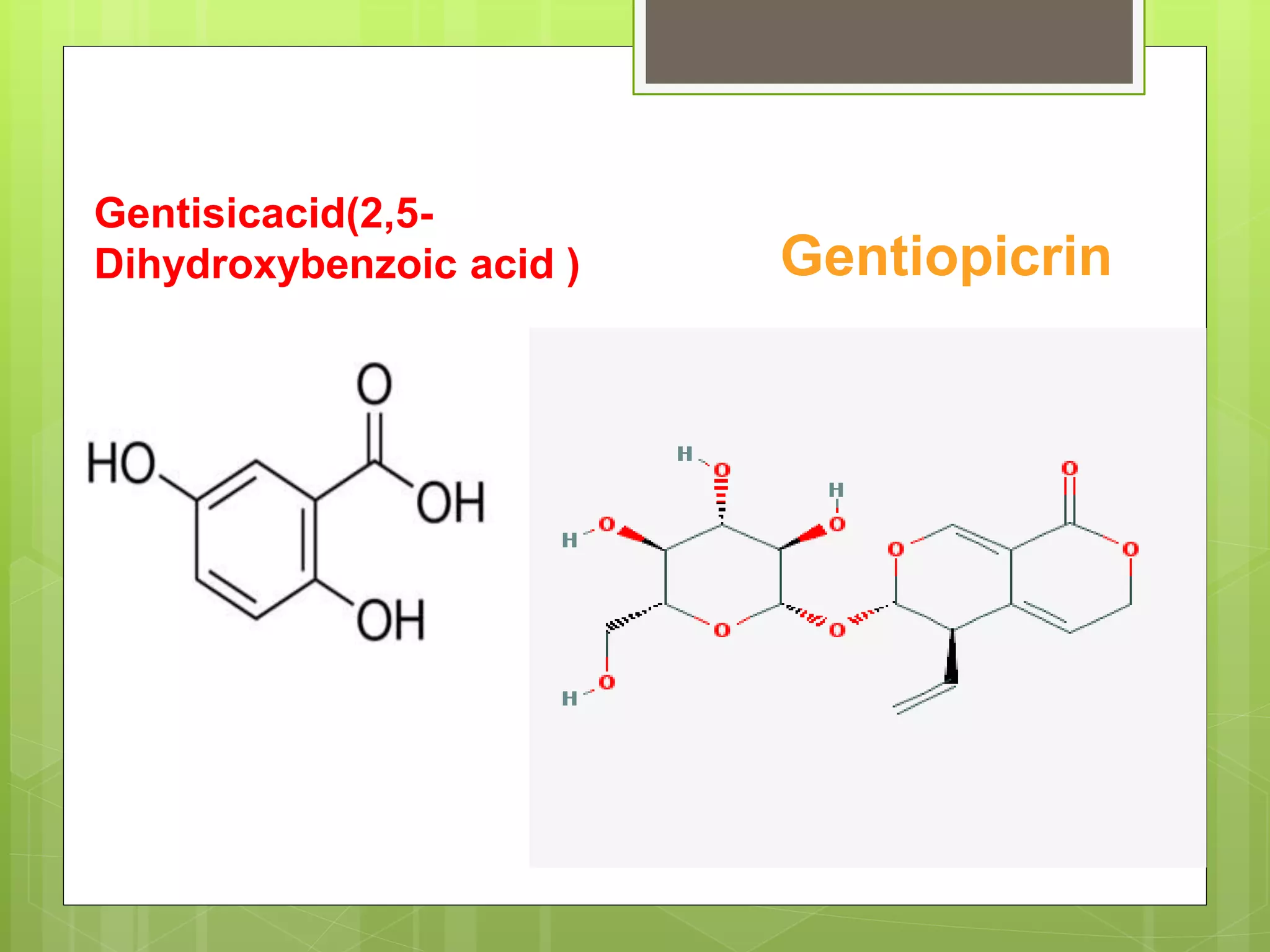
Gentian is a plant whose dried rhizome and roots are used as a bitter tonic. It contains several bitter glycosides such as gentiopicrin, which has an intensely bitter taste and is used to stimulate digestion. Gentian grows in central and southern Europe and Asia, and its rhizomes are harvested in autumn after 2-5 years of growth. Microscopically, transverse sections of gentian rhizome show a porous wood surrounded by parenchyma cells containing oil globules and calcium oxalate needles. Gentian is used as a stomachic to treat indigestion and other gastrointestinal issues.