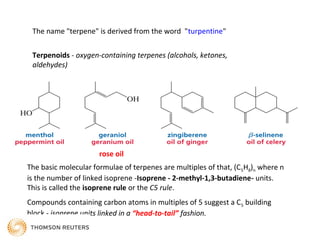
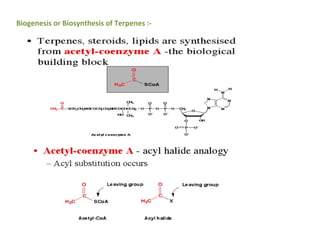
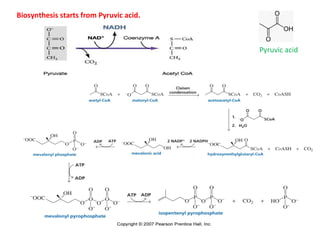
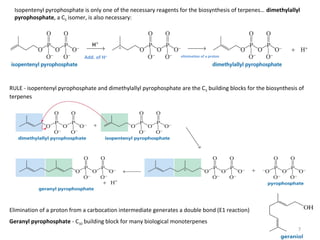
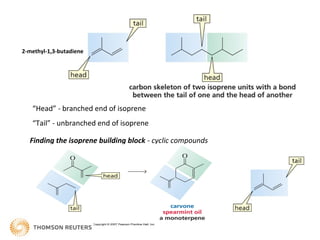
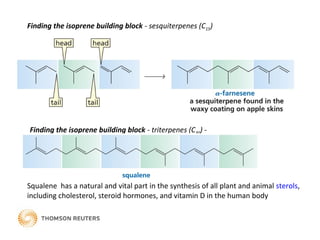
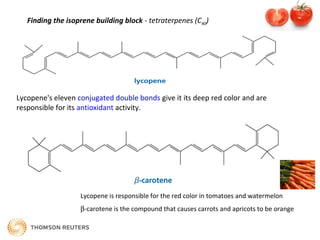
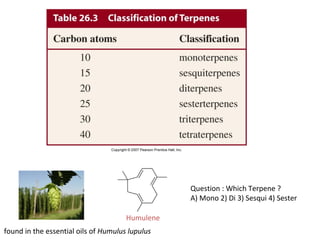
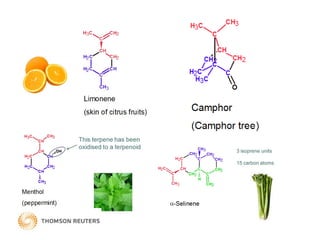
Terpenes are secondary metabolites formed by joining isoprene units together. Isoprene, which has the formula C5H8, is considered the basic building block of terpenes. Terpenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that vary in structure and size depending on the number of isoprene units linked together. They are used widely in fragrances, essential oils, and medicines. Terpenoids refer to oxygenated terpenes that result when terpenes are oxidized.