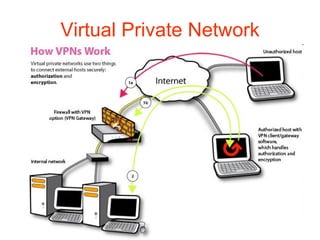
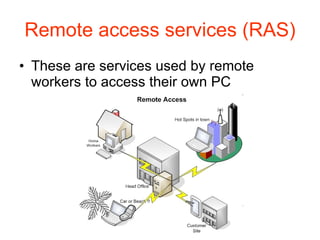
1. Teleworking, or working from home, has become possible due to developments in ICT such as portable devices, networks, broadband internet, and virtual private networks.
2. Video conferencing allows face-to-face meetings without travel via equipment like webcams and conferencing software. Other communication methods include phone conferencing, email, instant messaging, and faxing.
3. While teleworking provides benefits like reduced costs and increased flexibility, it also poses challenges such as less opportunities for in-person collaboration and temptation to be distracted from work. Managers must consider job roles and employee traits when deciding who can telework.