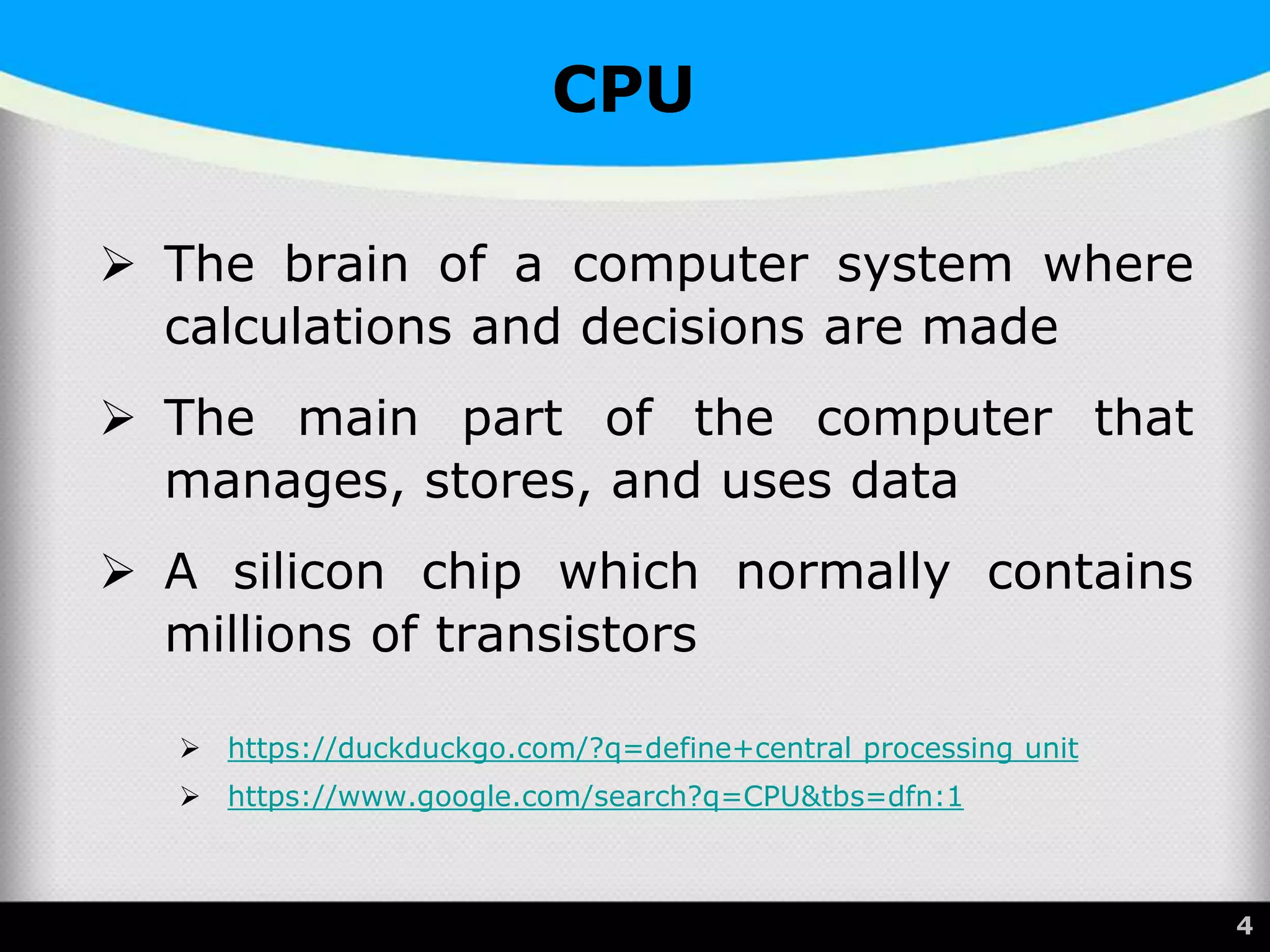
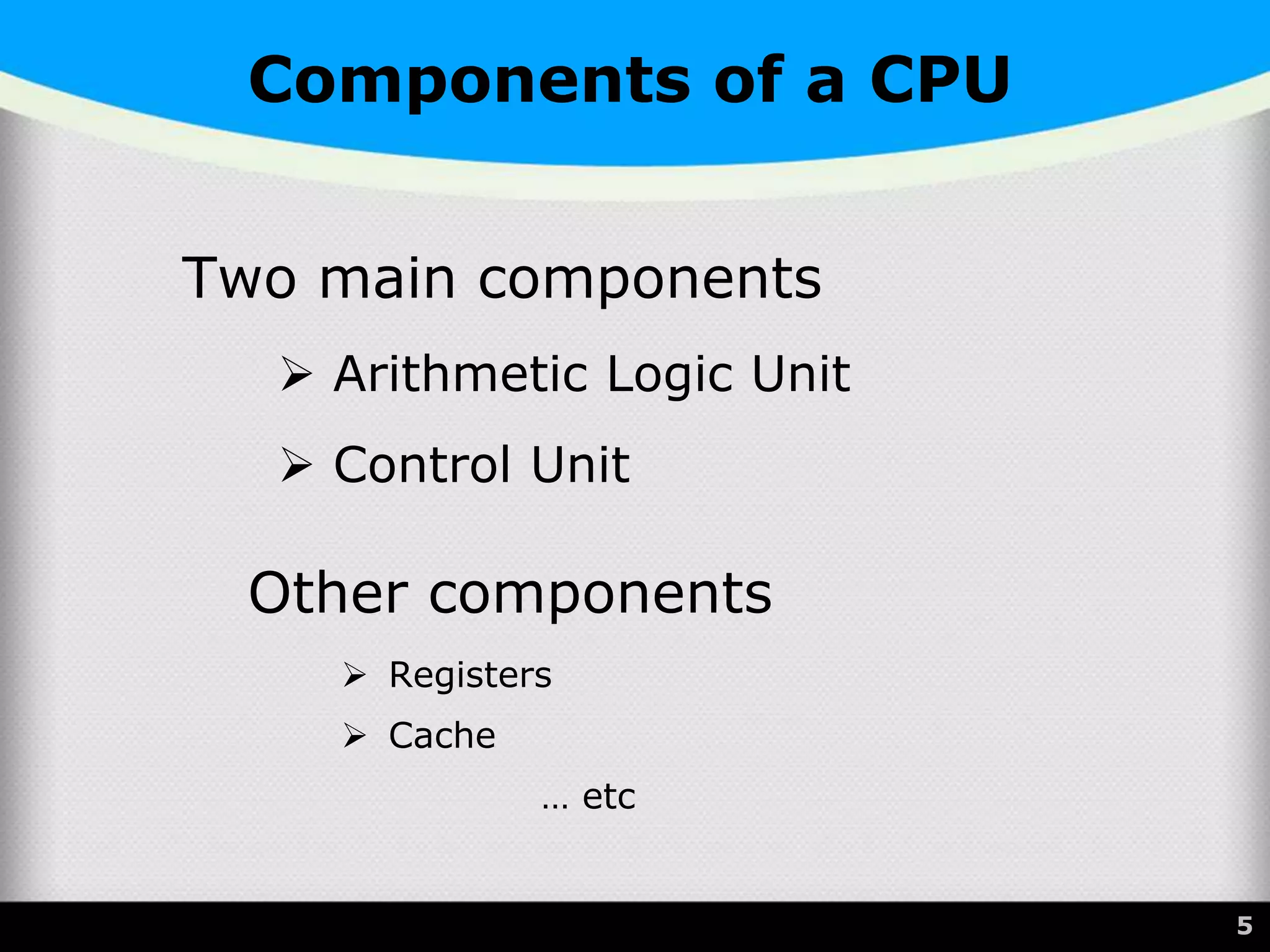
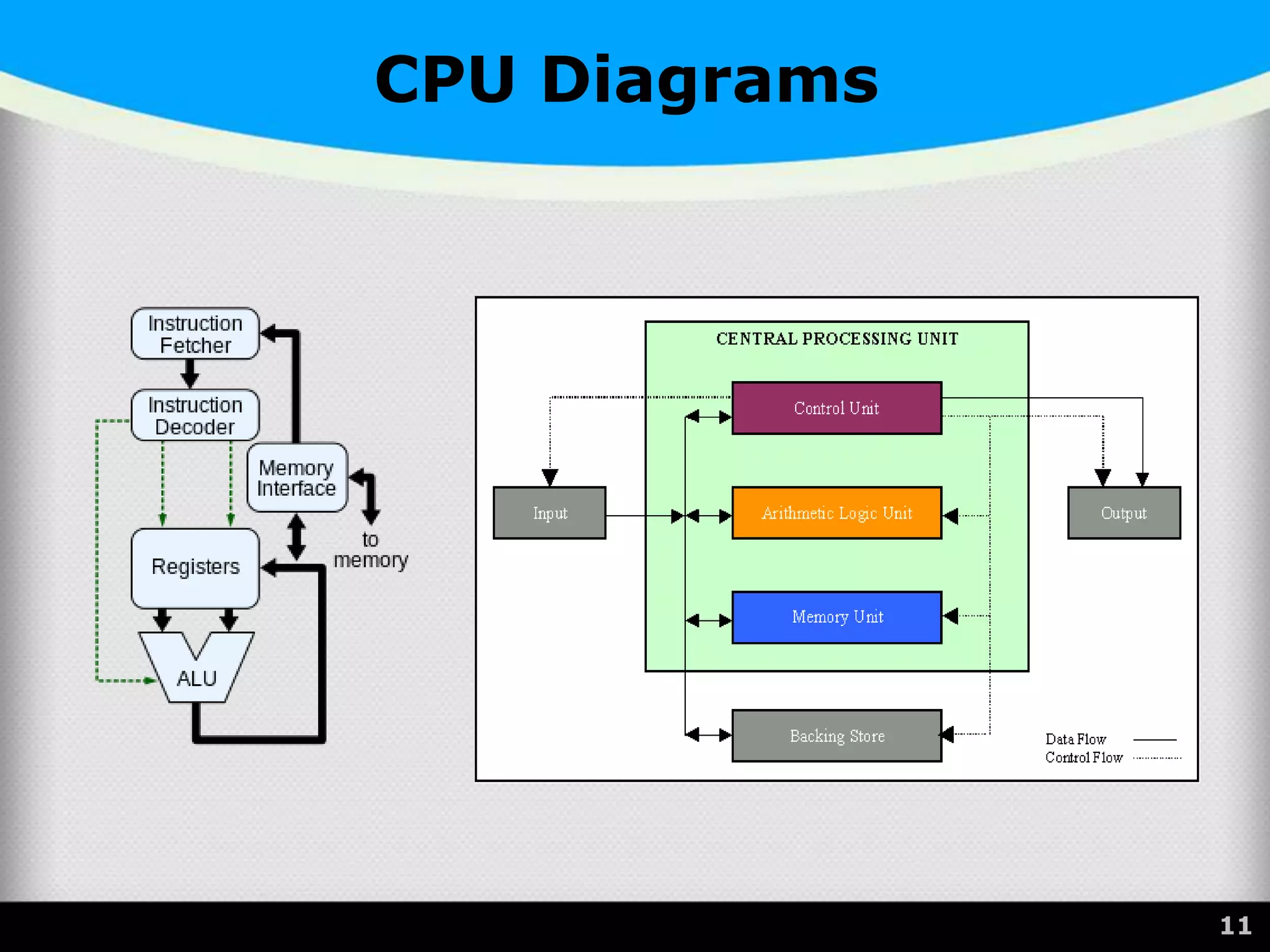
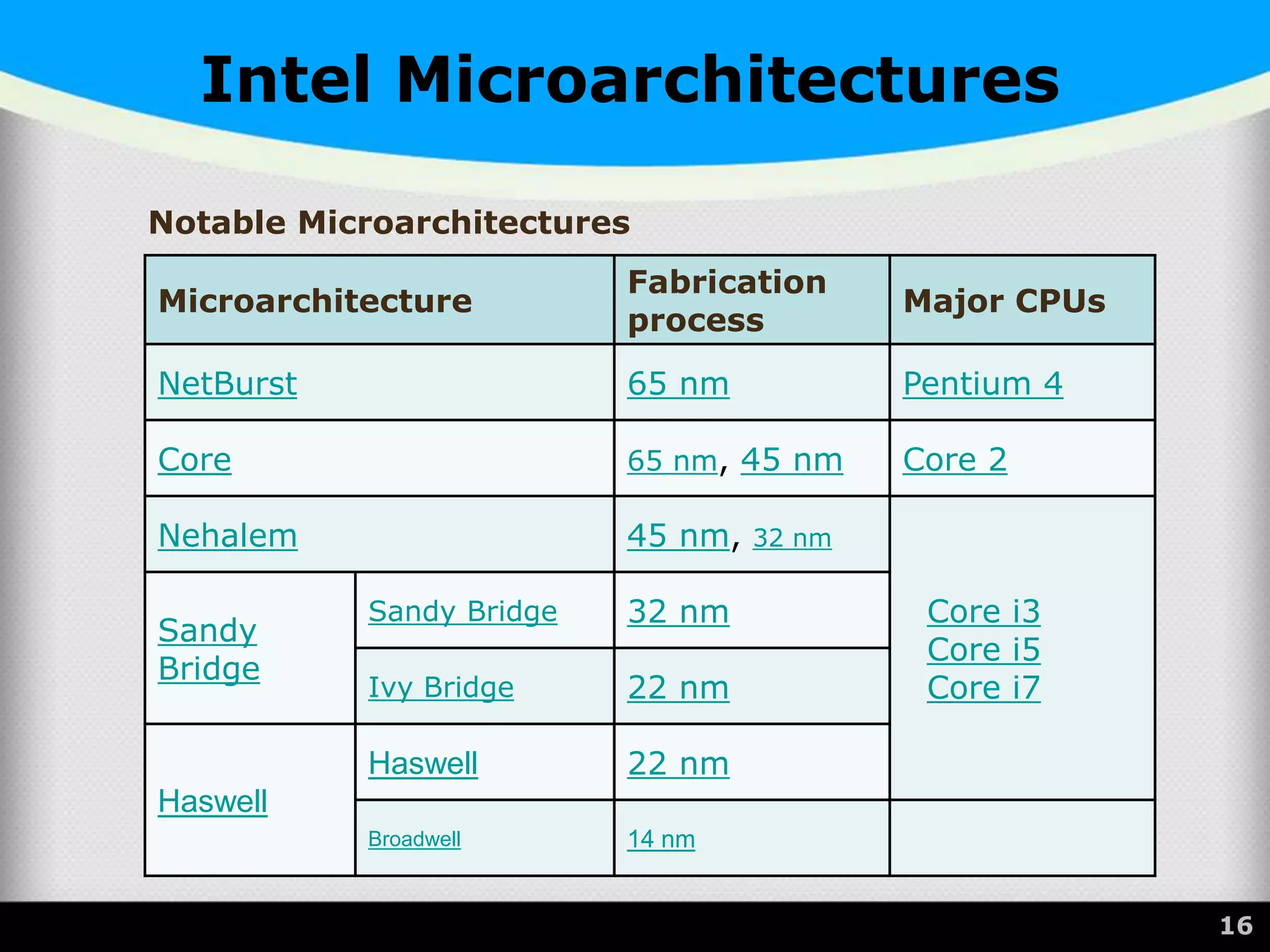
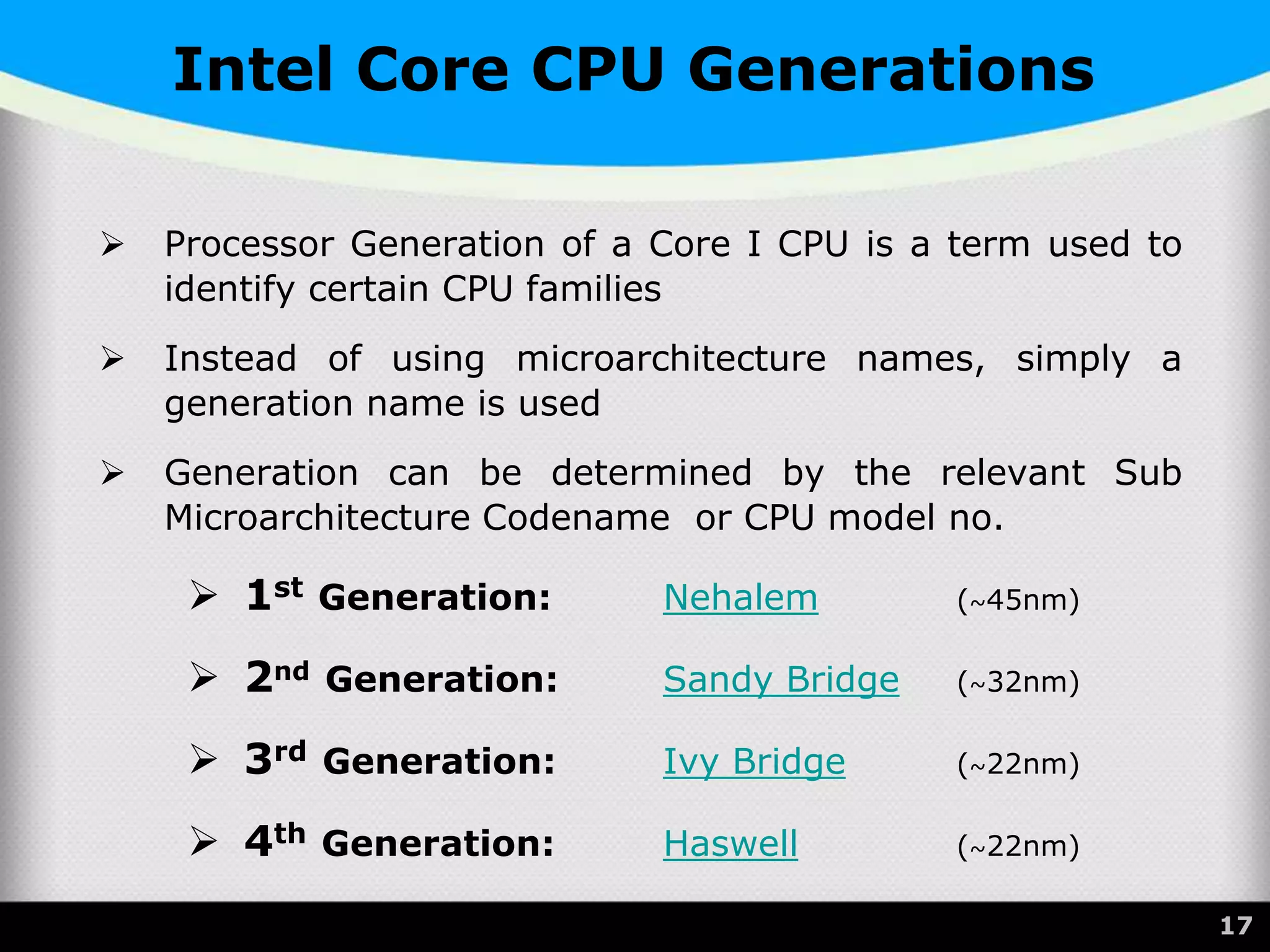
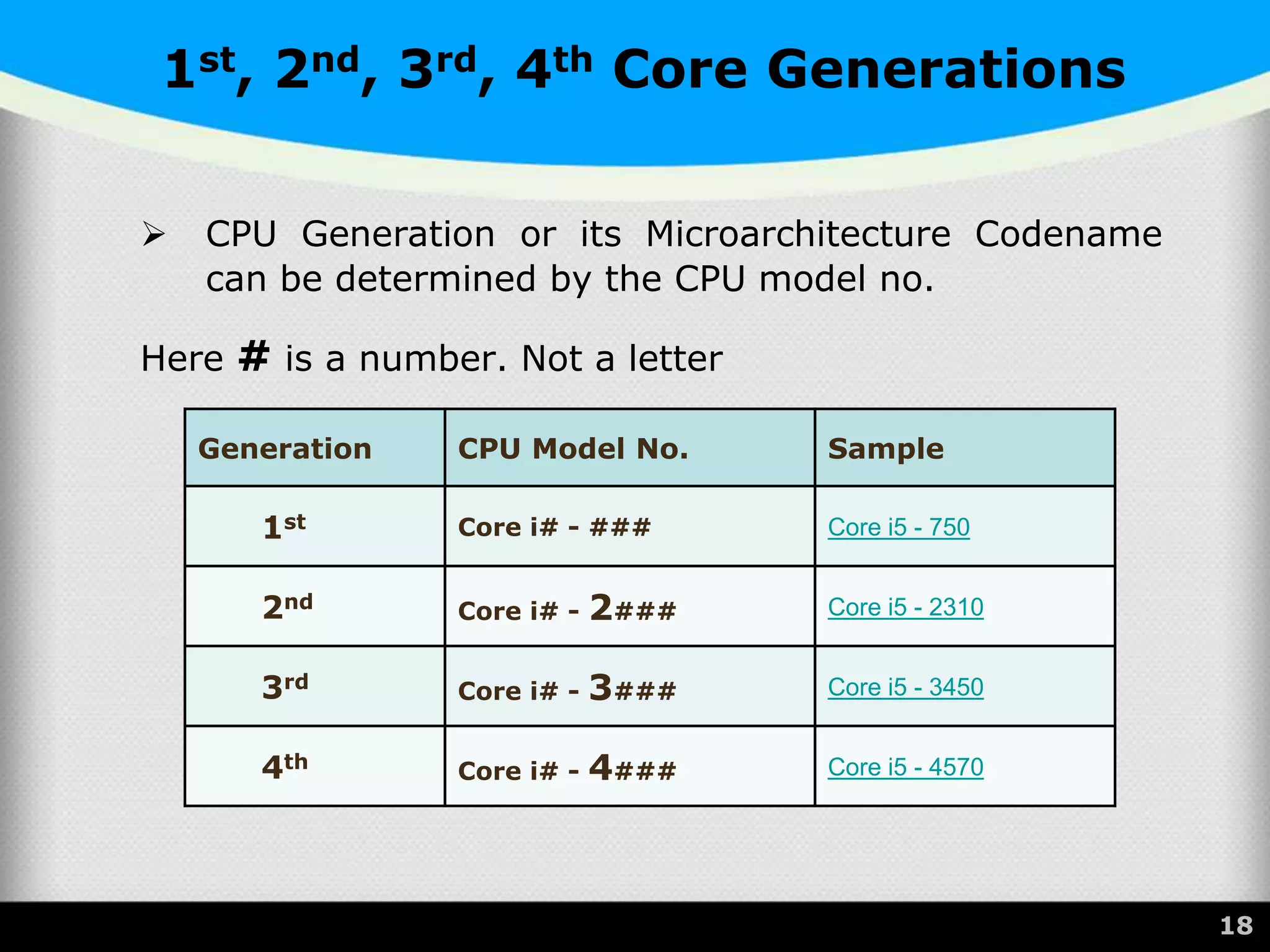
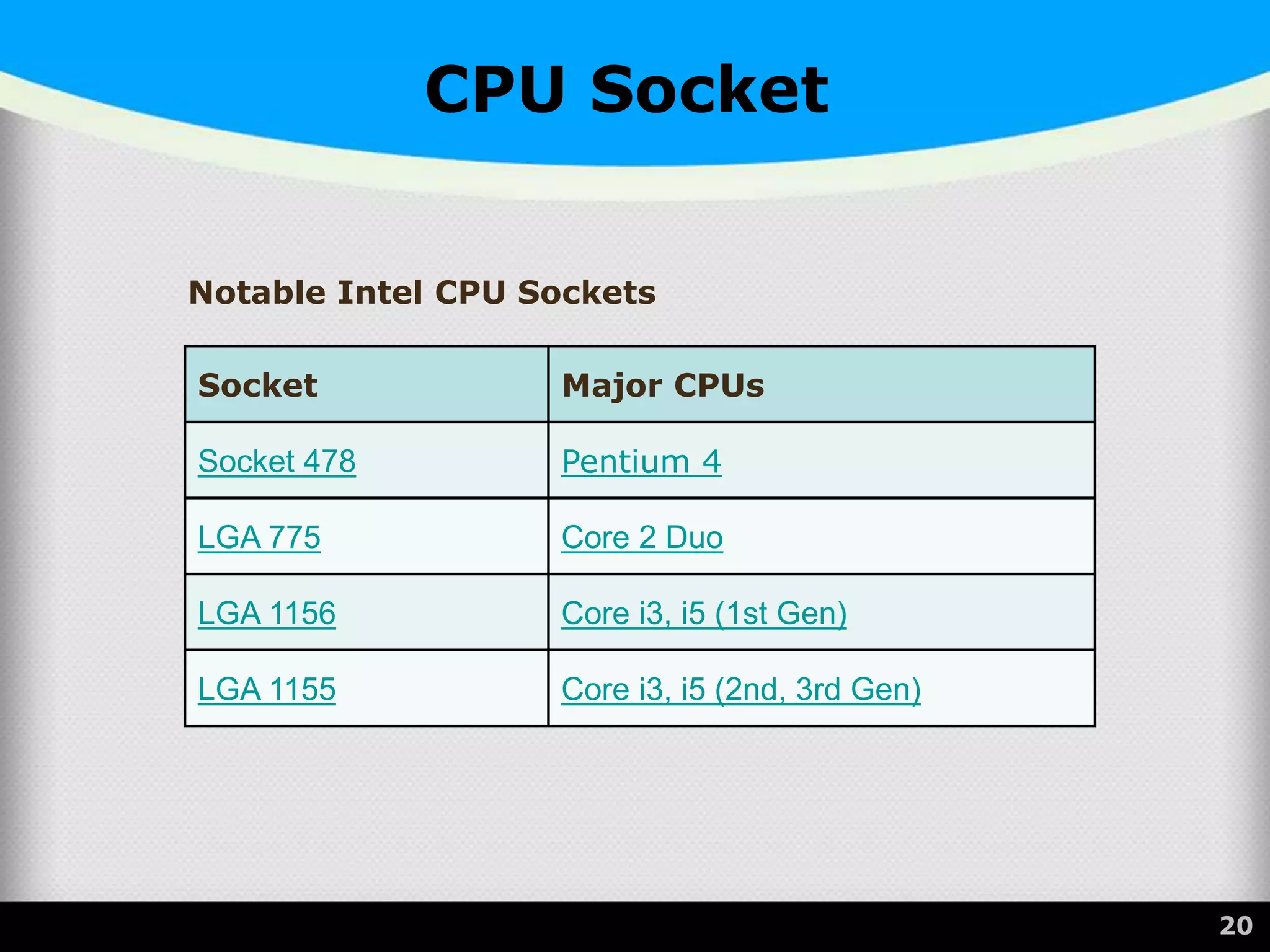
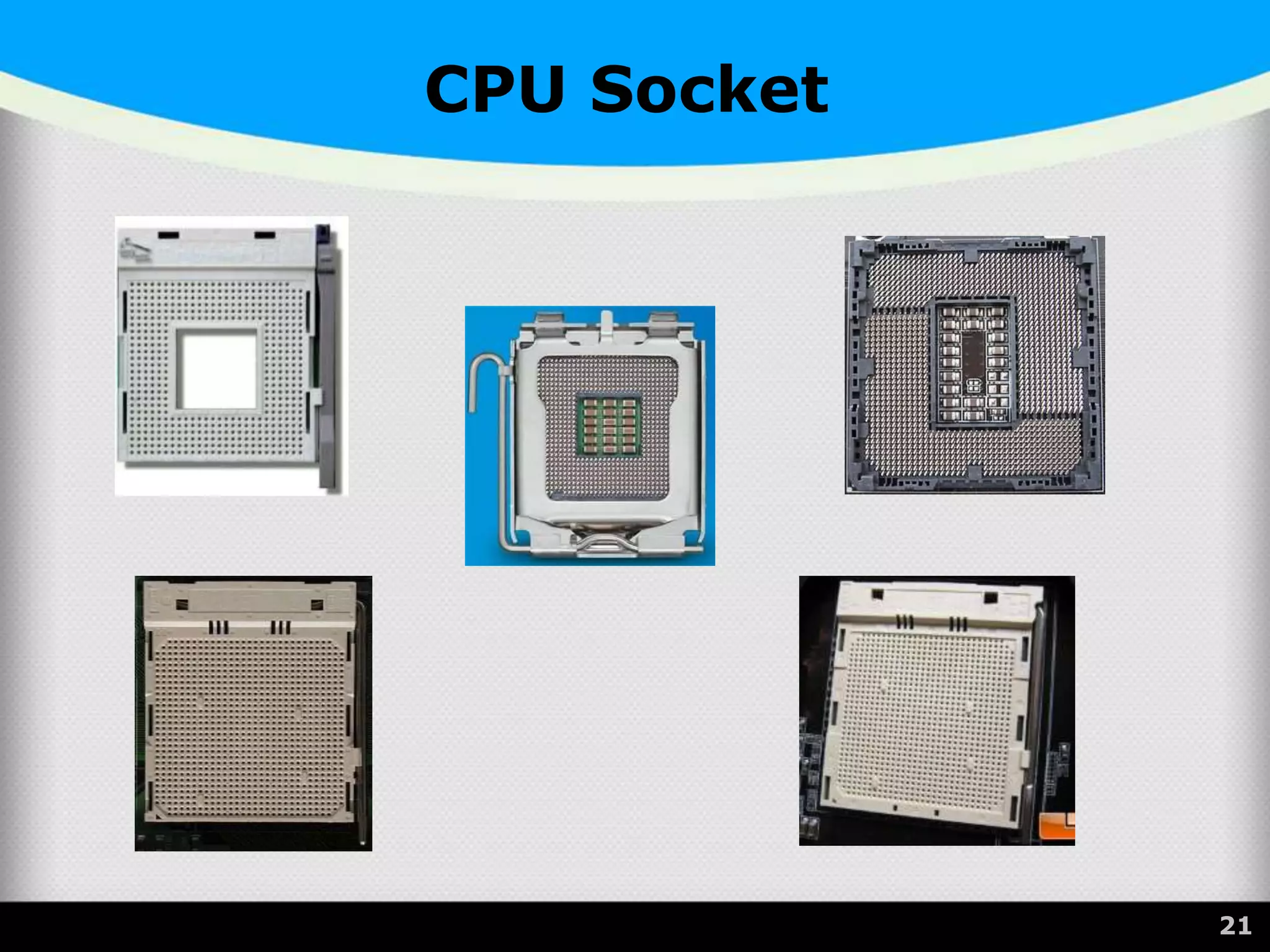
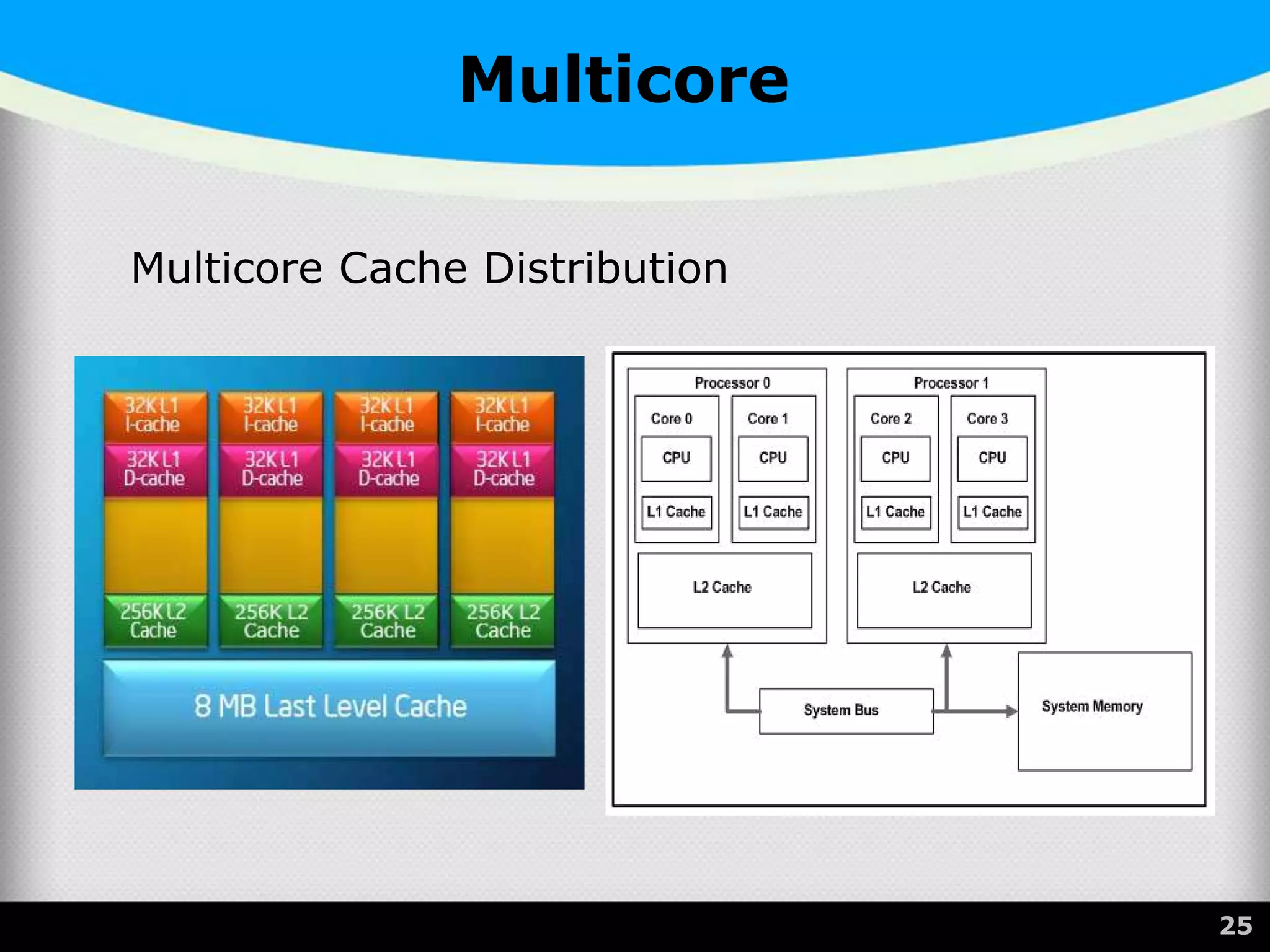
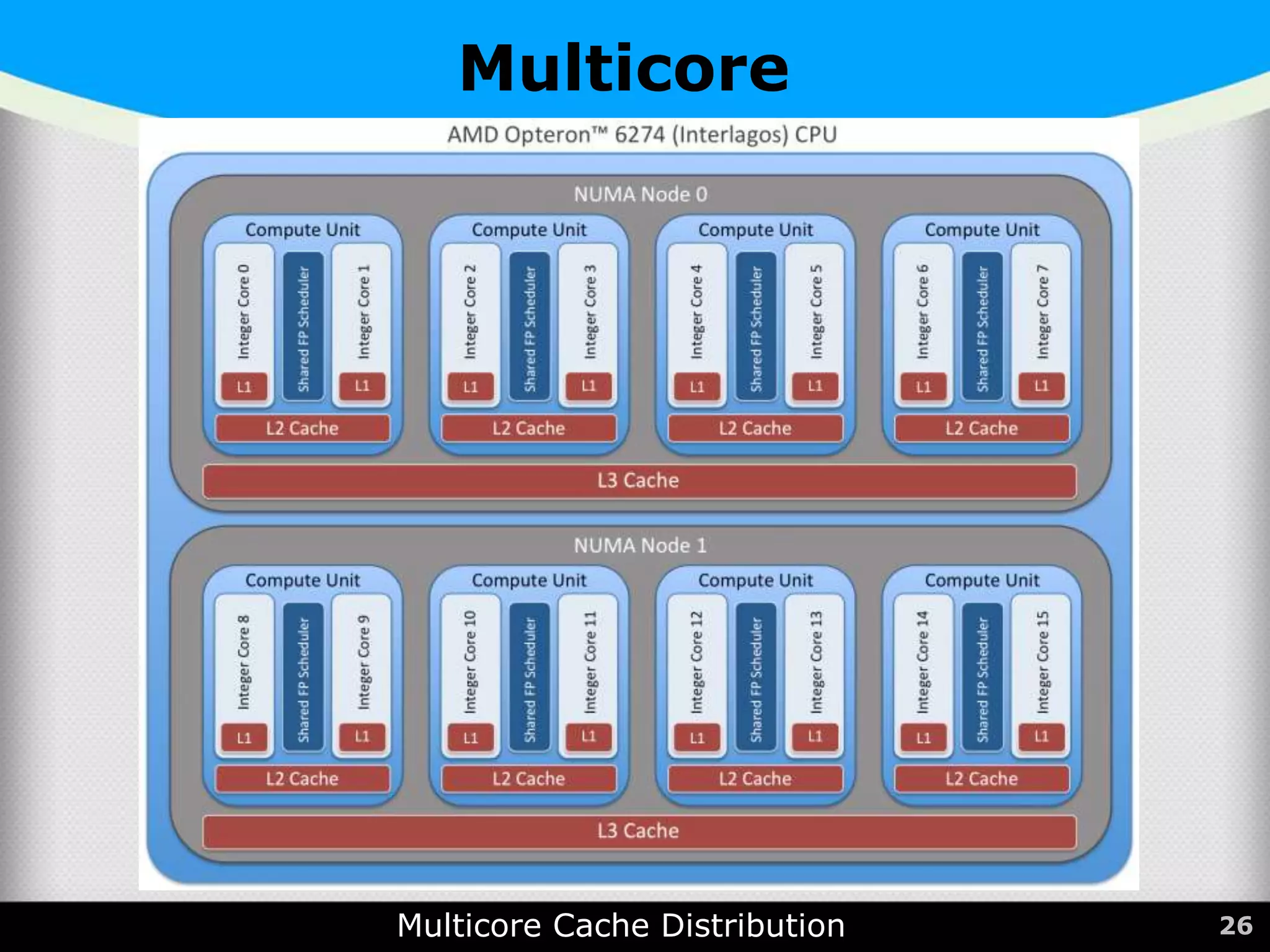
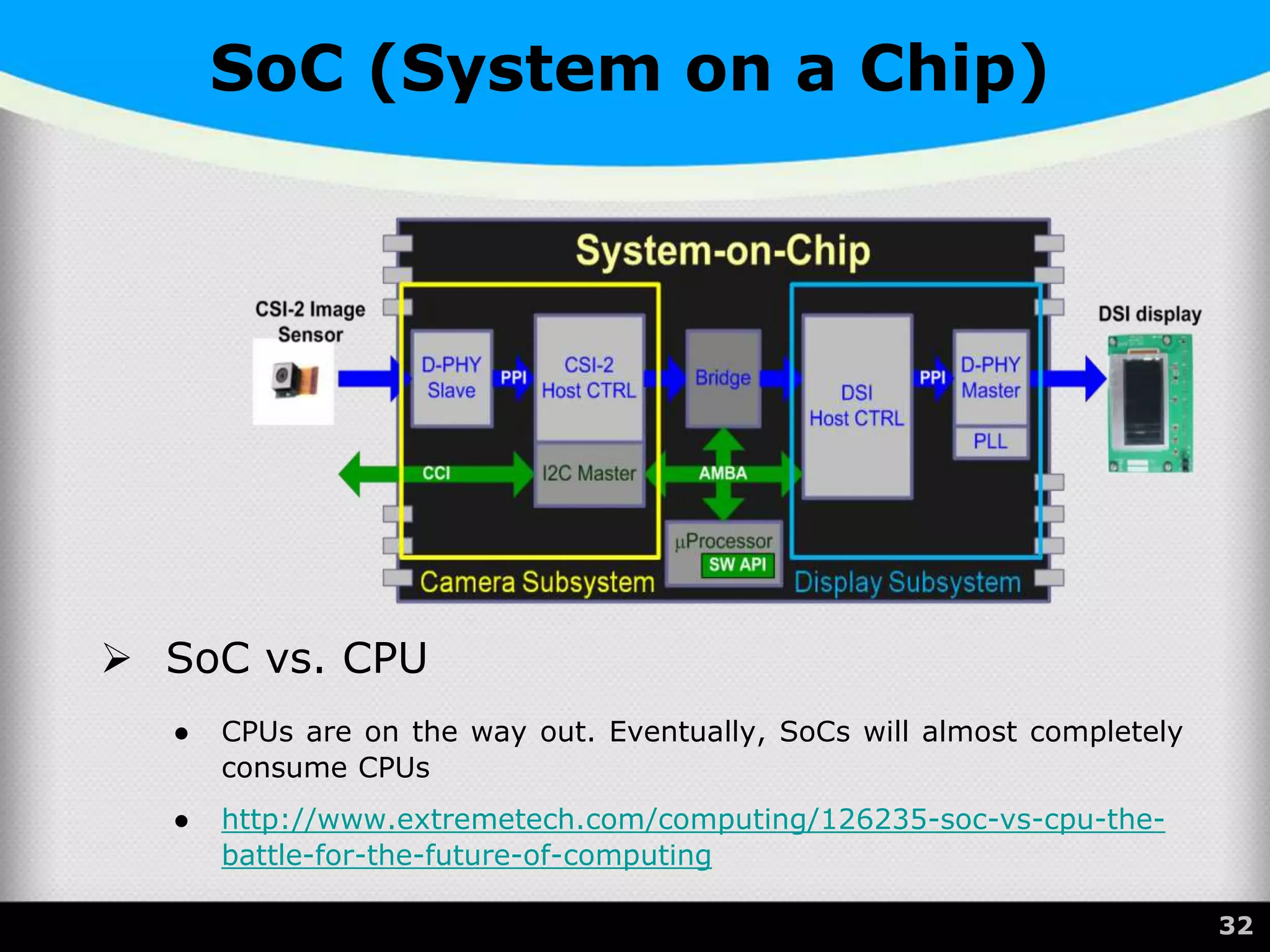
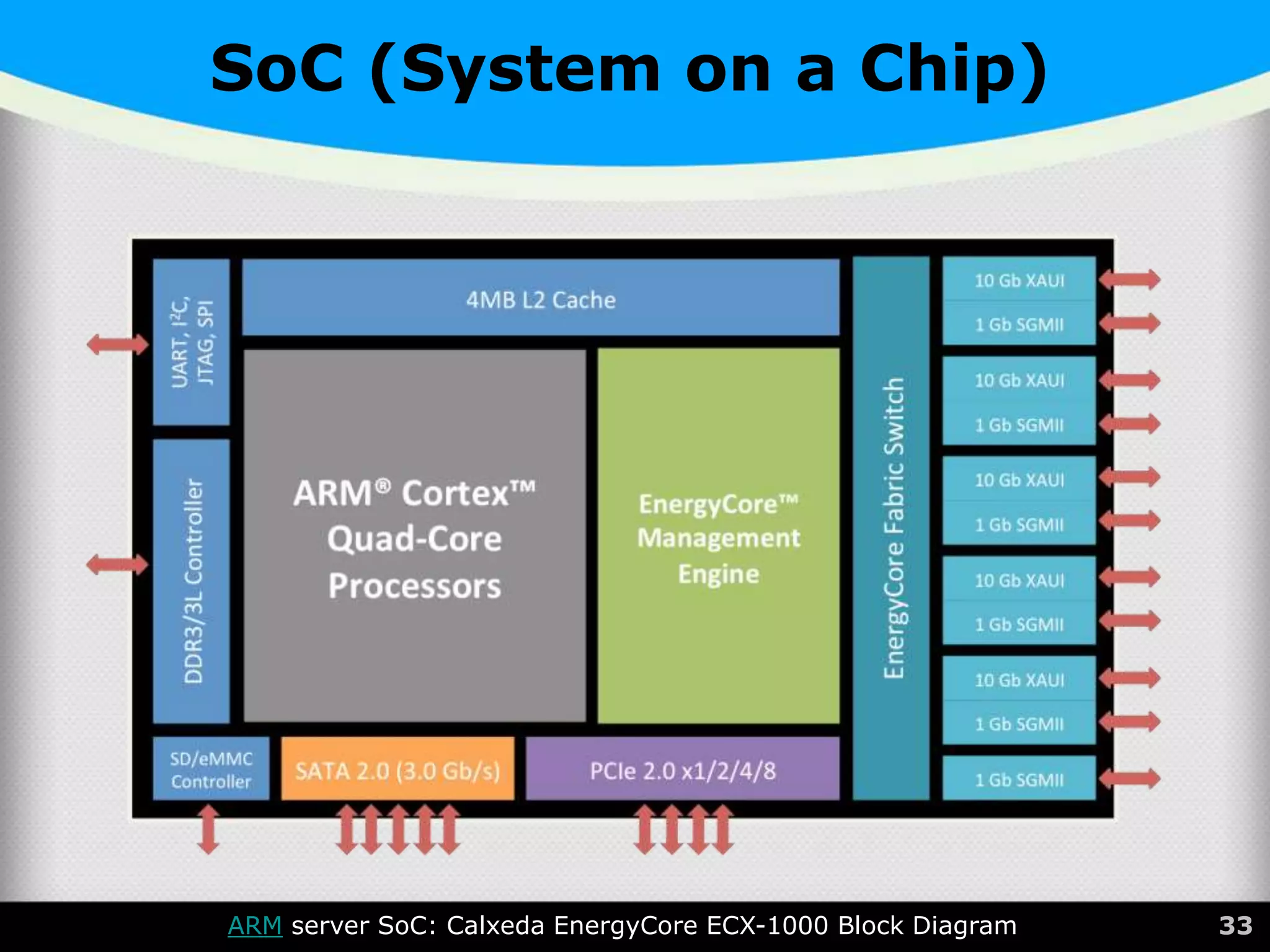
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the central processing unit (CPU), describing its components such as the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), control unit, registers, and cache. It explains the function, architecture, and types of CPUs, including multicore and system on a chip (SoC) designs, as well as notable CPU vendors like Intel and AMD. Additionally, it outlines the evolution of Intel's microarchitectures and the significance of CPU generations and sockets.