by over 90% of people using computers. Data modeling is the process of structuring and organizing data to be implemented in a database. Database administrators are responsible for ensuring the security, performance, and availability of organizational data.