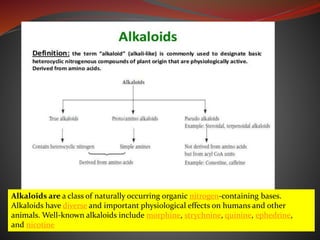
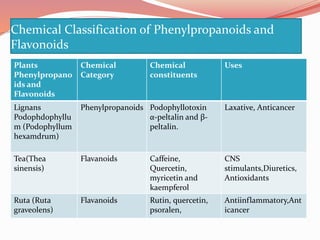
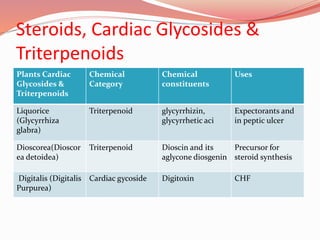
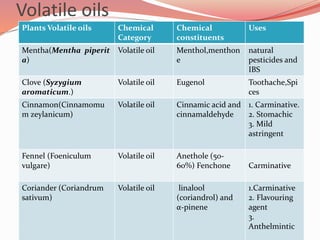
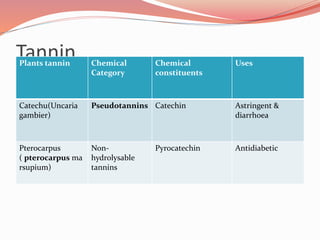
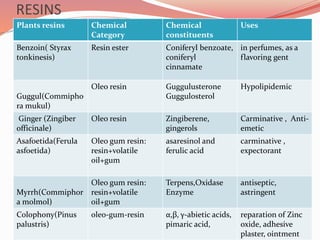
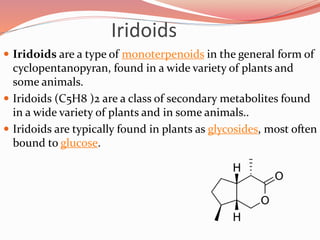
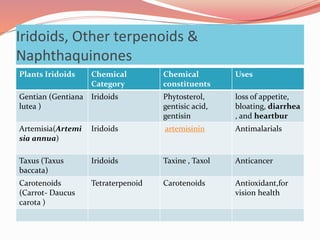
Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing organic compounds found in many plants. They have diverse physiological effects in humans and other animals. Well-known alkaloids include morphine, quinine, and nicotine. The document then provides tables summarizing various alkaloidal plants, the chemical categories and constituents of the alkaloids found in each plant, and their common uses. It also summarizes other classes of plant secondary metabolites including phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, steroids, terpenoids, volatile oils, tannins, resins, and glycosides. For each class, examples of plants containing those compounds are given along with the specific chemicals and their functions.