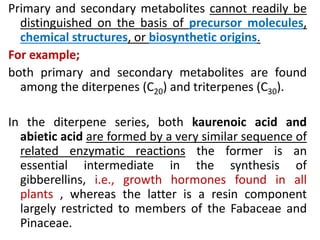
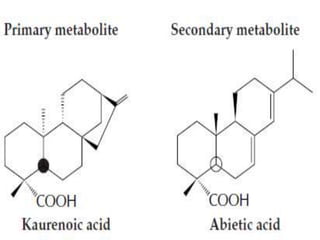
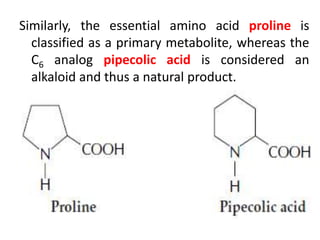
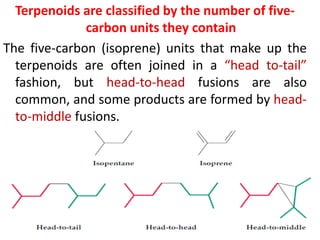
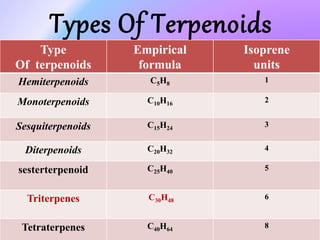
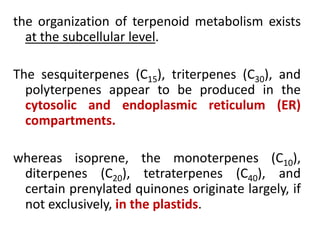
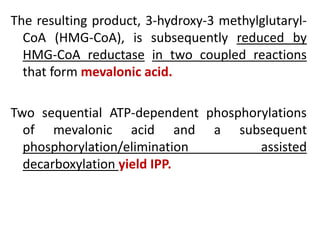
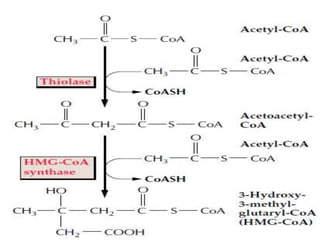
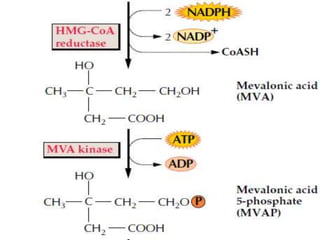
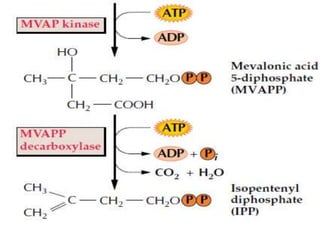
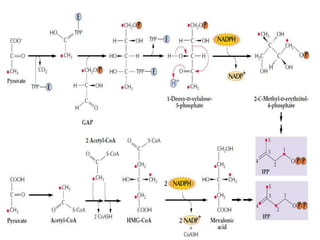
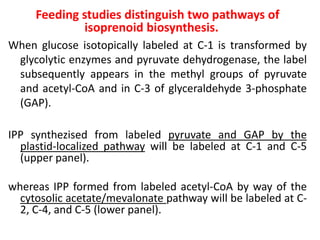
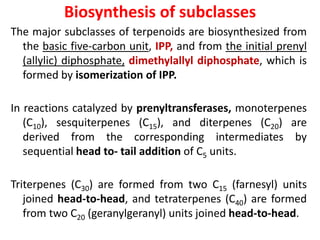
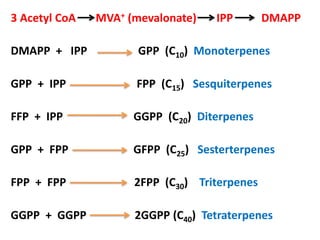
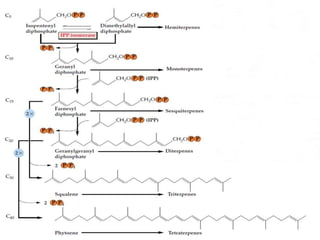
Plants produce a diverse range of organic compounds called secondary metabolites that differ from primary metabolites, which are essential for growth. These metabolites can be classified into terpenoids, alkaloids, and phenolic compounds, with terpenoids derived from isopentenyl diphosphate through various biosynthetic pathways. The biosynthesis of terpenoids involves specific enzymatic reactions and occurs in different cellular compartments, demonstrating the complexity and regulatory mechanisms of plant metabolism.