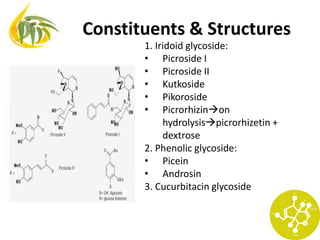
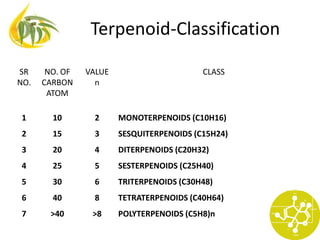
This document discusses various terpenoid compounds found in plants, including iridoids, terpenes, and modified terpenoids. It provides classifications of terpenoids based on carbon atom count and discusses the occurrence, extraction, biosynthesis, and biological activities of specific compounds like iridoids, gentian, picrorhiza, quassia, tinospora, artemisia, taxus, and andrographis. Structures of important constituents from each plant are also shown.


![Introduction-Iridoids
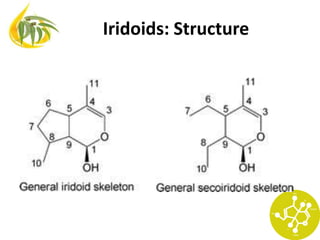
Monoterpene
Cyclopenta[c]pyranoid skeleton
Iridane skeleton cis-2-oxa-bicyclo-[4,3,0]-nonane
Type: Secoiridoids by cleavage of the 7,8 bond of the
cyclopentane ring
Some authors limits the definition up to: Methyl cyclopentane
Iridoid glycosides (>300)
Secoiridoid glycoside (>100)
Non-glycoside compounds (>100)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terpenoid-iridoid-131021053858-phpapp02/85/Terpenoid-iridoid-4-320.jpg)