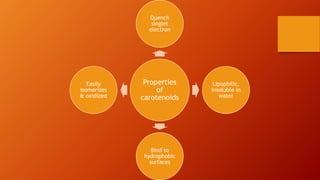
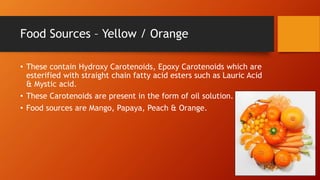
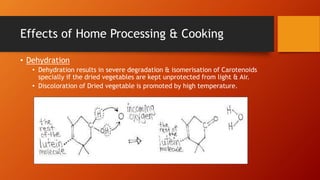
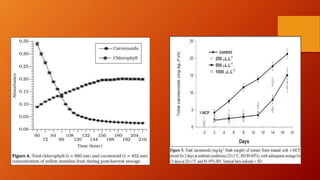
Carotenoids are organic pigments found in plants and photosynthetic bacteria that are precursors to vitamin A. They are fat-soluble tetraterpenoids produced from 8 isoprene molecules and contain 40 carbon atoms. Common carotenoids include lycopene, alpha-carotene, and beta-carotene. Carotenoids are important antioxidants and are found in foods like carrots, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, and leafy greens. Proper storage, avoidance of light and heat, and protection from oxygen are important to prevent carotenoid degradation.