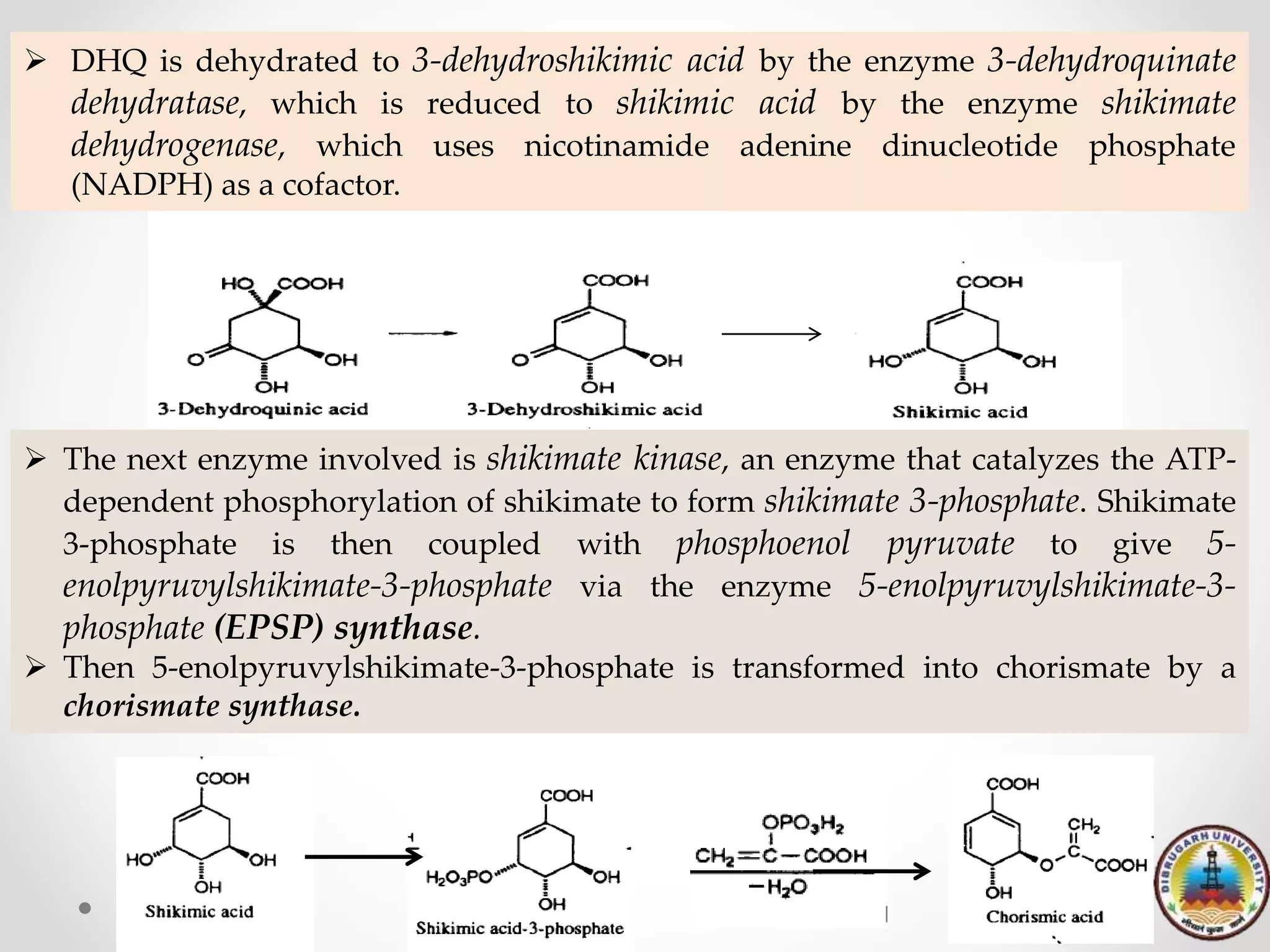
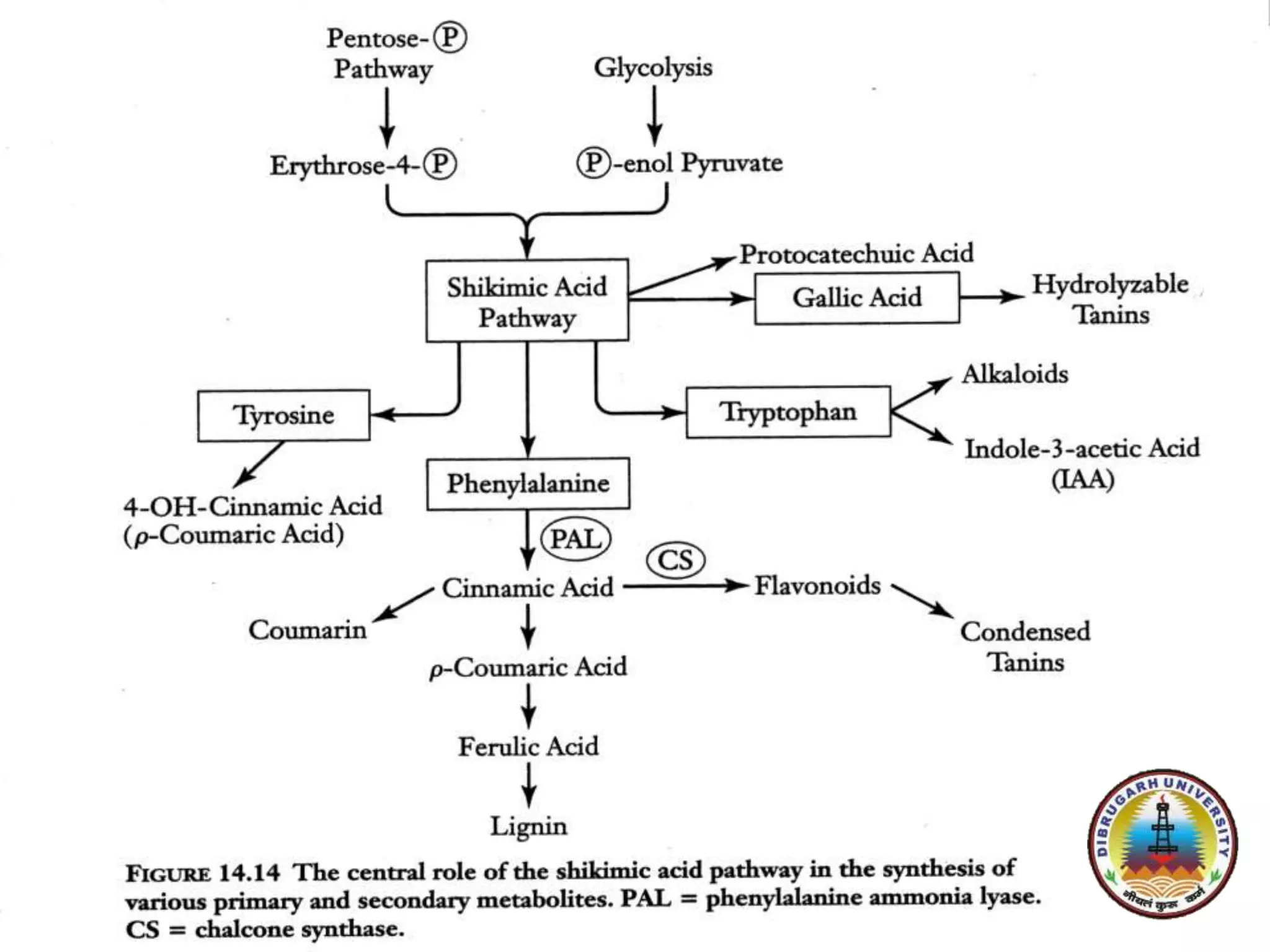
Shikimic acid is an important biochemical metabolite found in plants and microorganisms. It was first isolated from the Japanese star anise plant in 1885. The shikimate pathway is a seven step metabolic route used by plants and microbes to synthesize the aromatic amino acids phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. This pathway is not present in animals. Shikimic acid is the starting point for the biosynthesis of many important phenolic compounds like flavonoids, tannins, lignin, and gallic acid. It is also a precursor for indole derivatives and the psychedelic compound DMT. Glyphosate herbicide works by inhibiting the shikimate pathway in plants