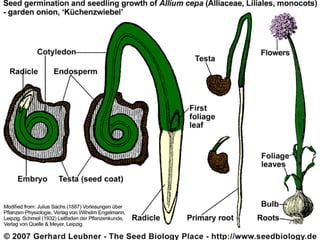
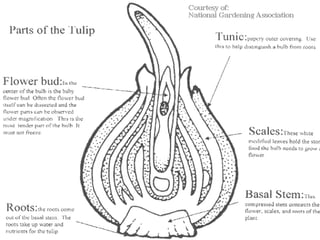
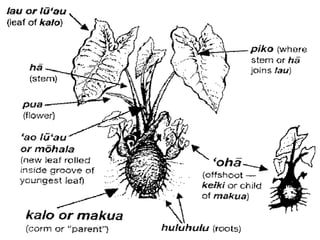
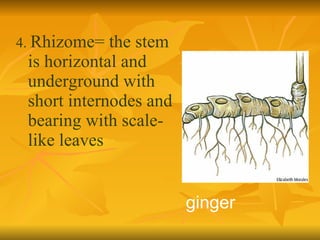
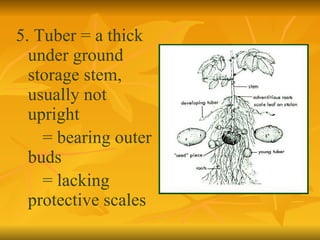
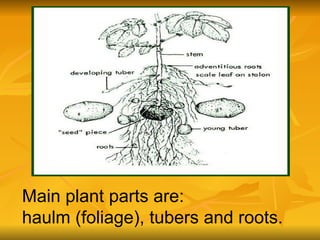
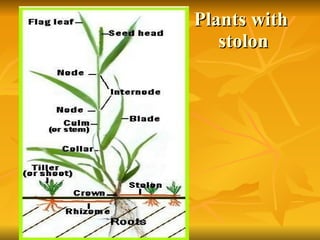
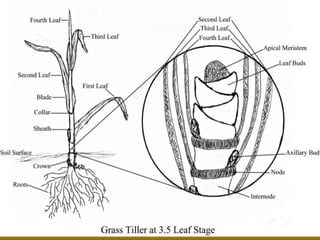
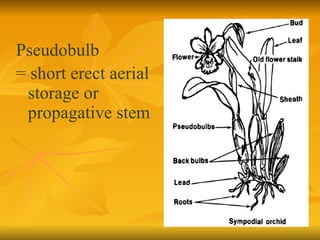
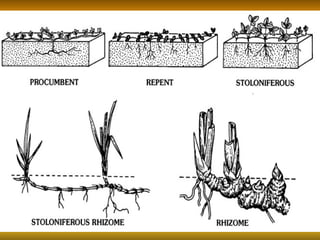
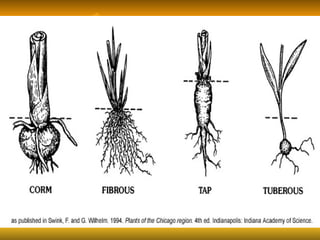
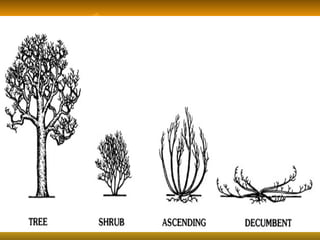
Stems serve both supportive and conductive functions for plants. They develop from the epicotyl of seeds and connect other plant organs like leaves, flowers, and fruit. Stems can be modified for storage, protection, or propagation. Some common modified stems include rootstocks, bulbs, corms, caudices, rhizomes, stolons, cladodes, and tubers. Rootstocks like bulbs, corms, and caudices remain underground during harsh conditions. Rhizomes are horizontal underground stems while tubers are thick underground storage stems lacking scales. Stolons are stems that propagate horizontally just below the soil surface.