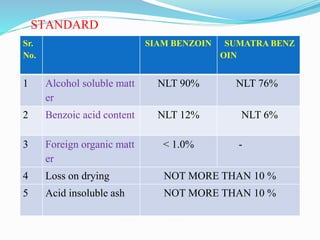
Benzoin is a balsamic resin obtained from incisions made on several species of Styrax trees native to Southeast Asia. There are two main types - Sumatra benzoin from Styrax benzoin and Siam benzoin from Styrax tonkinesis. Sumatra benzoin contains a higher amount of benzoic and cinnamic acids which give it an aromatic odor. Siam benzoin contains mainly coniferyl benzoate and has a vanilla-like odor. Both types are used as expectorants and antiseptics in preparations like compound tincture of benzoin. They are also used industrially to add fragrance to products.



















![Benzoin
• Marketed formulation :
1] Benzoin compound Tincture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benzoin1new-160912102152/85/Benzoin-21-320.jpg)



