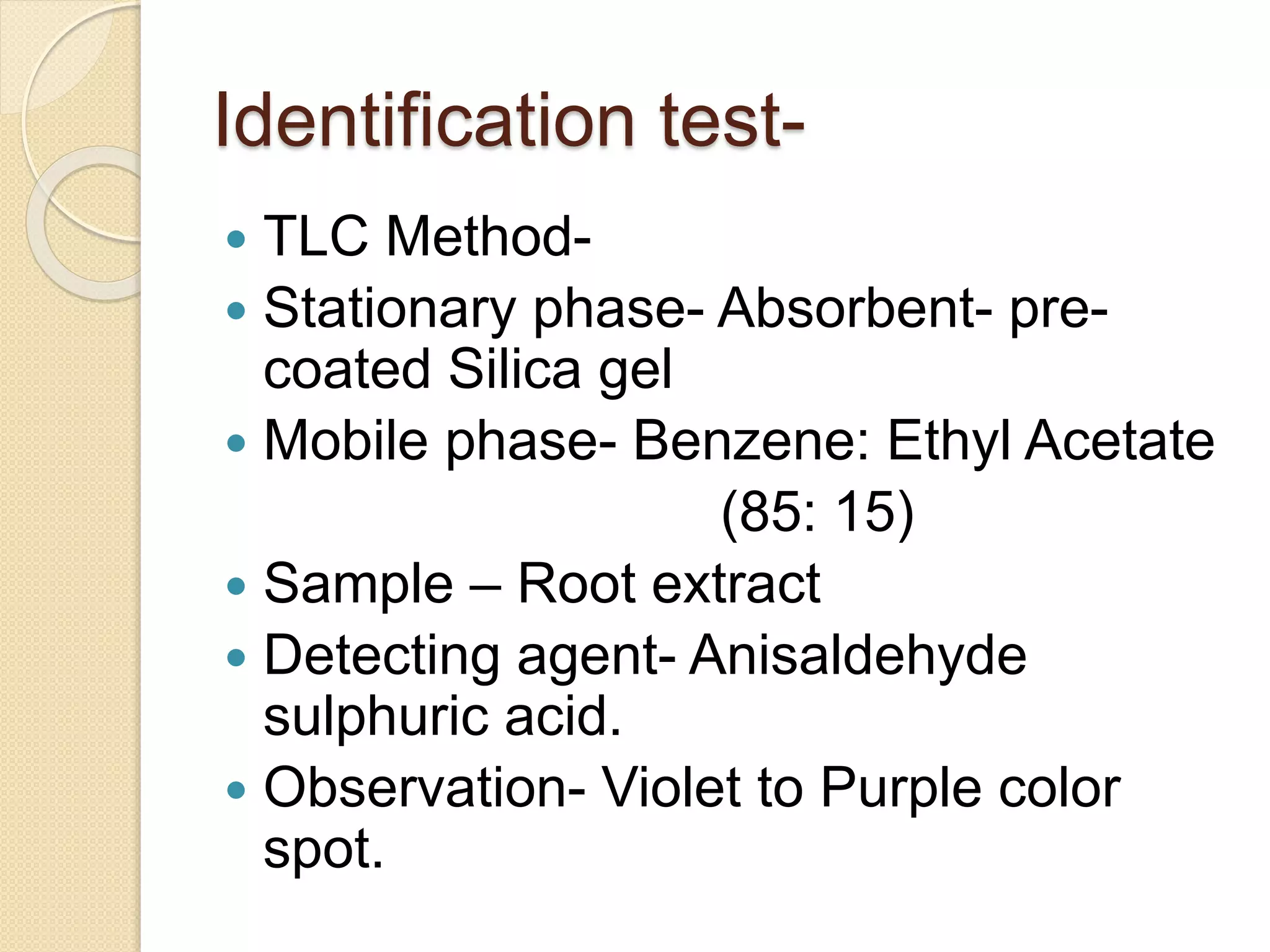
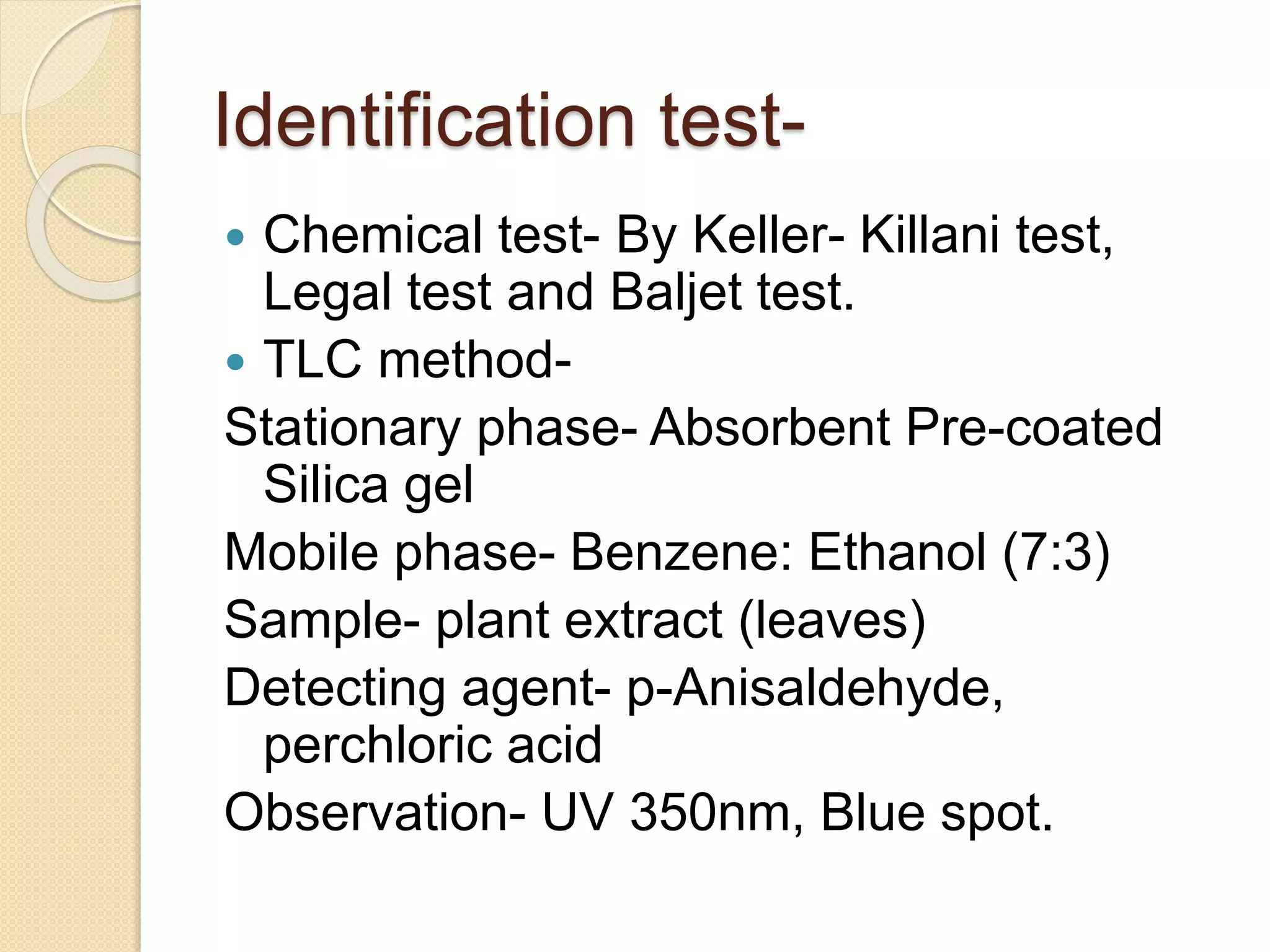
The document presents methods for the estimation and utilization of various phytoconstituents, including forskolin, digoxin, vinca alkaloids, and podophyllotoxin. It details their biological sources, extraction processes, identification tests, and utilization in treatment for conditions such as cardiovascular issues and cancer. Each compound's specific methods of cultivation and chemical properties are also outlined, alongside their therapeutic applications in traditional and modern medicine.